在cmd中实现生成器:
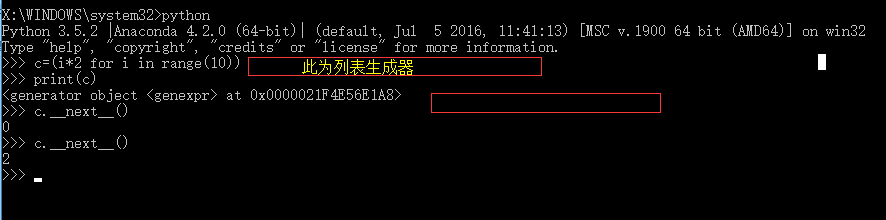
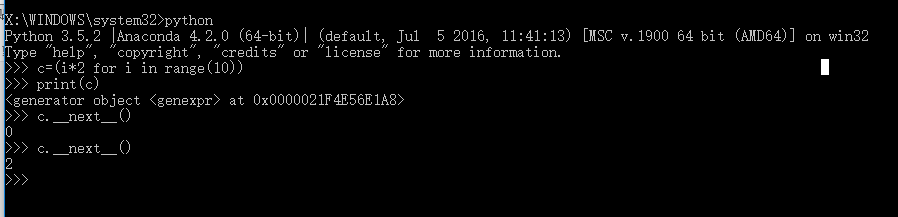
''' 生成器: (1)只有在调用时才会生成相应的数据 (2)只记录当前位置 (3)在python3中只有一个__next__()方法,在python2.7中该方法为next()方法 ''' ''' c=(i*2 for i in range(10)) #生成器 for i in c: print() ''' def fib(max): n,a,b=0,0,1 while n<max: #print(b) yield b #保存函数的中断状态,返回当前状态的值 a,b=b,a+b #相当于t=(a,a+b) a=t[0] b=t[1] n=n+1 return 'done' #出现异常时的打印信息 g=fib(5) print(g.__next__()) print(g.__next__()) print(g.__next__()) print("start loop") #代表某种操作,可以在函数执行的过程中执行 print(g.__next__()) # for i in g: # print(i) print(g.__next__()) # print(g.__next__()) # print(g.__next__()) # while True: # try: # #出异常的代码 # x=next(g) # print('g:',x) # except StopIteration as e: # print('Generator return value:',e.value) # break
生成器的并行效果:
'''协程:单线程下的并行效果''' import time def consumer(name): print(" %s 准备喝奶茶了" %name) while True: naicha=yield print("%s奶茶来了,被 %s 喝了" %(naicha ,name)) def procuder(name): c=consumer("A")#只是把函数变成了生成器 c1=consumer("B") c.__next__()#next以后才会向下继续运行 c1.__next__() print(" %s 准备做奶茶了" % name) for i in range(10): time.sleep(1) print("做了2个杯奶茶") c.send(i) #传值给yeild并继续向下运行 c1.send(i) f=procuder('lhy')
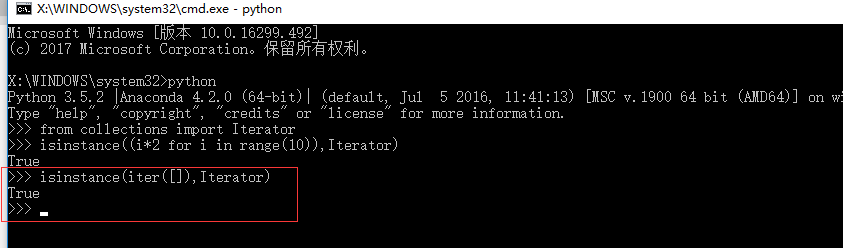
迭代器(Iterator):可以被next()函数调用并不断返回下一个值的对象。
调用isinstance()方法判断是否为迭代器时需要先导入 from collections import Iterator
生成器都是迭代器对象,但是迭代器对象未必是生成器。
把list,dict,str等Iterable变成Iterator可以使用iter()函数。

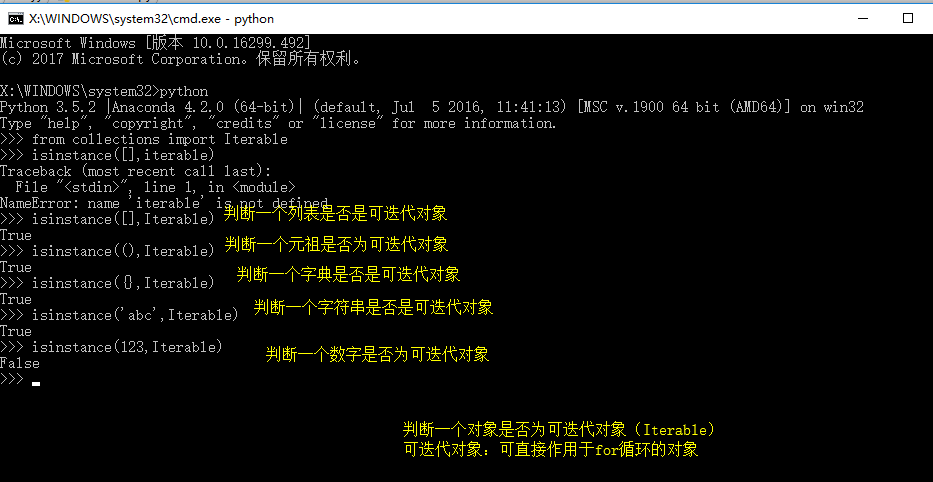
可迭代对象(Iterable):可以直接作用于for循环的对象统称为可迭代对象。
调用isinstance()方法判断是否为可迭代对象时需要先导入 from collections import Iterable