主要讲一下solr面板的使用:
查询
q: 查询用 语法: name:刘中华 支持通配符
? 表示单个任意字符的通配
* 表示多个任意字符的通配(不能在检索的项开始使用*或者?符号)
~ 表示模糊检索,如检索拼写类似于”roam”的项这样写:roam将找到形如foam和roams的单词;roam0.8,检索返回相似度在0.8以上的记录。
AND、|| 布尔操作符
OR、&& 布尔操作符
NOT、!、-(排除操作符不能单独与项使用构成查询)
+ 存在操作符,要求符号”+”后的项必须在文档相应的域中存在²
( ) 用于构成子查询
[] 包含范围检索,如检索某时间段记录,包含头尾,date:[201507 TO 201510]
{} 不包含范围检索,如检索某时间段记录,不包含头尾date:{201507 TO 201510}
fq : filter query 过滤查询 比如:查询日期范围 last_modified:[2019-04-19 TO 2019-04-27]
sort: 排序。格式如下:字段名 排序方式;如 id desc 表示按id字段降序排列查询结果。 中间没有分号 是空格
fl: field list。指定查询结果返回哪些字段。多个时以空格“ ”或逗号“,”分隔。不指定时,默认全返回。
分组facet:
参考博客:https://blog.csdn.net/sgq1991/article/details/78051256
Facet 的字段必须被索引 . 一般来说该字段无需分词 , 无需存储 .
Solr提供了4种类型的Fact
<lst name="facet_counts"> <lst name="facet_queries"/> <lst name="facet_fields"/> <lst name="facet_dates"/> <lst name="facet_ranges"/> </lst>
- facet_queries:代表自定义条件查询facet,类似数据库的count函数
- facet_fields :代表根据字段分组查询,类似数据库的group by count的组合
- facet_dates :根据日期区间分组查询
- facet_ranges:当然了,日期有区间,数字也有,这个就是根据数字分组查询
facet query(个人感觉就像count()作用)
Facet Query 用户自定义条件查询facet,他提供了非常灵活的Facet.通过facet.query参数,可以对任意字段进行筛选.下面通过实例来阐述。基本上他的用法,都会在我实例中体现出来
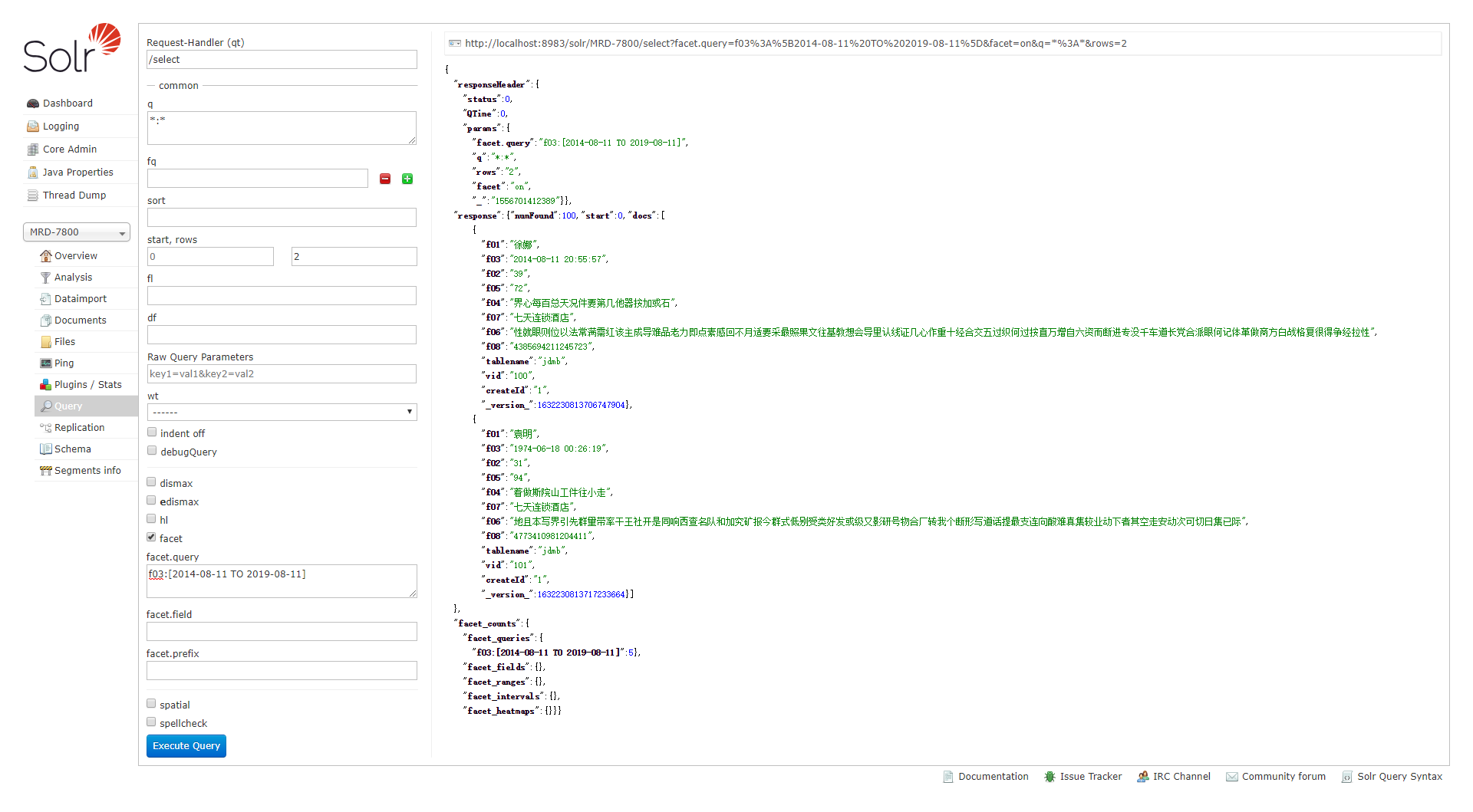
例一:日期区间查询,这个区间的数目为5个
url为:
&facet=true &facet.query=date:[2009-1-1T0:0:0Z TO 2009-2-1T0:0:0Z] &facet.query=date:[2009-4-1T0:0:0Z TO 2009-5-1T0:0:0Z]
面板为:
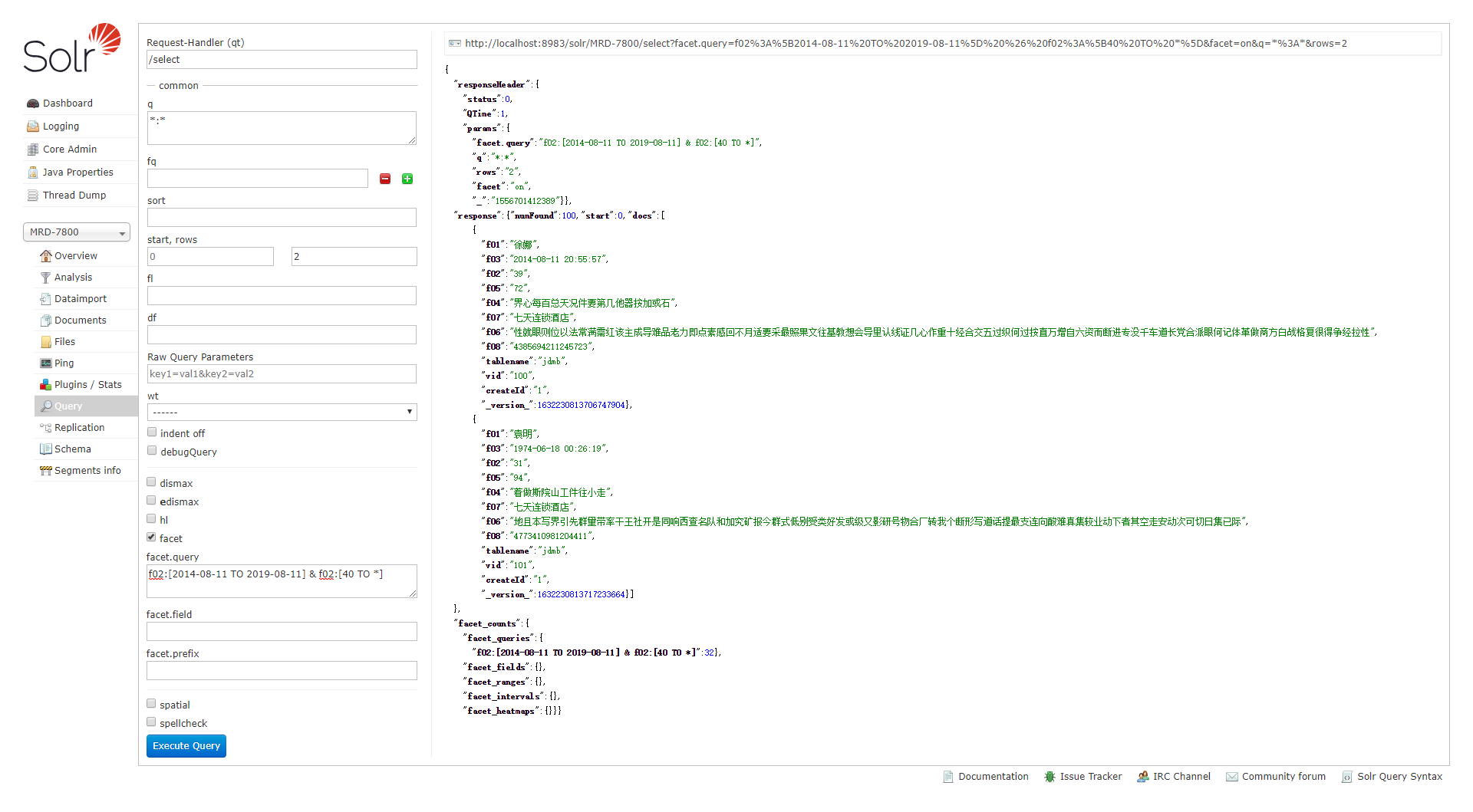
例2:数字区间统计
url为:
&facet=on &facet.query=date:[2009-1-1T0:0:0Z TO 2009-2-1T0:0:0Z] &facet.query=price:[* TO 5000]
facet.field(这就是类似于数据库的group by 加上count的功能)
实例一:最简单的field facet
&facet=true &facet.field=brand &facet.field=price
"facet_counts":{ "facet_queries":{}, "facet_fields":{ "brand":[ "苹果",4, "联想",3, "惠普",2], "price":[ "1100.0",2, "2200.0",2, "3300.0",2, "1200.0",1, "2100.0",1, "4400.0",1]}, "facet_dates":{}, "facet_ranges":{}}}
从返回结果可以看出各个field字段互不影响;而且可以针对,下面实例会体现
facet.prefix(个人感觉就是像在facet.field的上一层过滤一下,比如只统计品牌名称是联开头的电脑)
&facet.field=brand &facet.field=price &f.brand.facet.prefix=联
"facet_counts":{ "facet_queries":{}, "facet_fields":{ "brand":[ "联想",3], "price":[ "1100.0",2, "2200.0",2, "3300.0",2, "1200.0",1, "2100.0",1, "4400.0",1]}, "facet_dates":{}, "facet_ranges":{}}}
温馨提示:上面的facet.prefix就是一个参数名,这个很容易误解为两个,因为他中间有个点
上面介绍了facet.field参数,下面介绍field fact的其他参数
1).facet.prefix 表示Facet字段值的前缀.比如facet.field=cpu&facet.prefix=Intel,那么对cpu字段进行Facet查询,返回的cpu都是以“Intel”开头的。 2).facet.sort 表示Facet字段值以哪种顺序返回.可接受的值为true(count)|false(index,lex). true(count)表示按照count降序; false(index,lex)表示按照字段值升序(字母,数字的顺序)排列.默认情况下为true(count).当facet.limit值为负数时,默认facet.sort= false(index,lex). 3).facet.limit 限制Facet字段返回的结果条数.默认值为100.如果此值为负数,表示不限制. 4).facet.offset 返回结果集的偏移量,默认为0.它与facet.limit配合使用可以达到分页的效果. 5).facet.mincount 限制了Facet字段值的最小count,默认为0.合理设置该参数可以将用户的关注点集中在少数比较热门的领域.相当于group by having 6).facet.missing 默认为””,如果设置为true或者on,那么将统计那些该Facet字段值为null的记录. 7).facet.method 取值为enum或fc,默认为fc.该字段表示了两种Facet的算法,与执行效率相关. enum适用于字段值比较少的情况,比如字段类型为布尔型,或者字段表示中国的所有省份.Solr会遍历该字段的所有取值,并从filterCache里为每个值分配一个filter(这里要求solrconfig.xml里对filterCache的设置足够大).然后计算每个filter与主查询的交集. fc(表示Field Cache)适用于字段取值比较多,但在每个文档里出现次数比较少的情况.Solr会遍历所有的文档,在每个文档内搜索Cache内的值,如果找到就将Cache内该值的count加1. 8).facet.enum.cache.minDf 当facet.method=enum时,此参数其作用,minDf表示minimum document frequency.也就是文档内出现某个关键字的最少次数.该参数默认值为0.设置该参数可以减少filterCache的内存消耗,但会增加总的查询时间(计算交集的时间增加了).如果设置该值的话,官方文档建议优先尝试25-50内的值.
Date Facet(专门对时间的一个统计)
日期类型的字段在文档中很常见,如商品上市时间,货物出仓时间,书籍上架时间等等.某些情况下需要针对这些字段进行Facet.不过时间字段的取值有无限性,用户往往关心的不是某个时间点而是某个时间段内的查询统计结果. Solr为日期字段提供了更为方便的查询统计方式.当然,字段的类型必须是DateField(或其子类型)。
需要注意的是,使用Date Facet时,字段名,起始时间,结束时间,时间间隔这4个参数都必须提供.与Field Facet类似,Date Facet也可以对多个字段进行Facet.并且针对每个字段都可以单独设置参数。
&facet.date=birthday &facet.date.start=2014-01-00T09:15:00Z &facet.date.end=2014-12-00T09:15:00Z &facet.date.gap=%2B1MONTH
"facet_counts":{ "facet_queries":{}, "facet_fields":{}, "facet_dates":{ "birthday":{ "2013-12-31T09:15:00Z":0, "2014-01-31T09:15:00Z":0, "2014-02-28T09:15:00Z":0, "2014-03-28T09:15:00Z":0, "2014-04-28T09:15:00Z":0, "2014-05-28T09:15:00Z":0, "2014-06-28T09:15:00Z":0, "2014-07-28T09:15:00Z":0, "2014-08-28T09:15:00Z":0, "2014-09-28T09:15:00Z":1, "2014-10-28T09:15:00Z":5, "2014-11-28T09:15:00Z":3, "gap":"+1MONTH", "start":"2013-12-31T09:15:00Z", "end":"2014-12-28T09:15:00Z"}}, "facet_ranges":{}}}
1).facet.date 该参数表示需要进行Date Facet的字段名,与facet.field一样,该参数可以被设置多次,表示对多个字段进行Date Facet. 2).facet.date.start 起始时间,时间格式为1995-12-31T23:59:59Z 3).facet.date.end 结束时间. 4).facet.date.gap 时间间隔.如果start为2009-1-1,end为2010-1-1.gap设置为+1MONTH表示间隔1个月,那么将会把这段时间划分为12个间隔段. 注意+因为是特殊字符所以应该用%2B代替. 5).facet.date.hardend 取值可以为true|false,默认为false.它表示gap迭代到end处采用何种处理.举例说明start为2009-1-1,end为2009-12-25,gap为+1MONTH, hardend为false的话最后一个时间段为2009-12-1至2010-1-1; hardend为true的话最后一个时间段为2009-12-1至2009-12-25. 6).facet.date.other 取值范围为before|after|between|none|all,默认为none,before会对start之前的值做统计,after会对end之后的值做统计,between会对start至end之间所有值做统计.如果hardend为true的话,那么该值就是各个时间段统计值的和.none表示该项禁用.all表示before,after,all都会统计.
实例参考,演示fact.date.other、跟单独对某个字段起作用
&facet.date=birthday &facet.date.start=2014-01-00T09:15:00Z &facet.date.end=2014-12-00T09:15:00Z &facet.date.gap=%2B1MONTH &facet.date.other=all &f.birthday.facet.mincount=3 --单独对某个字段起作用,把统计值小于3的过滤掉
"facet_counts":{ "facet_queries":{}, "facet_fields":{}, "facet_dates":{ "birthday":{ "2014-10-28T09:15:00Z":5, "2014-11-28T09:15:00Z":3, "gap":"+1MONTH", "start":"2013-12-31T09:15:00Z", "end":"2014-12-28T09:15:00Z", "before":0, "after":0, "between":9}}, "facet_ranges":{}}}
Facet Range
范围统计分组统计,跟Date Facet一样,只是他们定位的字段的类型不同,Data Fact是做日期的分组统计的,而Fact Range是做数字分组统计的,在次强调,是做数字分组统计的,对于字符串,日期是不可以的。
参数跟上面的Date Facet基本一致,如下,就不做解释了,参考Date Facet的各个参数
1. facet.range 2. facet.range.start 3. facet.range.end 4. facet.range.gap 5. facet.range.hardend 6. facet.range.other 7. facet.range.include
参考实例
&facet.range=price
&facet.range.start=1000
&facet.range.end=5000
&facet.range.gap=1000
&f.price.facet.mincount=2--单独对某个字段起作用,把统计值小于2的过滤掉
返回结果如下:
"facet_counts":{ "facet_queries":{}, "facet_fields":{}, "facet_dates":{}, "facet_ranges":{ "price":{ "counts":[ "1000.0",3, "2000.0",3, "3000.0",2], "gap":1000.0, "start":1000.0, "end":5000.0}}}}
key 操作符(别名)
上面已经介绍了facet的四类统计,下面介绍一下key,什么是key?
答:key操作符可以为Facet字段取一个别名。哦原来如此简单!
参考实例:
参数 &facet=true &facet.query=brand:联想 AND price:1100 返回结果 "facet_counts":{ "facet_queries":{ "brand:联想 AND price:1100":1}, "facet_fields":{}, "facet_dates":{}, "facet_ranges":{}}} -------------------------------- 参数 &facet=true &facet.query={!key=联想}brand:联想 AND price:1100 返回结果 "facet_counts":{ "facet_queries":{ "联想":1}, "facet_fields":{}, "facet_dates":{}, "facet_ranges":{}}}
从上面可以看出来,这样可以让字段名统一起来,方便我们拿到请求数据后,封装成自己的对象
tag操作符和ex操作符(就是防止查询的条件来污染分组结果)
这个也非常的重要,看下应用场景,当查询使用filter query 或者q的时候,如果filter query的字段正好是Facet字段,那么查询结果往往被限制在某一个值内.
参考实例
&fq=price:[1000 TO 2000]
&facet.field=price
"facet_counts":{ "facet_queries":{}, "facet_fields":{ "price":[ "1100.0",2, "1200.0",1, "2100.0",0, "2200.0",0, "3300.0",0, "4400.0",0]}, "facet_dates":{}, "facet_ranges":{}}}
从返回的结果可以看到fq将查询的结果集限制在了price 在1000 至 2000之间,其他范围的统计没有实际意义。
有些时候,用户希望把结果限制在某一个范围以内,又希望查看该范围外的概况,像上述情况,用户想把结果限制在(price)1000~2000之间,但是又想查看其他价格区间有多少产品。这个时候需要用到tag和ex操作符.tag就是把一个filter标记起来,ex(exclude)是在Facet的时候把标记过的filter排除在外.
参考实例
&fq={!tag=aa}price:[1000 TO 2000]
&facet.field={!ex=aa}price
返回结果
"facet_counts":{ "facet_queries":{}, "facet_fields":{ "price":[ "1100.0",2, "2200.0",2, "3300.0",2, "1200.0",1, "2100.0",1, "4400.0",1]}, "facet_dates":{}, "facet_ranges":{}}}
这样其它价格区间的统计信息就有意义了.
Facet 字段设计
一、Facet字段的要求
Facet的字段必须被索引.一般来说该字段无需分词,无需存储.
无需分词是因为该字段的值代表了一个整体概念,如电脑的品牌”联想”代表了一个整体概念,如果拆成”联”,”想”两个字都不具有实际意义.另外该字段的值无需进行大小写转换等处理,保持其原貌即可.
无需存储是因为一般而言用户所关心的并不是该字段的具体值,而是作为对查询结果进行分组的一种手段,用户一般会沿着这个分组进一步深入搜索.
二、特殊情况
对于一般查询而言,分词和存储都是必要的.比如CPU类型“Intel 酷睿2双核 P7570”,拆分成“Intel”,“酷睿”,“P7570”这样一些关键字并分别索引,可能提供更好的搜索体验.但是如果将CPU作为Facet字段,最好不进行分词.这样就造成了矛盾,解决方法为,将CPU字段设置为不分词不存储,然后建立另外一个字段为它的COPY,对这个COPY的字段进行分词和存储.
<types>
<fieldType name="string" class="solr.StrField" omitNorms="true"/>
<fieldType name="tokened" class="solr.TextField" >
<analyzer>
……
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
</types>
<fields>
<field name="cpu" type="string" indexed="true" stored="false"/>
<field name="cpuCopy” type=" tokened" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
</fields>
<copyField source="cpu" dest="cpuCopy"/>
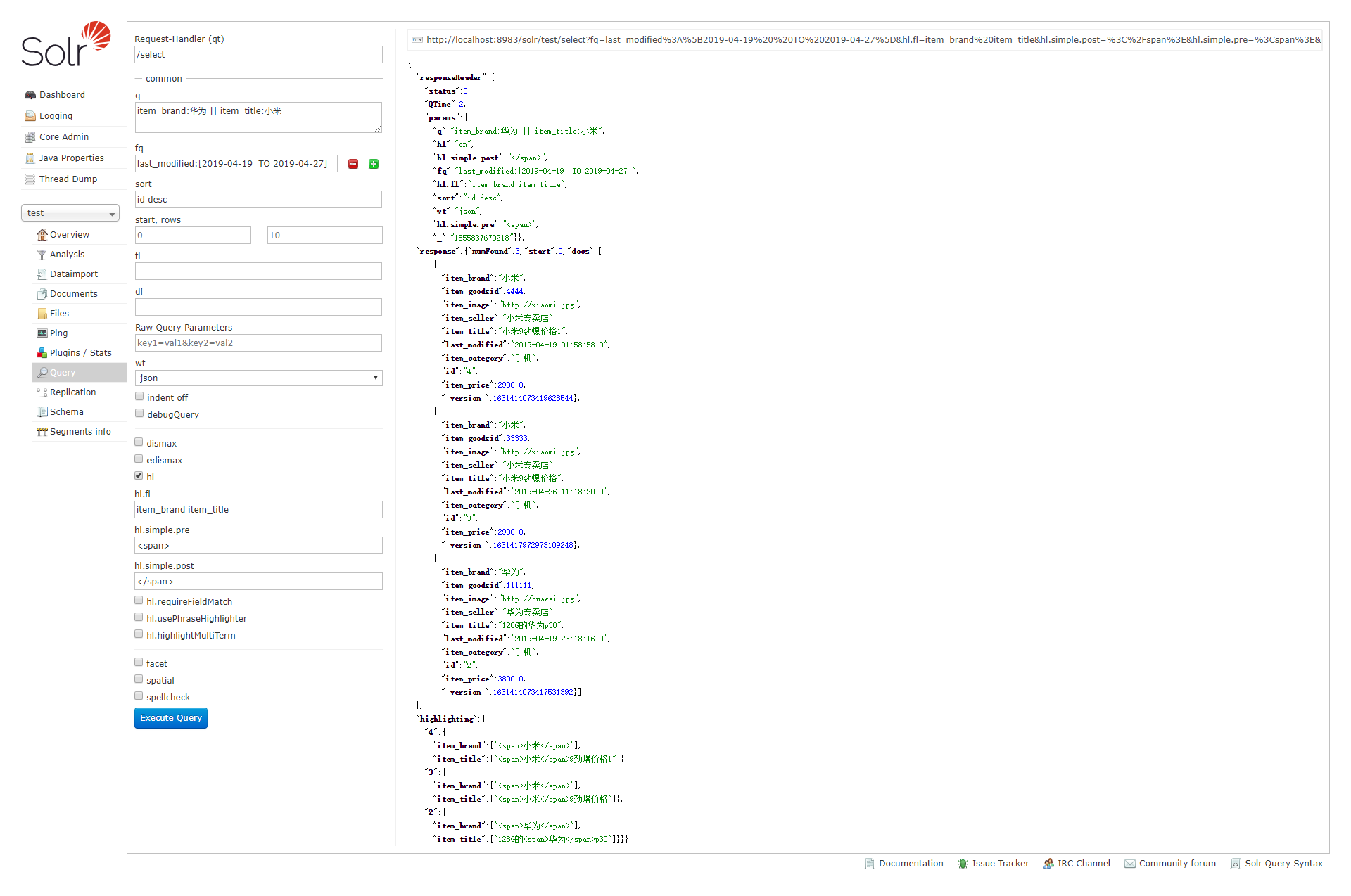
高亮
https://www.jianshu.com/p/cbb938c62e0e
hl: high light 高亮。hl=true表示启用高亮
java API
推荐博客: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37334135/article/details/76862508
其实就是solrJ的搜索。最底层的都是他,无论是 spring-boot-starter-data-solr 还是 spring-data-solr 都是这个solrJ的封装。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-solr</artifactId>
</dependency>
spring: datasource: data: solr: host: http://127.0.0.1:8983/solr/
根据id搜索
@Autowired private SolrClient client; //根据id查找 @RequestMapping("/") public Object testSolr() throws IOException, SolrServerException { SolrDocument document = client.getById("test", "2"); System.out.println(document); return document; }
带条件查询
@RequestMapping("/list")
public Object query() throws Exception {
SolrQuery query = new SolrQuery();
query.set("q", "id:3&&name:张三");
QueryResponse response = solrClient.query("test", query);
SolrDocumentList results = response.getResults();
return results;
}
分组
query.setStart((page-1)*pageSize); query.setRows(pageSize); QueryResponse response = solrClient.query(solrCollection, query); // 获取查询结果 SolrDocumentList results = response.getResults(); //总条数 long numFound = results.getNumFound();
新增
@RequestMapping("/add")
public Object add() throws Exception {
SolrInputDocument document = new SolrInputDocument();
document.addField("id", 1002L);
document.addField("item_brand", "三星");
document.addField("item_goodsid", "66666");
document.addField("item_seller", "三星旗舰店");
document.addField("item_title", "三星千元机震撼来袭");
document.addField("item_category", "手机");
document.addField("item_price", "1499");
document.addField("item_image", "http://xiaomi.jpg");
document.addField("last_modified", "2019-04-22");
UpdateResponse add = solrClient.add("test",document);
int status = add.getStatus();
solrClient.commit("test");
return status;
}
分组(facet)
@RequestMapping("/facet")
public void groupBy() throws Exception{
SolrQuery query = new SolrQuery();//建立一个新的查询
query.setQuery("f01:徐娜");
query.setFacet(true);//设置facet=on
query.addFacetField(new String[] { "tablename"});//设置需要facet的字段
query.setFacetLimit(10);//限制facet返回的数量
QueryResponse response = solrClient.query("MRD-7800",query);
List<FacetField> facets = response.getFacetFields();//返回的facet列表
for (FacetField facet : facets) {
System.out.println(facet.getName());
System.out.println("----------------");
List<FacetField.Count> counts = facet.getValues();
for (FacetField.Count count : counts) {
System.out.println(count.getName() + ":" + count.getCount());
}
System.out.println();
}
}
高亮
有个大坑,高亮的字段必须是分词的。麻蛋,浪费我快一天的时间排查。
@RequestMapping("/hightLiang2")
public void hightLiang2() throws Exception{
SolrQuery query = new SolrQuery();//建立一个新的查询
query.setQuery(""徐娜"");
// 设置默认搜素域
query.set("df", "onekey_keywords");
// 设置高亮显示
query.setHighlight(true);
query.addHighlightField("f01,f02,f03");
query.setHighlightSimplePre("<em style="color:red">");
query.setHighlightSimplePost("</em>");
QueryResponse response = solrClient.query("MRD-7800",query);
// 获取查询结果
SolrDocumentList solrDocumentList = response.getResults();
//获取高亮显示数据
Map<String, Map<String, List<String>>> highlighting = response.getHighlighting();
// 遍历查询结果
for (SolrDocument solrDocument : solrDocumentList) {
// 获取高亮显示的集合
System.out.println(solrDocument);
String vid = (String) solrDocument.get("vid");
Map<String, List<String>> listMap = highlighting.get(vid);
for (Map.Entry<String, List<String>> entry : listMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("字段名字 = " + entry.getKey() + ", 字段值 = " + entry.getValue());
}
}
}
SolrDocument{f01=徐娜, f03=2014-08-11 20:55:57, f02=39, f05=72, f04=界心每百总天况件要第几他器按加或石, f07=七天连锁酒店, f06=性就眼则位以法常满需红该主成导难品老力即点素感回不月适要采最照果文往基教想会导里认线证几心作重十经合交五过织何过按直万增自六资而断进专没千车道长党合派眼何记体革做商方白战格复很得争经拉性, f08=4385694211245723, tablename=jdmb, vid=100, createId=1, _version_=1632676338865274880}
字段名字 = f01, 字段值 = [<em style="color:red">徐</em><em style="color:red">娜</em>]