Mybatis的基本使用
一、Mybatis的概念
1. mybatis的概念
mybatis是一个持久层的框架,用java写的,简化了jdbc操作的很多细节,是开发者只需要关注sql语句本身,而无需关注注册驱动,创建等繁杂过程,它使用了ORM思想实现了结果集的封装
2. ORM思想
Object Releational Mappging 对象关系映射:
简单的说,就是把数据库和实体类及实体类的属性对应起来,让我们可以操作实体类就实现操作数据库表。
今天我们需要做到实体类的属性和数据库表的字段保持一致
三、Mybatis的入门和CRUD
1. Mybatis的结构以及执行 分析


2. 引入依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.4.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.32</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
3. 创建实体类 部分代码省略
3.1. 创建User实体类
import java.util.Date;
public class User implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private Date birthday;
private String sex;
private String address;
}
3.2 创建QueryVo实体类
package com.github.domain;
/**
*
* 将所有的实体类封装到QueryVo中,将来执行dao的方法参数为实体类时,
* 只需要传递vo即可,实体类的属性通过OGNL表达式获取即可
*
* 使用
*
* @param
* @return
*/
public class QueryVo {
private User user;
public QueryVo(User user) {
this.user=user;
}
public User getUser() {
return user;
}
public void setUser(User user) {
this.user = user;
}
}
4. IUserDao接口
package com.github.dao;
import com.github.domain.QueryVo;
import com.github.domain.User;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @param
* @return
*/
public interface IUserDao {
/**
* 查询所有
* @return
*/
List<User> findAll();
/**
* 添加用户
* @param user
*/
int userSave(User user);
/**
* 更新用户
* @param user
*/
int updateUser(User user);
/**
* 根据id删除用户
* @param id 用户id
*/
int removeUser(Integer id);
/**
* 根据用户id查询用户信息
* @param userId 用户id
* @return
*/
User findById(int userId);
/**
* 根据用户名查询模糊用户
* @param username
* @return
*/
List<User> findByName(String username);
/**
* 查询总记录条数
* @return
*/
int findTotal();
/**
* 使用vo进行模糊查询
* @param vo
* @return
*/
List<User> findUserByVo(QueryVo vo);
}
5. 编写Mybatis的主配置文件SqlMapConfig.xml
5.1 使用mapper标签进行注册映射文件
使用mapper标签注册映射文件地址,使用resource属性指定注册映射文件位置
5.2 使用package标签注册映射文件
使用package的name属性注册指定的包下所有映射文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 环境的配置 -->
<!--配置mysql的环境-->
<environments default="mysql"><!-- 选择使用id=mysql的 environment -->
<environment id="mysql">
<!--配置事务管理器-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<!--配置数据源-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy_mybatis"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="123"></property>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!--指定映射文件位置-->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/qf/dao/IUserDao.xml"></mapper>
<!--使用该标签后,注册指定的包下所有类-->
<!--<package name="com.github.dao"></package>-->
</mappers>
</configuration>
6. 编写映射配置文件IUserDao.xml
6.3. OGNL表达式
Object Graphic Navigation Language(对象 图 导航 语言)
通过对象中的取值方法获取数据,在写法上将get省略了
比如:我们获取用户名称的写法
类中的写法:user.getUsername( );
OGNL表达式写法:#{user.username}
mybatis中为什么能直接写username而不用user.呢?
因为在parameterType中提供了属性所属的类,所以此时不需要写对象名
6.2. mapper标签
作用:指定映射配置文件所对应的接口
属性:
namespace:指定映射的接口,注意,一定要是接口的全限定类名
6.3. select标签
作用:执行查询的指定方法
属性:
id:指定接口类要执行的方法
parameterType:执行方法的参数类型的全限定类名,基本数据和String类型直接写名称,
resultType:指定查询返回结果全限定类名
6.4. insert标签
作用:执行增删改的指定方法,返回值为影响数据库的行数
属性
id:指定接口类要执行的方法
parameterType:执行方法的参数类型的全限定类名,基本数据和String类型直接写名称
6.5. 主键回填
使用selectKe标签
select last_insert_id() 返回的主键id会封装到插入对象中
模糊查询也可以使用以下方法:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.github.dao.IUserDao">
<!--查询所有-->
<select id="findAll" resultType="com.github.domain.User">
select * from user
</select>
<!--保存用户-->
<insert id="userSave" parameterType="com.github.domain.User">
<!-- 插入数据后返回插入数据的id,
属性:keyColumn:数据库的主键 keyProperty:数据库实体类的对应的id resultType:主键的类型 order:返回的时期-->
<selectKey keyColumn="id" keyProperty="id" resultType="int" order="AFTER">
select last_insert_id()
</selectKey>
insert into user(username,birthday,sex,address) values(#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address})
</insert>
<!--更新用户-->
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="com.github.domain.User">
update user set username=#{username},birthday=#{birthday},sex=#{sex},address=#{address} where id =#{id}
</update>
<!--根据id删除用户-->
<update id="removeUser" parameterType="int">
delete from user where id =#{id}
</update>
<!--根据id查询用户-->
<select id="findById" parameterType="int" resultType="com.github.domain.User">
select * from user where id =#{id}
</select>
<!--根据名称模糊查询用户-->
<select id="findByName" parameterType="String" resultType="com.github.domain.User">
select * from user where username like #{username}
</select>
<!--查询总记录条数-->
<select id="findTotal" resultType="int">
select count(*) from user
</select>
<!--使用pojo类型作为参数实现查询所有-->
<select id="findUserByVo" resultType="com.github.domain.User" parameterType="com.github.domain.QueryVo">
select * from user where username like #{user.username}
</select>
</mapper>
6.6 配置dao的别名(typeAliases标签)
使用typeAliases配置该包下面的类默认设置别名为类名首字母小写,如果需要自定义名称可使用@Alias注解配置别名
7. 编写测试类
Mybatis默认不会自动提交事务,需要手动提交事务
sqlSession.commit( );
Mybatis也可以设置默认自动提交事务
sqlSession.commit( true )
package com.github;
import com.github.dao.IUserDao;
import com.github.domain.QueryVo;
import com.github.domain.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @param
* @return
*/
public class TestMybatis {
private IUserDao dao = null;
private InputStream is = null;
private SqlSession sqlSession = null;
/**初始化方法
* @throws IOException
*/
@Before
public void init() throws IOException {
//1、加载配置文件SqlMapConfig.xml进内存
is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
//2、创建SqlSessionFactoryBuild
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
//3、创建工厂类
//使用构建者模式 因为SqlSessionFactory是抽象类
// 不能直接创建 为了省略创建SqlSessionFactory的实类所带来的麻烦,mybatis提供构建者模式屏蔽这些繁琐的步骤
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
//4、使用工厂类生产sqlSession
sqlSession = factory.openSession();
//5、使用sqlSession创建dao代理对象
dao = sqlSession.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
}
/**关闭资源方法
* @throws IOException
*/
@After
public void after() throws IOException {
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
is.close();
}
/**
* mybatis查询所有操作测试
*/
@Test
public void testFindAll() throws IOException {
List<User> users = dao.findAll();
for (User user : users) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
/**
* mybatis保存操作测试,并封装添加后生成的主键的id到user对象
*/
@Test
public void testSaveUser(){
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("James");
user.setBirthday(new Date());
user.setSex("男");
user.setAddress("深圳市宝安区");
System.out.println("======保存前的user = " + user+"======");
int i = dao.userSave(user);
System.out.println("======保存后的user = " + user+"======");
}
/**
* mybatis更新测试
*/
@Test
public void testUpdate(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(60);
user.setUsername("test的账户");
user.setBirthday(new Date());
user.setAddress("更新后的地址");
user.setSex("男");
int i = dao.updateUser(user);
if(i == 1){
System.out.println("更新成功");
}else {
System.out.println("更新失败");
}
}
/**
* mybatis查询单个操作测试
*/
@Test
public void testDeleteById(){
int i = dao.removeUser(60);
if(i == 1){
System.out.println("删除成功");
}else {
System.out.println("删除失败");
}
}
/**
* mybatis查询单个操作测试
* @return
*/
@Test
public void testFindById(){
User user = dao.findById(62);
System.out.println("user = " + user);
}
/**
* mybatis模糊查询操作测试
* @return
*/
@Test
public void testFindByName(){
List<User> users = dao.findByName("%James%");
for (User user : users) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
/**
* mybatis聚合函数操作
* @return
*/
@Test
public void testFindTotal(){
int total = dao.findTotal();
System.out.println(total);
}
/**
* 测试使用queryVo作为参数实现模查询
*/
@Test
public void testFindUserByVo(){
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("%James%");
QueryVo vo = neQueryVo(user);
List<User> users = dao.findUserByVo(vo);
for (User user1 : users) {
System.out.println(user1);
}
}
}
8. 细节问题
8.1. 配置文件位置引发的问题
放在src/main/java下面的*.xml文件没有编译到classpath中,在pom.xml中添加依赖,一般是把mapper文件放到resources下面。
<build>
<!-- 通过这种方式可以设置java下面的*.xml文件编译到classpath下面-->
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
8.2. 关于查询的数据绑定问题
8.2.1 序号参数绑定
public interface UserDao {
//使用原生参数绑定
public User selectUserByIdAndPwd(Integer id , String pwd);
}
<select id="selectUserByIdAndPwd" resultType="user">
SELECT * FROM t_users
WHERE id = #{arg0} AND password = #{arg1} <!--arg0 arg1 arg2 ...-->
</select>
<select id="selectUserByIdAndPwd" resultType="user">
SELECT * FROM t_users
WHERE id = #{param1} AND password = #{param2} <!--param1 param2 param3 ...-->
</select>
8.2.2 注解参数绑定【推荐】
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param; //引入注解
public interface UserDao {
//使用MyBatis提供的@Param进行参数绑定
public User selectUserByIdAndPwd(@Param("id") Integer id , @Param("pwd") String pwd);
}
<select id="selectUserByIdAndPwd" resultType="user">
SELECT * FROM t_users
WHERE id = #{id} AND password = #{pwd} <!-- 使用注解值 @Param("pwd") -->
</select>
8.2.3 Map参数绑定
public interface UserDao {
//添加Map进行参数绑定
public User selectUserByIdAndPwd_map(Map values);
}
Map values = new HashMap(); //测试类创建Map
values.put("myId",1); //自定义key,绑定参数
values.put("myPwd","123456");
User user = userDao.selectUserByIdAndPwd_map(values);
<select id="selectUserByIdAndPwd_map" resultType="user">
SELECT * FROM t_users
WHERE id = #{myId} AND password = #{myPwd} <!-- 通过key获得value -->
</select>
8.2.4 对象参数绑定
public interface UserDao {
//使用对象属性进行参数绑定
public User selectUserByUserInfo(User user);
}
<select id="selectUserByUserInfo" resultType="user">
SELECT * FROM t_users
WHERE id = #{id} AND password = #{password} <!-- #{id}取User对象的id属性值、#{password}同理 -->
</select>
四、Mybatis的ORM关系结果映射
MyBatis只能自动维护库表”列名“与”属性名“相同时的一一对应关系,二者不同时,无法自动ORM。

1. 方法一 查询使用别名
在SQL中使用 as 为查询字段添加列别名,以匹配属性名。
<mapper namespace="com.github.dao.IUserDao">
<select id="findAll" resultType=com.github.domain.User">
select id ad uid username as username birthday as userBirthday sex as userSex address ad userAddress from usre
</select>
</mapper>
2. 方案二:结果映射(ResultMap - 查询结果的封装规则)
使用ResultMap 标签
实体类的对象属性使用collection标签
在select标签中要使用reslutType属性指定ResultMap的id
public class User implements Serializable {
private Integer uid;
private String username;
private Date userBirthday;
private String userSex;
private String userAddress;
//todo get、set方法省略
}
<!--定义封装account和User的resultMap-->
<resultMap id="userMap" type="com.github.domain.User">
<!--一对一的关系映射,指定关联片段,并且封装user的内容 主键使用id标签 非主键使用result标签-->
<id column="id" property="uid"></id>
<result column="username" property="username"></result>
<result column="birthday" property="userBirthday"></result>
<result column="sex" property="userSex"></result>
<result column="address" property="userAddress"></result>
</resultMap>
<!--查询所有-->
<select id="findAll" resultMap="userMap">
select * from user
</select>
细节:关于时间类型的转换
如果数据库时间对应是deteTime类型的,在映射配置文件中的配置的
中对应的实体类属性配置javaType为java.sql.Timestamp类型
五、使用properties文件配置数据源环境
5.1使用配置文件配置数据源
jdbc.properties文件 规范:尽量满足规范加上jdbc前缀加以区分
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy_mybatis
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=123
Mybatis主配置文件使用${key}的形式从properties中取值
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<!--Mybatis主配置文件-->
<configuration>
<!--使用properties配置mysql环境-->
<properties resource="jdbc.properties"></properties>
<!--环境配置-->
<environments default="mysql">
<environment id="mysql">
<!--配置事务管理器-->
<transactionManager type="jdbc"></transactionManager>
<!--配置数据源(连接池)-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<package name="com.github.dao"></package>
</mappers>
</configuration>Mybatis中的连接池
5.2 Mybatis连接池配置提供了3种方式配置:
配置的位置:
主配置文件SqlMapConfig.xml中的dataSource标签,type属性就是表示采用何种方式
type属性的取值:
-
POOLED(开发常用): 采用传统的javax.sql.DataSource规范的连接池,Mybatis中有针对规范的实现
-
UNPOOLDE:采用传统的获取连接方式,虽然也实现的javax.sqlDataSource接口,但是并没有使用连接池的思想
-
JNDI:采用服务器提供的JNDI技术实现,来获取DataSource对象,不同的服务器所能拿到的DataSou是不一样的 注意:如果不是web或者maven的war工程是不能使用的
六、动态SQL语句
1. sql标签
作用:可以定义公共sql语句片段
属性:指定公共SQL语句的id,使用该片段使用include引入即可
<sql id="selectSql">
select * from user
</sql>
<!--应用SQL标签语句查询所有-->
<select id="findAll" resultMap="userMap">
<include refid="selectSql"/> where id = 45
</select>

2. where 标签
作用:where标签会自动添加where关键字,去掉多余的and
- if标签
作用:判断
属性:test test的值是参数中的值
<!--动态SQL语句进行模糊查询-->
<select id="findUserByCondition" resultMap="userMap" >
<!-- where标签会自动添加where关键字,去掉多余的and -->
<where>
<!--判断参数user的username属性是否为null 如果不为null则会自动拼接where语句 -->
<if test=" username != null and username!=''">
and username = #{username}
</if>
<if test="userSex != null and userSex!=''">
and sex=#{userSex}
</if>
</where>
</select>
/**
* 测试根据用户名和性别查询用户
*/
@Test
public void testFindUserByCondition(){
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("James");
user.setUserSex("女");
List<User> users = dao.findUserByCondition(user);
for (User user1 : users) {
System.out.println(user1);
}
}

4. set标签
作用:添加set关键字,去掉多余的逗号
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="user">
update user
<set>
<if test="username!=null and username!=''">
username=#{username},
</if>
<if test="userBirthday!=null">
birthday=#{userBirthday},
</if>
<if test="userSex!=null and userSex!=''">
sex=#{userSex},
</if>
<if test="userAddress!=null and userAddress!=''">
address=#{userAddress},
</if>
</set>
<where>
<if test=" uid != null">
id = #{uid}
</if>
</where>
</update>
/**
* 测试更新用户
*/
@Test
public void testUpdateUser(){
User user = new User();
user.setUid(64);
user.setUsername("mybatis测试数据");
user.setUserSex("女");
user.setUserAddress("深圳市硅谷区");
user.setUserBirthday(new Date());
int i = dao.updateUser(user);
sqlSession.commit();
}

5. foreach标签
作用:用于循环集合或数组
属性:
collection:循环的集合
open:语句片段的开头,每次循环开始都会执行一次
close:结束的语句片段,每次循环结束都会执行一次
separator:每次都循环都执行片段
item:每次遍历的对象,要保持和下面#{}内名字一至
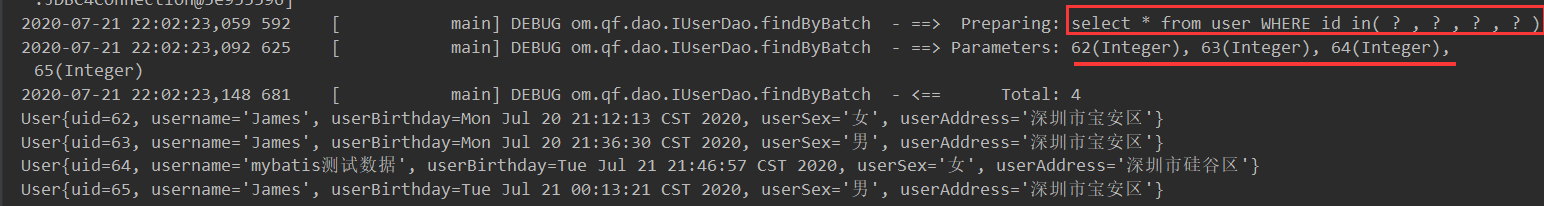
/**
* 批量查询
* @param ids
* @return
*/
List<User> findByBatch(List<Integer> ids);
<!--使用foreach进行批量查询-->
<select id="findByBatch" parameterType="list" resultMap="userMap">
select * from user
<where>
<if test="list != null and list.size > 0">
<!-- 说明 collection:循环的集合
open:语句片段的开头 close:结束的语句片段 separator:每次都循环都执行片段
item:要保持和下面#{}内名字一至-->
<foreach collection="list" open="id in(" close=")" separator="," item="uid">
#{uid}
</foreach>
</if>
</where>
</select>
7. trim标签
< trim prefix="" suffix="" prefixOverrides="" suffixOverrides="" >代替< where > 、< set >
<select id="selectBookByCondition" resultType="com.github.mybatis.day2.dynamic.Book">
SELECT id,name,author,publish,sort
FROM t_books
<trim prefix="WHERE" prefixOverrides="AND|OR"> <!-- 增加WHERE前缀,自动忽略前缀 -->
<if test="id != null">
and id = #{id}
</if>
<if test="name != null">
and name = #{name}
</if>
<if test="author != null">
and author = #{author}
</if>
<if test="publish != null">
and publish = #{publish}
</if>
<if test="sort != null">
and sort = #{sort}
</if>
</trim>
</select>
<update id="updateBookByCondition">
UPDATE t_books
<trim prefix="SET" suffixOverrides=","> <!-- 增加SET前缀,自动忽略后缀 -->
<if test="name != null">
name = #{name} ,
</if>
<if test="author != null">
author = #{author} ,
</if>
<if test="publish != null">
publish = #{publish} ,
</if>
<if test="sort != null">
sort = #{sort}
</if>
</trim>
WHERE id = #{id}
</update>
7. 使用#和$的区别
使用#进行查询()
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: select ? from t_user
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: id,username,age,email(String)
使用$进行查询
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: select id,username,age,email from t_user
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters:
这种方式会出现SQL注入的问题,比较危险
两个符号的使用场景
1、#
a)一般使用在参数的传递
b)最后别解析为占位符的
2、$(危险,灵活)
a)动态表的查询
七、Mybatis的多表查询
7.1 表之间的对应关系
表之间的关系有几种:
一对多、多对一、一对一、多对多
举例:
用户和订单就是一对多,订单和用户就是多对一,一个用户可以下多个订单、多个订单属于同一个用户人和身份证号就是一对一,一个人只能有一个身份证号,一个身份证号只能属于一个人老师和学生之间就是多对多,一个学生可以被多个老师教过,一个老师可以教多个学生.
特例:
如果拿出每一个订单,他都只能属于一个用户。所以Mybatis就把多对一看成了一对一。
7.1.1 collection标签
作用:指定关系表的实体类型 指定多方关系时(集合)使用collection标签
属性:
property:多的实体类属性名称
ofType:多的实体类属性类型
7.1.2 association标签
作用:指定关系表的实体类型 指定一方关系时(对象属性)使用association标签
属性:
property:集合名称
javaType:多的一方的类型,这里也是支持别名
7.2 mybatis的一对多查询
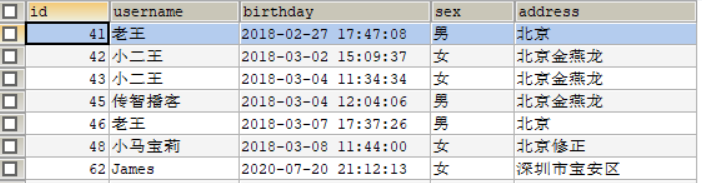
在查询一对多时,在对应实体类添加用于存放对应关系表实体类的集合属性
用户表 user
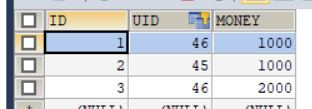
账户表 account
userDao接口
public interface IUserDao {
/**
* 查询所有
* @return
*/
List<User> findAll();
}
映射配置文件
<mapper namespace="com.github.dao.IUserDao">
<!--定义封装account和User的resultMap-->
<resultMap id="userMap" type="com.github.domain.User">
<!--一对一的关系映射,指定关联片段,并且封装user的内容 主键使用id标签 非主键使用result标签-->
<id column="id" property="uid"></id>
<result column="username" property="username"></result>
<result column="birthday" property="userBirthday"></result>
<result column="sex" property="userSex"></result>
<result column="address" property="userAddress"></result>
<!--指定关系表的实体类型 指定多方关系时(集合)使用collection标签 property:多的实体类属性名称 ofType:多的实体类属性类型 -->
<!--
配置对多
property:集合名称
ofType:多的一方的类型,这里也是支持别名
-->
<collection property="accounts" ofType="account">
<result column="aid" property="aid"></result>
<result column="uid" property="uid"></result>
<result column="money" property="money"></result>
</collection>
</resultMap>
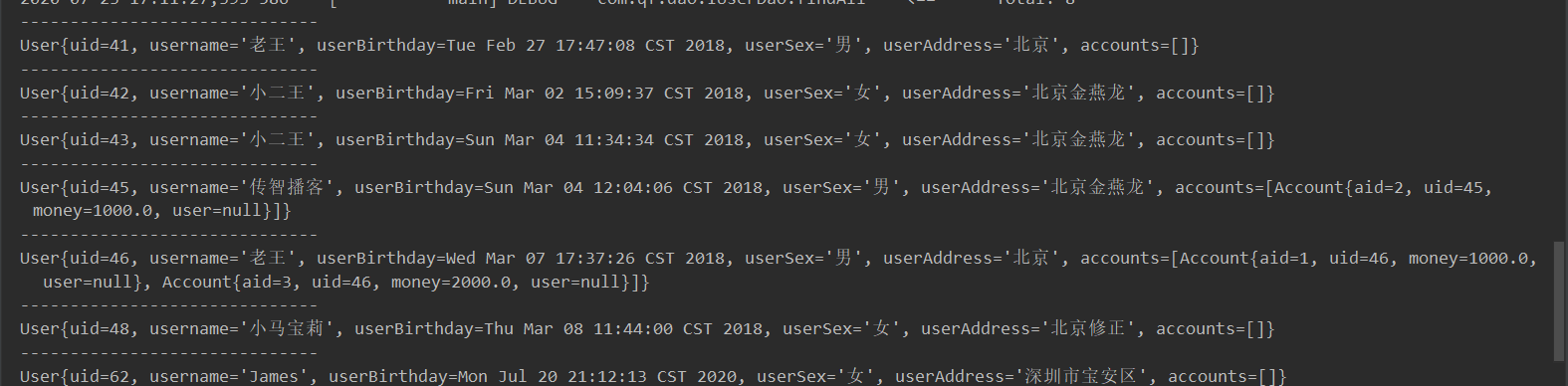
<!--查询所有 一对多查询 多表连接查询-->
<select id="findAll" resultMap="userMap">
select *,u.id as uid,a.id as aid from user u left join account a on u.id = a.uid
</select>
</mapper>
usre实体类
public class User implements Serializable {
//user表与account表是一对多关系,需要添加List集合用于存储account
private Integer uid;
private String username;
private Date userBirthday;
private String userSex;
private String userAddress;
private List<Account> accounts;
//get set toString方法省略
}
account实体类
public class Account implements Serializable {
//account与user表是多对一的关系,添加User类型的属性
private Integer aid;//主键id
private Integer uid;//外键id
private Double money;//金额
private User user;
}
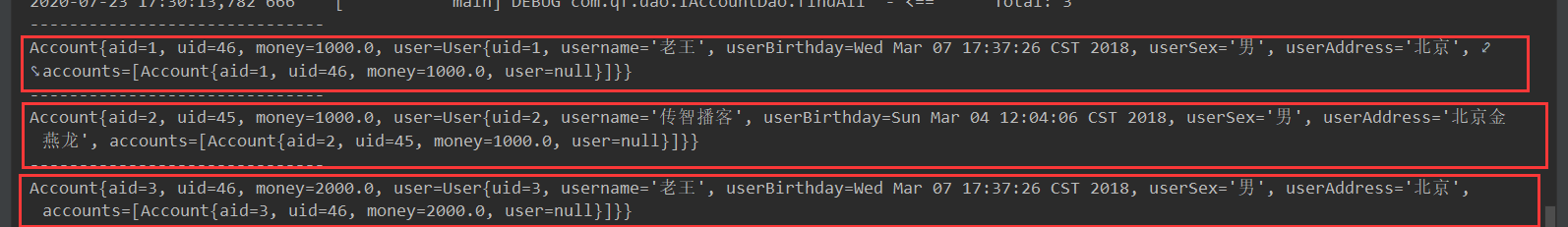
执行findAll()方法的结果
7.3 Mybatis的多对一查询
在多对一中,在多的实体类中添加一对应的实体类的属性(account实体类 和 user 实体类请参考7.2一对多查询)
IAccountDao接口
public interface IAccountDao {
/**
* 查询所有
* @return
*/
List<Account> findAll();
}
IAccountDao.xml映射配置文件
<mapper namespace="com.github.dao.IAccountDao">
<resultMap id="accountMap" type="account">
<id column="aid" property="aid"></id>
<result column="money" property="money"></result>
<result column="uid" property="uid"></result>
<!--
配置对多
property:集合名称
javaType:多的一方的类型,这里也是支持别名
-->
<association property="user" javaType="user" column="uid">
<id column="id" property="uid"></id>
<result column="username" property="username"></result>
<result column="birthday" property="userBirthday"></result>
<result column="sex" property="userSex"></result>
<result column="address" property="userAddress"></result>
<collection property="accounts" ofType="account">
<id column="aid" property="aid"></id>
<result column="money" property="money"></result>
<result column="uid" property="uid"></result>
</collection>
</association>
</resultMap>
<!--多对一查询 等价于一对一 使用多表连接查询-->
<select id="findAll" resultMap="accountMap">
select *,a.id as aid,u.id as uid from account a left join user as u on a.uid = u.id;
</select>
</mapper>
查询结果
7.4 Mybatis的多对多查询
在多对多查询中,需要借助第三张关系表进行关联
用户表uesr
角色表role

第三张关系表user_role

role表对应的实体类
public class Role implements Serializable {
private Integer rid;//角色id
private String roleName;//角色姓名
private String roleDesc;//角色描述
private List<User> users;
//get set toStirng 方法省略
}
IRoleDao接口
public interface IRoleDao {
/**
* 多对多查询所有
* @return
*/
List<Role> findAll();
}
IRoleDao的映射配置文件
<mapper namespace="com.github.dao.IRoleDao">
<resultMap id="roleMap" type="role">
<id column="id" property="rid"></id>
<result property="roleName" column="ROLE_NAME"></result>
<result property="roleDesc" column="ROLE_DESC"></result>
<collection property="users" ofType="user">
<id column="uid" property="uid"></id>
<result column="username" property="username"></result>
<result column="birthday" property="userBirthday"></result>
<result column="sex" property="userSex"></result>
<result column="address" property="userAddress"></result>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findAll" resultMap="roleMap">
select
r.*,u.*,u.id as uid
from
role r
left join
user_role ur
on
r.id = ur.rid
left join
user u
on
u.id = ur.uid
</select>
</mapper>
查询结果
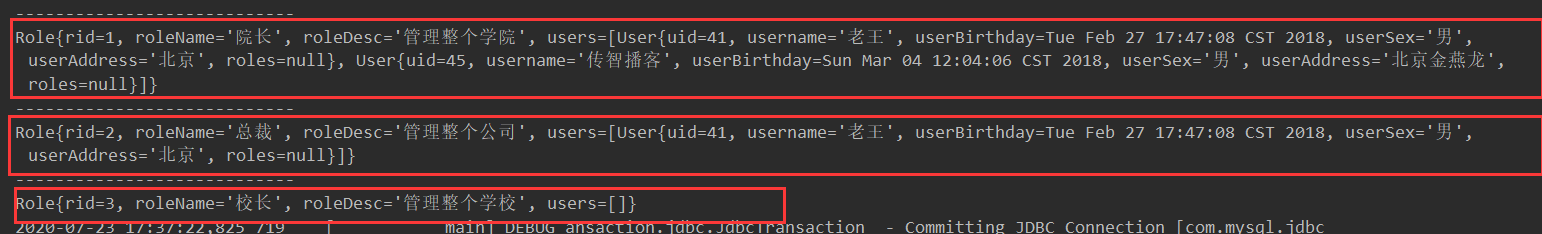
八、Mybatis的缓存
缓存的重要性是不言而喻的。 使用缓存, 我们可以避免频繁的与数据库进行交互, 尤其是在查询越多、缓存命中率越高的情况下, 使用缓存对性能的提高更明显。
mybatis 也提供了对缓存的支持, 分为一级缓存和二级缓存。 但是在默认的情况下, 只开启一级缓存(一级缓存是对同一个 SqlSession 而言的)
8.1 一级缓存
同一个
SqlSession对象, 在参数和 SQL 完全一样的情况先, 只执行一次 SQL 语句(如果缓存没有过期)也就是只有在参数和 SQL 完全一样的情况下, 才会有这种情况。一级缓存的特点
1、一级缓存在SqlSession关闭或者提交的时候才会清空
2、MyBatis中的一级缓存默认是开启的
3、一级缓存只对SqlSession有效
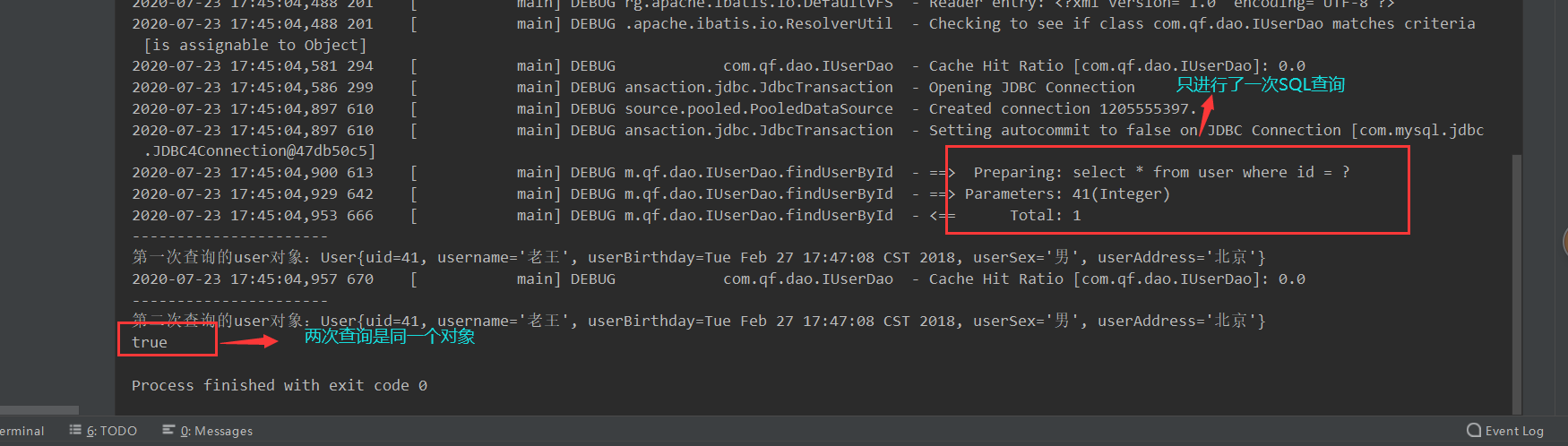
测试一级缓存的存在
/**
* 测试一级缓存 一级缓存是因为是同一个sqlsession里面的,最终用的是同一个map作缓存,所以缓存取出的对象是同一个对象
*/
@Test
public void testFindUserById1() throws IOException {
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
IUserDao dao = sqlSession.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
User user = dao.findUserById(41);
System.out.println("----------------------");
System.out.println("第一次查询的user对象:"+user);
User user2 = dao.findUserById(41);
System.out.println("----------------------");
System.out.println("第二次查询的user对象:"+user2);
System.out.println(user == user2);
}
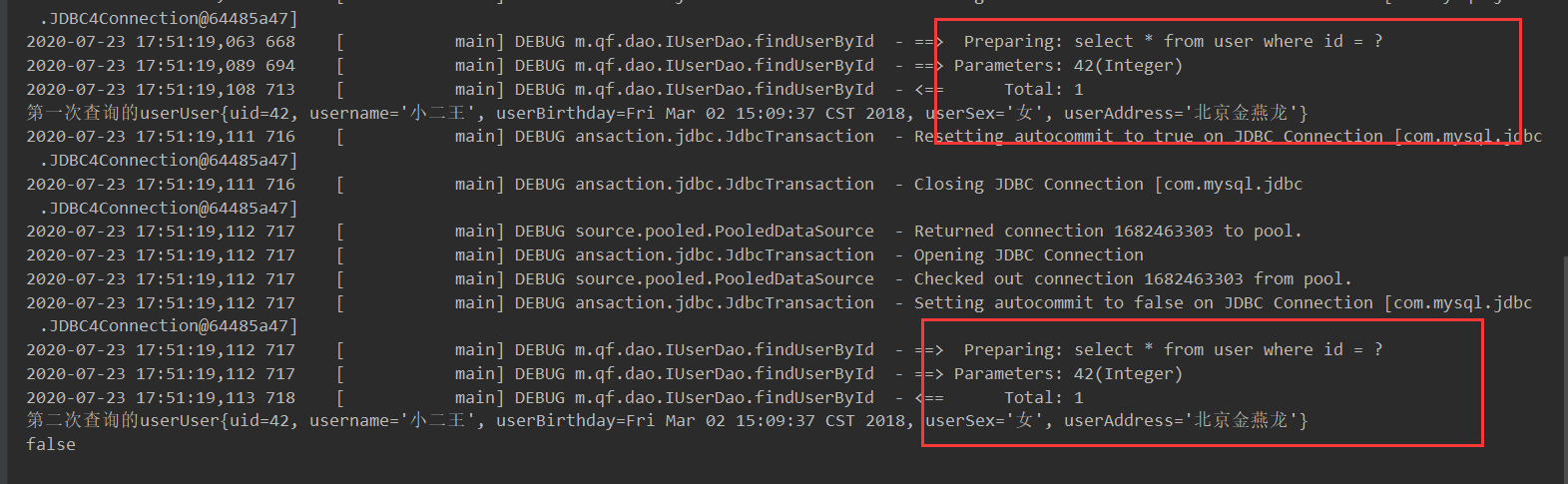
测试一级缓存的关闭
/**
* 测试一级缓存关闭
*/
@Test
public void testFindUserById2() throws IOException {
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
SqlSessionFactory build = builder.build(is);
SqlSession sqlSession = build.openSession();
IUserDao dao = sqlSession.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
User user = dao.findUserById(42);
System.out.println("第一次查询的user"+user);
//sqlSession关闭,一级缓存消失
sqlSession.close();
//创建新的sqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession1 = build.openSession();
IUserDao dao1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
User user1 = dao1.findUserById(42);
System.out.println("第二次查询的user"+user1);
System.out.println(user == user1);
}
8.2 二级缓存
二级缓存的作用是整个Mapper,也可以说是整个SqlSessionFactory,域SqlSession无关,二级缓存的特点
1、二级缓存默认是关闭的,需要手动开启
2、二级缓存指的是SqlSessionFactory级别的,对所有的SQLSession共享
3、放入到二级缓存中的对象必须要实现对象序列化接口
4、如果要二级缓存有效必须要事务提交或者session关闭。
开启二级缓存需要的配置
1、在Mybatis的配置文件中添加setting属性
2、需要在映射配置文件中添加
表示开启二级缓存 3、catch属性:
* size:可以存放多个对象 * flushInterval:缓存刷新(清空)的时间,默认是不刷新,单位是毫秒
- readOnly:放在缓存中的对象是否只读
- a)如果是true,放进去的和获取到的是同一个对象
- b)如果是false,从缓存中获取到是这个对象的拷贝
- eviction:缓存清空的策略
- LRU:最少使用原则,移除最长时间不使用的对象,默认是LRU。
- FIFO:先进先出原则,按照对象进入缓存顺序进行回收
九、延时加载
9.1 延时加载
就是在需要用到数据时才进行加载,不需要用到数据时就不加载数据。延迟加载也称懒加载.
好处:先从单表查询,需要时再从关联表去关联查询,大大提高数据库性能,因为查询单表要比关联查询多张表速度要快。
坏处:
因为只有当需要用到数据时,才会进行数据库查询,这样在大批量数据查询时,因为查询工作也要消耗
时间,所以可能造成用户等待时间变长,造成用户体验下降。
9.2 延时加载的策略
我们需要在 Mybatis 的配置文件 SqlMapConfig.xml 文件中添加延迟加载的配置。
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>
十、PageHelper(分页插件)
10.1 概念
PageHelper是适用于MyBatis框架的一个分页插件,使用方式极为便捷,支持任何复杂的单表、多表分页查询操作。
10.2 访问与下载
10.3 开发步骤
PageHelper中提供了多个分页操作的静态方法入口。
10.3.1 引入依赖
pom.xml中引入PageHelper依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId>
<version>5.1.10</version>
</dependency>
10.3.2 配置MyBatis-config.xml
在MyBatis-config.xml中添加< plugins >。
<configuration>
<typeAliases></typeAliases>
<plugins>
<!-- com.github.pagehelper为PageHelper类所在包名 -->
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor"></plugin>
</plugins>
<environments></environments>
</configuration>
10.3.3 PageHelper应用方式
使用PageHelper提供的静态方法设置分页查询条件。
/**
* 测试分页查询
*/
@Test
public void testFindUserByPage(){
IUserDao dao = sqlSession.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
//1、开启分页 pageNum:查询的页数,pageSize:每页的行数
PageHelper.startPage(2,3);
//2、查询当页的数据,参数mybatis会自动转换在sql语句内
List<User> userList = dao.findUserByPage();
//3、com.github.pagehelper.Page是继承List集合的
Page page = (Page) userList;
//4、创建PageInfo对象,并把page中的数据赋值给pageInfo
PageInfo<User> pageInfo = new PageInfo<User>(page);
System.out.println("当前页数:"+pageInfo.getPageNum());
System.out.println("每页的大小:"+pageInfo.getPageSize());
System.out.println("总页数:"+pageInfo.getPages());
System.out.println("总记录条数:"+pageInfo.getTotal());
System.out.println("分页数据集合:"+pageInfo.getList());
}
10.4 PageInfo对象
PageInfo对象中包含了分页操作中的所有相关数据。
| PageInfo结构图 |
|---|
 |

10.4.1 PageInfo应用方式
使用PageInfo保存分页查询结果。
@Test
public void testPageInfo(){
UserDao userDao = MyBatisUtils.getMapper(UserDao.class);
PageHelper.startPage(6, 2);
List<User> users = userDao.selectAllUsers();
PageInfo<User> pageInfo = new PageInfo<User>(users);//将分页查询的结果集保存在PageInfo对象中
System.out.println(pageInfo);
}
10.4.2 注意事项
- 只有在PageHelper.startPage()方法之后的第一个查询会有执行分页。
- 分页插件不支持带有“for update”的查询语句。
- 分页插件不支持“嵌套查询”,会导致结果集折叠。