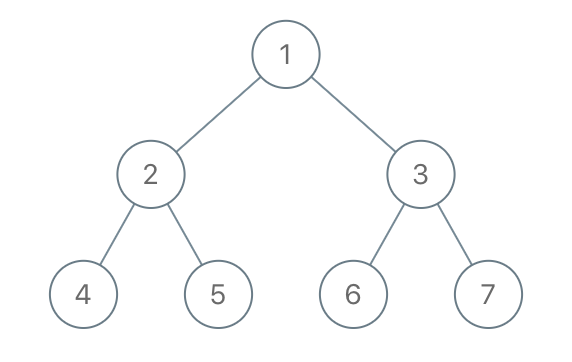
Given the root of a binary tree, each node in the tree has a distinct value.
After deleting all nodes with a value in to_delete, we are left with a forest (a disjoint union of trees).
Return the roots of the trees in the remaining forest. You may return the result in any order.
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], to_delete = [3,5] Output: [[1,2,null,4],[6],[7]]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the given tree is at most
1000. - Each node has a distinct value between
1and1000. to_delete.length <= 1000to_deletecontains distinct values between1and1000.
删点成林。题意是给一棵二叉树和一个to_delete数组,请你从树中删除to_delete中出现的节点,返回一个森林。这道题BFS和DFS都能做。
首先是BFS的做法。首先用一个hashset存储所有需要删除的节点。接着开始遍历树的每一个节点,遍历的方式还是跟层序遍历类似。从queue中弹出节点的时候,要做如下几件事情
- 如果这个节点是需要被删除的节点,需要从结果集里面删除这个节点
- 如果被删除的节点有孩子节点,需要把孩子节点加入结果集,因为他们没有父节点了,他们现在是自己这个子树的根节点了
- 当前节点如果有左孩子和右孩子,则分别加入queue继续下面的遍历,同时遍历的时候检查他们是否需要被删除,如果需要,在把他们放入queue之后需要断开他们和父节点的连接
时间O(n)
空间O(n)
Java实现
1 class Solution { 2 public List<TreeNode> delNodes(TreeNode root, int[] to_delete) { 3 List<TreeNode> res = new ArrayList<>(); 4 Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); 5 queue.offer(root); 6 res.add(root); 7 HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(); 8 for (int node : to_delete) { 9 set.add(node); 10 } 11 12 while (!queue.isEmpty()) { 13 TreeNode cur = queue.poll(); 14 if (set.contains(cur.val)) { 15 res.remove(cur); 16 if (cur.left != null) { 17 res.add(cur.left); 18 } 19 if (cur.right != null) { 20 res.add(cur.right); 21 } 22 } 23 if (cur.left != null) { 24 queue.offer(cur.left); 25 if (set.contains(cur.left.val)) { 26 cur.left = null; 27 } 28 } 29 if (cur.right != null) { 30 queue.offer(cur.right); 31 if (set.contains(cur.right.val)) { 32 cur.right = null; 33 } 34 } 35 } 36 return res; 37 } 38 }
DFS的做法也不难。做法也是类似前序遍历那样,先处理当前节点,再处理左孩子和右孩子。用DFS的时候,需要想一想,下面的孩子节点一般是需要返回什么信息给父节点,以帮助定义DFS的helper函数的参数。这里我判断的是当前节点他自己是不是一个根节点,或者说他自己是不是已经跟自己的父节点断开了。helper函数里面,如果这个节点存在于hashset,则说明这个节点需要被删除,deleted变量为true。如果当前节点不需要被删除,同时他也是一个根节点的话,则加入结果集。如果这个节点需要被删除,helper函数往上一级返回的信息是null,因为已经被删除了;否则就返回这个节点。
时间O(n)
空间O(n)
Java实现
1 class Solution { 2 Set<Integer> set; 3 List<TreeNode> res; 4 5 public List<TreeNode> delNodes(TreeNode root, int[] to_delete) { 6 set = new HashSet<>(); 7 res = new ArrayList<>(); 8 for (int i : to_delete) { 9 set.add(i); 10 } 11 helper(root, true); 12 return res; 13 } 14 15 // is_root 判断的是当前节点有没有父母节点,true就是没有 16 private TreeNode helper(TreeNode node, boolean is_root) { 17 if (node == null) { 18 return null; 19 } 20 boolean deleted = set.contains(node.val); 21 if (is_root && !deleted) { 22 res.add(node); 23 } 24 node.left = helper(node.left, deleted); 25 node.right = helper(node.right, deleted); 26 return deleted ? null : node; 27 } 28 }