特征抽取sklearn.feature_extraction 模块提供了从原始数据如文本,图像等众抽取能够被机器学习算法直接处理的特征向量。

1.特征抽取方法之 Loading Features from Dicts


measurements=[
{'city':'Dubai','temperature':33.},
{'city':'London','temperature':12.},
{'city':'San Fransisco','temperature':18.},
]
from sklearn.feature_extraction import DictVectorizer
vec=DictVectorizer()
print(vec.fit_transform(measurements).toarray())
print(vec.get_feature_names())
#[[ 1. 0. 0. 33.]
#[ 0. 1. 0. 12.]
#[ 0. 0. 1. 18.]]
#['city=Dubai', 'city=London', 'city=San Fransisco', 'temperature']
2.特征抽取方法之 Features hashing



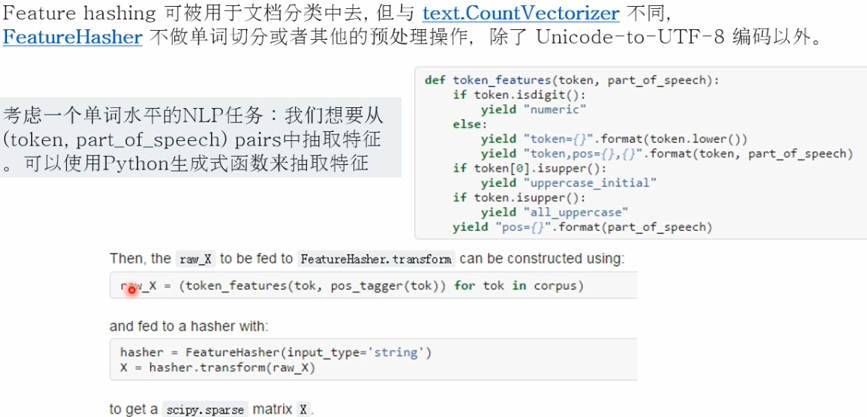
3.特征抽取方法之 Text Feature Extraction
词袋模型 the bag of words represenatation



#词袋模型
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
#查看默认的参数
vectorizer=CountVectorizer(min_df=1)
print(vectorizer)
"""
CountVectorizer(analyzer='word', binary=False, decode_error='strict',
dtype=<class 'numpy.int64'>, encoding='utf-8', input='content',
lowercase=True, max_df=1.0, max_features=None, min_df=1,
ngram_range=(1, 1), preprocessor=None, stop_words=None,
strip_accents=None, token_pattern='(?u)\b\w\w+\b',
tokenizer=None, vocabulary=None)
"""
corpus=["this is the first document.",
"this is the second second document.",
"and the third one.",
"Is this the first document?"]
x=vectorizer.fit_transform(corpus)
print(x)
"""
(0, 1) 1
(0, 2) 1
(0, 6) 1
(0, 3) 1
(0, 8) 1
(1, 5) 2
(1, 1) 1
(1, 6) 1
(1, 3) 1
(1, 8) 1
(2, 4) 1
(2, 7) 1
(2, 0) 1
(2, 6) 1
(3, 1) 1
(3, 2) 1
(3, 6) 1
(3, 3) 1
(3, 8) 1
"""
默认是可以识别的字符串至少为2个字符
analyze=vectorizer.build_analyzer()
print(analyze("this is a document to anzlyze.")==
(["this","is","document","to","anzlyze"]))
#True
在fit阶段被analyser发现的每一个词语都会被分配一个独特的整形索引,该索引对应于特征向量矩阵中的一列
print(vectorizer.get_feature_names()==(
["and","document","first","is","one","second","the","third","this"]
))
#True
print(x.toarray())
"""
[[0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1]
[0 1 0 1 0 2 1 0 1]
[1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0]
[0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1]]
"""
获取属性
print(vectorizer.vocabulary_.get('document'))
#1
对于一些没有出现过的字或者字符,则会显示为0
vectorizer.transform(["somthing completely new."]).toarray() """ [[0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1] [0 1 0 1 0 2 1 0 1] [1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0] [0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1]] """
在上边的语料库中,第一个和最后一个单词是一模一样的,只是顺序不一样,他们会被编码成相同的特征向量,所以词袋表示法会丢失了单词顺序的前后相关性信息,为了保持某些局部的顺序性,可以抽取2个词和一个词
bigram_vectorizer=CountVectorizer(ngram_range=(1,2),token_pattern=r"w+",min_df=1)
analyze=bigram_vectorizer.build_analyzer()
print(analyze("Bi-grams are cool!")==(['Bi','grams','are','cool','Bi grams',
'grams are','are cool']))
#True
x_2=bigram_vectorizer.fit_transform(corpus).toarray()
print(x_2)
"""
[[0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0]
[0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 2 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0]
[1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0]
[0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1]]
"""
