一.模拟Get请求(无参)
首先导入HttpClient依赖
1 <dependency> 2 <groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId> 3 <artifactId>httpclient</artifactId> 4 <version>4.5.2</version> 5 </dependency>
测试代码
1 //Get请求 2 public static void getRequest() throws IOException { 3 //创建一个默认的链接 4 CloseableHttpClient client = HttpClients.createDefault(); 5 //创建一个请求 6 HttpGet httpGet=new HttpGet("https://www.cnblogs.com/chx9832"); 7 //执行请求获取响应的结果 8 CloseableHttpResponse response = client.execute(httpGet); 9 //获取响应的状态码 10 int statusCode = response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode(); 11 System.out.println("服务器返回状态码:"+statusCode); 12 //服务器正常响应 13 if(statusCode ==200){ 14 //获取响应结果 15 System.out.println(EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(),"UTF-8")); 16 } 17 //关闭结果对象 18 response.close(); 19 //关闭链接 20 client.close(); 21 }
通过main方法调用就可拿到目标地址的代码段

一.模拟Post请求(带参)
与get请求类似,不同的是带参需要创建参数队列,并把参数封装到请求体再set进请求中.
1 //模拟Post请求 2 public static void postRequest() throws IOException { 3 //创建链接 4 CloseableHttpClient client = HttpClients.createDefault(); 5 //创建请求 6 HttpPost httpPost=new HttpPost("http://localhost:8080/HttpClientServlet"); 7 8 //创建参数队列 9 List<NameValuePair> pairList=new ArrayList<>(); 10 pairList.add(new BasicNameValuePair("username","怀鑫")); 11 //创建请求体,封装参数 12 UrlEncodedFormEntity entity=new UrlEncodedFormEntity(pairList,"UTF-8"); 13 //将请求体交给当前请求 14 httpPost.setEntity(entity); 15 16 //发送请求,接收结果 17 CloseableHttpResponse response = client.execute(httpPost); 18 System.out.println("接收到的结果为:"+EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(),"UTF-8")); 19 20 21 //关闭资源 22 response.close(); 23 client.close(); 24 }
新建一个web项目,创建一个servlet模拟服务器,启动tomcat等待请求
1 package com.chx; 2 3 import javax.servlet.ServletException; 4 import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; 5 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; 6 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; 7 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; 8 import java.io.IOException; 9 10 @WebServlet("/HttpClientServlet") 11 public class HttpClientServlet extends HttpServlet { 12 @Override 13 protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { 14 //获取数据 15 String username = req.getParameter("username"); 16 System.out.println("接收的数据:"+username); 17 resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8"); 18 resp.getWriter().write("服务器正确接收到数据~"); 19 } 20 21 @Override 22 protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { 23 doPost(req,resp); 24 } 25 }
回到post请求方法启动后执行效果
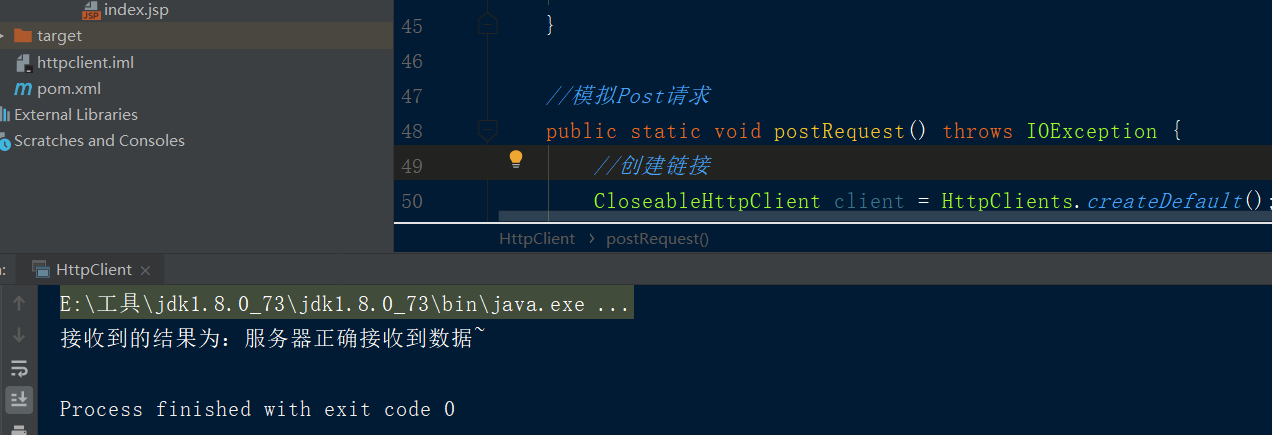
服务器端
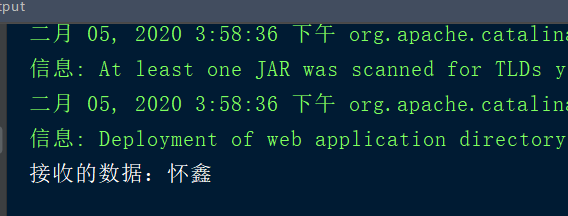
这样,就完成了简单的httpclient的get和post请求...
总结:
1. 创建HttpClient对象。
2. 创建请求方法的实例,并指定请求URL。如果需要发送GET请求,创建HttpGet对象;如果需要发送POST请求,创建HttpPost对象。
3. 如果需要发送请求参数,可调用HttpGet、HttpPost共同的setParams(HttpParams params)方法来添加请求参数;对于HttpPost对象而言,也可调用setEntity(HttpEntity entity) 方法来设置请求参数。
4. 调用HttpClient对象的execute(HttpUriRequest request)发送请求,该方法返回一个HttpResponse。
5. 调用HttpResponse的getAllHeaders()、getHeaders(String name)等方法可获取服务器的响应头;调用HttpResponse的getEntity()方法可获取HttpEntity对象,该对象包装了服务 器的响应内容。程序可通过该对象获取服务器的响应内容。
6. 释放连接。无论执行方法是否成功,都必须释放连接