什么是注解
传统的Spring做法是使用.xml文件来对bean进行注入或者是配置aop、事物,这么做有两个缺点:
1、如果所有的内容都配置在.xml文件中,那么.xml文件将会十分庞大;如果按需求分开.xml文件,那么.xml文件又会非常多。总之这将导致配置文件的可读性与可维护性变得很低
2、在开发中在.java文件和.xml文件之间不断切换,是一件麻烦的事,同时这种思维上的不连贯也会降低开发的效率
为了解决这两个问题,Spring引入了注解 (注解是jdk1.5新特性),通过"@XXX"的方式,让注解与Java Bean紧密结合,既大大减少了配置文件的体积,又增加了Java Bean的可读性与内聚性。
本篇博文将演示如何使用注解的方式完成注入对象的效果
修改applicationContext.xml
1. 在15行添加 <context:annotation-config/> 表示告诉Spring要用注解的方式进行配置
2. 注入对象的21行注释掉,这个行为在后面将使用注解来完成
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" 4 xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" 5 xsi:schemaLocation=" 6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd 8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop 9 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd 10 http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx 11 http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd 12 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context 13 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd"> 14 15 <context:annotation-config/> 16 <bean name="c" class="com.spring.pojo.Category"> 17 <property name="name" value="category 1" /> 18 </bean> 19 <bean name="p" class="com.spring.pojo.Product"> 20 <property name="name" value="product1" /> 21 <!-- <property name="category" ref="c" /> --> 22 </bean> 23 24 </beans>
@Autowired
@Autowired顾名思义,就是自动装配,其作用是为了消除代码Java代码里面的getter/setter与bean属性中的property。当然,getter看个人需求,如果私有属性需要对外提供的话,应当予以保留。
在Product.java的category属性前加上@Autowired注解
@Autowired private Category category;
除了在属性前加上 @Autowired这种方式外,也可以在setCategory方法前加上@Autowired,这样来达到相同的效果
@Autowired public void setCategory(Category category)
1 package com.spring.pojo; 2 3 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; 4 5 public class Product { 6 7 private int id; 8 private String name; 9 @Autowired 10 private Category category; 11 12 public int getId() { 13 return id; 14 } 15 16 public void setId(int id) { 17 this.id = id; 18 } 19 20 public String getName() { 21 return name; 22 } 23 24 public void setName(String name) { 25 this.name = name; 26 } 27 28 public Category getCategory() { 29 return category; 30 } 31 //@Autowired加在这里也可以 32 public void setCategory(Category category) { 33 this.category = category; 34 } 35 }
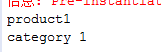
运行测试
package com.spring.test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.spring.pojo.Product; public class TestSpring { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[] { "applicationContext.xml" }); Product p = (Product) context.getBean("p"); System.out.println(p.getName()); System.out.println(p.getCategory().getName()); } }
@Resource
除了@Autowired之外,@Resource也是常用的手段,也能得到相同的结果
@Resource(name="c")//默认通过name属性去匹配bean
//Resource(type=Category.class)//找不到再按type去匹配 private Category category;
这是详细一些的用法,说一下@Resource的装配顺序:
1、@Resource后面没有任何内容,默认通过name属性去匹配bean,找不到再按type去匹配
2、指定了name或者type则根据指定的类型去匹配bean
3、指定了name和type则根据指定的name和type去匹配bean,任何一个不匹配都将报错
然后,区分一下@Autowired和@Resource两个注解的区别:
1、@Autowired默认按照byType方式进行bean匹配,@Resource默认按照byName方式进行bean匹配
2、@Autowired是Spring的注解,@Resource是J2EE的注解,这个看一下导入注解的时候这两个注解的包名就一清二楚了
Spring属于第三方的,J2EE是Java自己的东西,因此,建议使用@Resource注解,以减少代码和Spring之间的耦合。
注解@Autowired和@Resource的字段(成员变量)注入和setter注入的区别,请点击此处查看
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
对Bean的注解
上述例子是对注入对象行为的注解,那么bean对象本身,比如Category,Product也可以移出applicationContext.xml配置文件,通过注解进行。
修改applicationContext.xml
什么都去掉,只新增:
<context:component-scan base-package="com.spring.pojo"/>
其作用是告诉Spring,bean都放在com.spring.pojo这个包下
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" 4 xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" 5 xsi:schemaLocation=" 6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd 8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop 9 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd 10 http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx 11 http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd 12 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context 13 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd"> 14 15 <context:component-scan base-package="com.spring.pojo"/> 16 17 </beans>
@Component
(@Component注解、@Service注解、@Repository注解、@Controller注解区别,请点击此处查看)
为Product类加上@Component注解,即表明此类是bean
@Component("p")
public class Product {
@Component("c")
public class Category {
另外,因为配置从applicationContext.xml中移出来了,所以属性初始化放在属性声明上进行了。
private String name="product 1"; private String name="category 1";
Product代码:
package com.spring.pojo; import javax.annotation.Resource; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component("p") public class Product { private int id; private String name="product 1"; @Autowired private Category category; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Category getCategory() { return category; } public void setCategory(Category category) { this.category = category; } }
Category代码:
package com.spring.pojo; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component("c") public class Category { private int id; private String name="category 1"; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
运行TestSpring,可以发现运行结果跟之前是一样的
