spring也支持注解方式实现AOP,相对于配置文件方式,注解配置更加的轻量级,配置、修改更加方便。
1.开启AOP的注解配置方式
<!-- 开启aop属性注解 --> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
2.将定制的类标志为一个切面
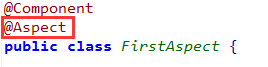
3.配置通知,指定切入点规则
前置通知 @Before
环绕通知 @Around
后置通知 @AfterReturning
异常通知 @AfterThrowing
最终通知 @After
@Before("execution(* cn.tedu.service.*.*(..))") public void before(JoinPoint jp){ Class clz = jp.getTarget().getClass(); Signature signature = jp.getSignature(); String name = signature.getName(); System.out.println("before...["+clz+"]...["+name+"]..."); }
** 通过注解的配置 等价于 配置文件的配置
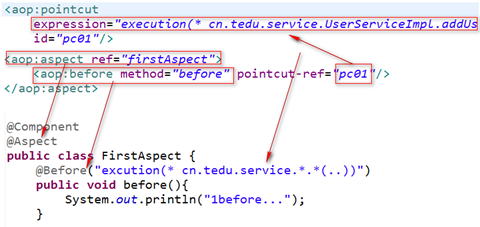
4.重复使用同一个切入点表达式
如果一个切面中多个通知 重复使用同一个切入点表达式,则可以将该切入点表达式单独定义,后续引用。
注意,在当前切面中通过注解定义的切入点只在当前切面中起作用,其他切面看不到。

5.额外配置一个returning属性
在后置通知的注解中,也可以额外配置一个returning属性,来指定一个参数名接受目标方法执行后的返回值。

6.异常通知的注解
在异常通知的注解中,也可以额外配置一个throwing属性,来指定一个参数名接受目标方法抛出的异常对象。

源码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.2.xsd " > <!-- 注解属性注入 --> <context:annotation-config></context:annotation-config> <!-- 注解bean扫描 --> <context:component-scan base-package="cn.tedu.service,cn.tedu.aop"></context:component-scan> <!-- 开启aop属性注解 --> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy> </beans>
package cn.tedu.service; public interface UserService { public String addUser(String name); public void updateUser(); public void deleteUser(); public void query(); }
package cn.tedu.service; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service("userService") public class UserServiceImple implements UserService { @Override public String addUser(String name) { // int i = 10/0; System.out.println("增加用户。。"); return "cjj"; } @Override public void updateUser() { System.out.println("修改用户。。"); } @Override public void deleteUser() { System.out.println("删除用户。。"); } @Override public void query() { System.out.println("查询用户。。"); } }
package cn.tedu.aop; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.Signature; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @Aspect public class FirstAspect { @Pointcut("execution(* cn.tedu.service.*.*(..))") public void ms(){ } @Before("ms()") public void before(JoinPoint jp){ Class clz = jp.getTarget().getClass(); Signature signature = jp.getSignature(); String name = signature.getName(); System.out.println("before...["+clz+"]...["+name+"]..."); } @Around("ms()") public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) throws Throwable{ System.out.println("1around before..."); Object obj = jp.proceed();//--显式的调用目标方法 System.out.println("1around after..."); return obj; } @AfterReturning(value="ms()",returning="msg") public void afterReturn(String msg){ System.out.println("1 -- afterReturn..." + msg); } @AfterThrowing(value="ms()",throwing="e") public void aftrThrow(Throwable e){ System.out.println("1 -- afterThrow..." + e.getMessage()); } @After("ms()") public void after(){ System.out.println("1 -- after.."); } }
package cn.tedu.test; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import cn.tedu.service.UserService; public class AOPTest { @Test public void test01(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService"); userService.addUser("cjj"); // 一个连接点 } }