7.1 Inverse Functions and Their Derivatives
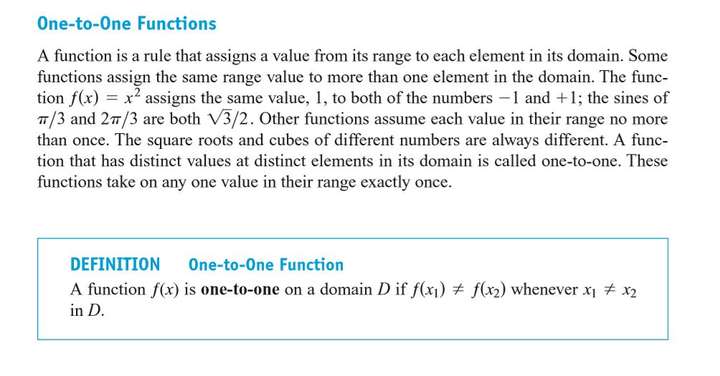
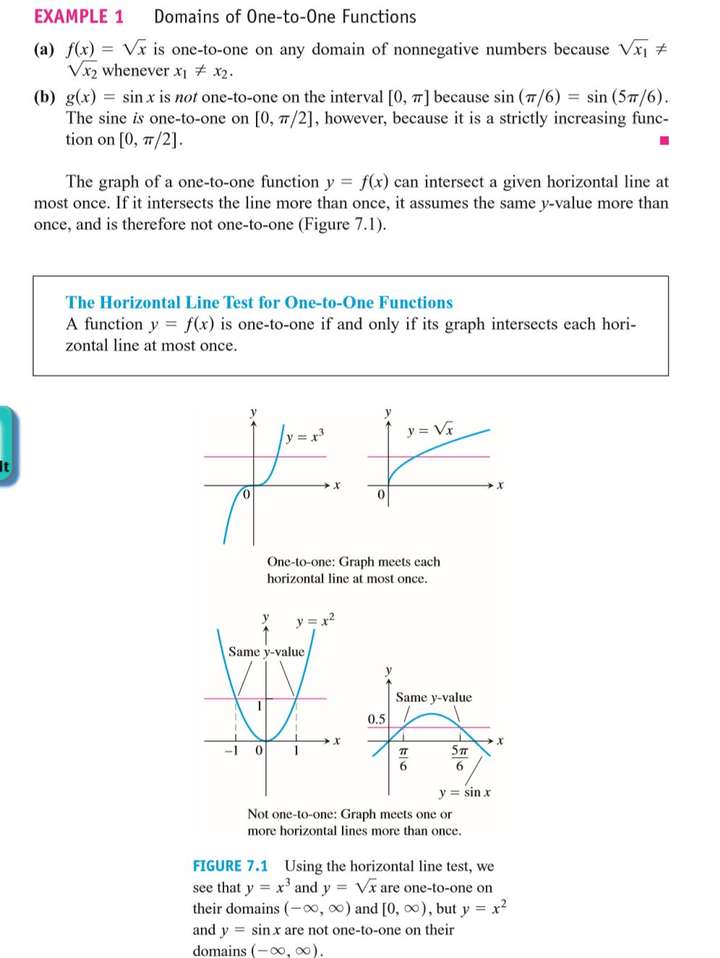
One-to-One Functions
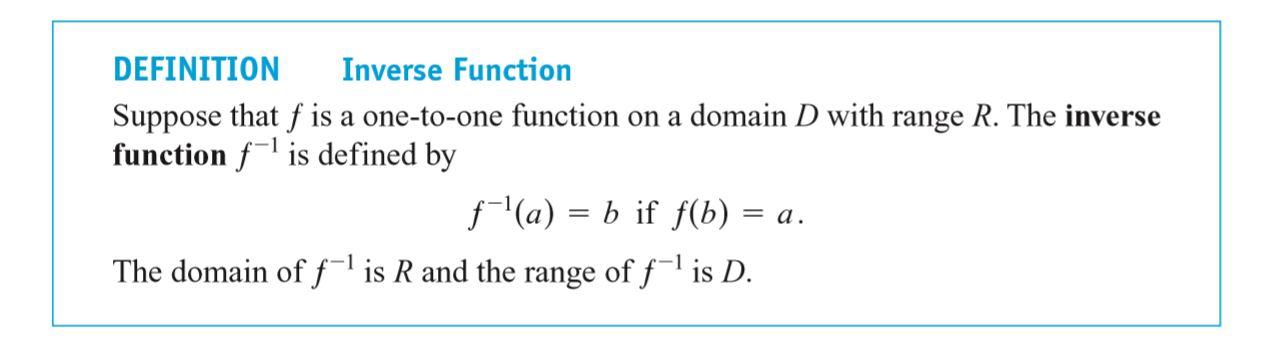
Inverse Functions
Since each output of a one-to-one function comes from just one input, the effect of the function can be inverted to send an output back to the input from which it came.
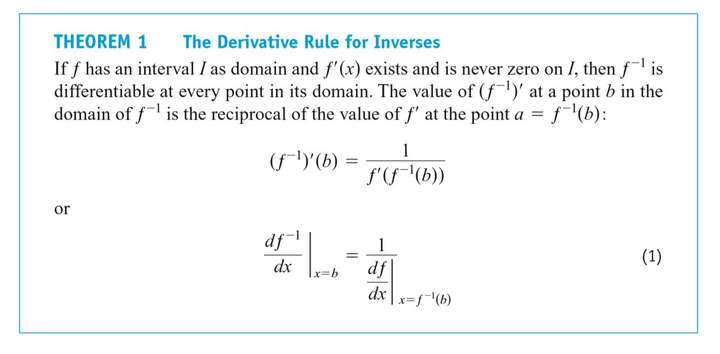
Derivatives of Inverses of Differentiable Functions

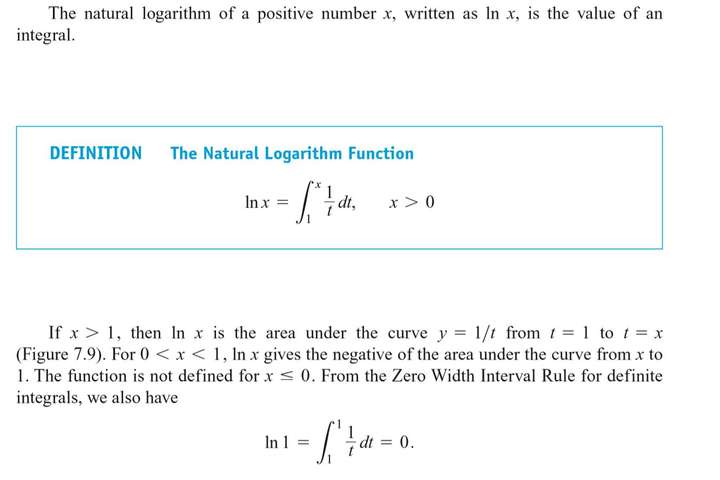
7.2 Natural Logarithms


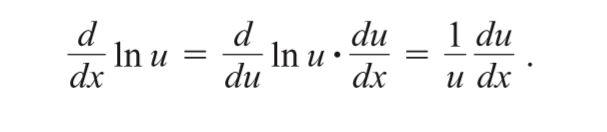
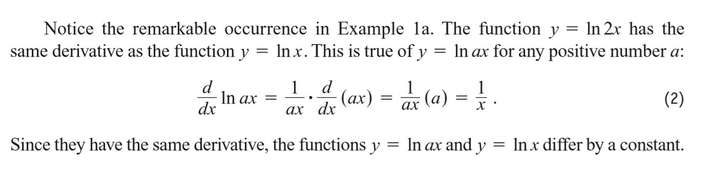
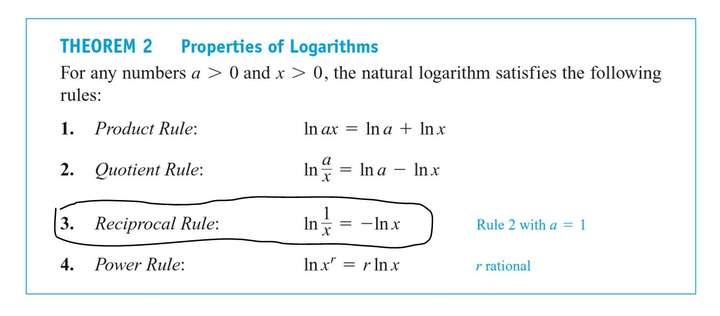

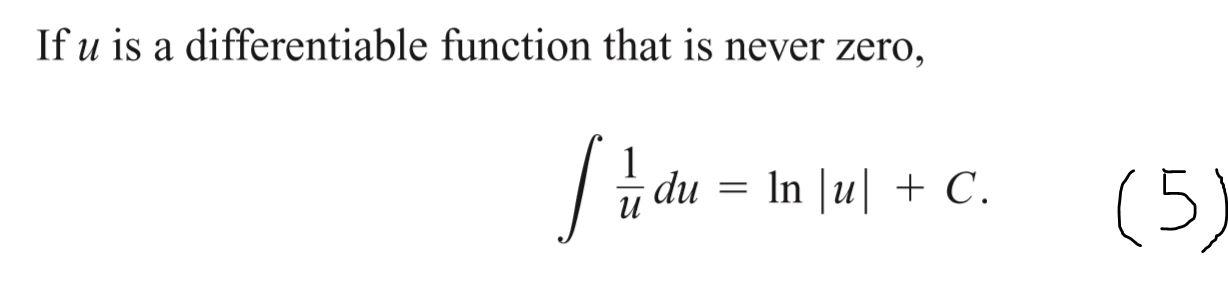

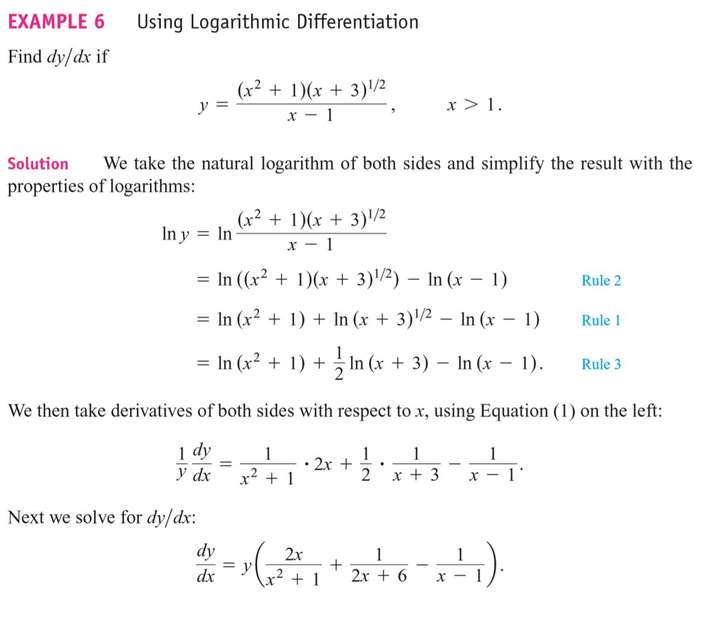
Logarithmic Differentiation
The derivatives of positive functions given by formulas that involve products, quotients, and powers can often be found more quickly if we take the natural logarithm of both sides before differentiating. This enables us to use the laws of logarithms to simplify the formulas before differentiating. The process, called logarithmic differentiation, is illustrated in the next example.

7.3 The Exponential Functions
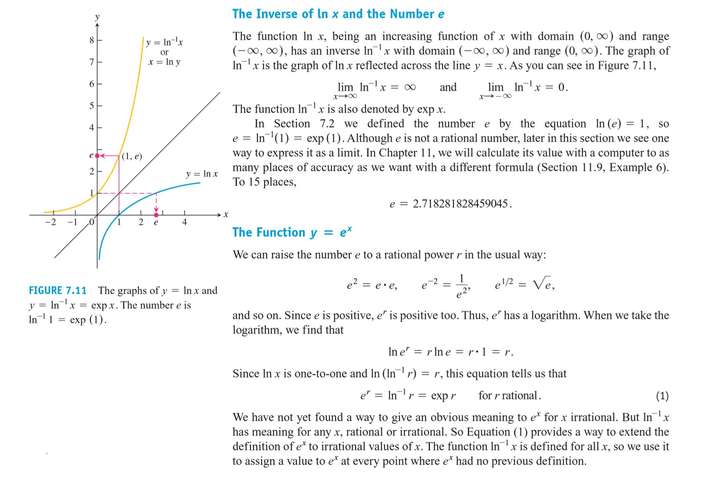
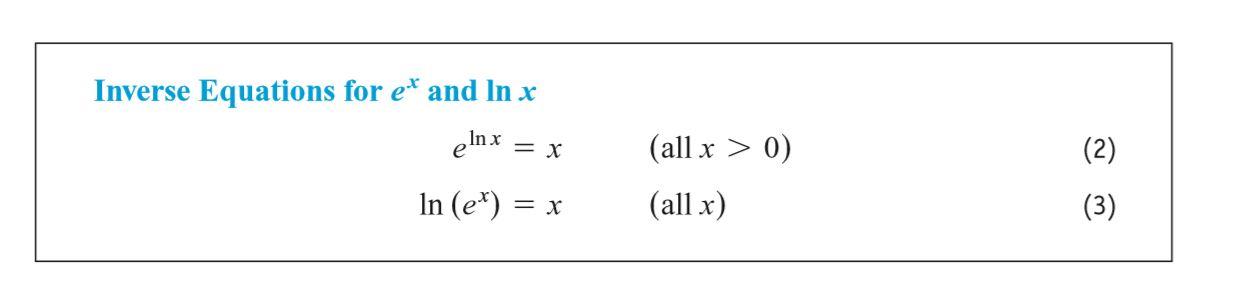
The Derivative and Integral of e^x

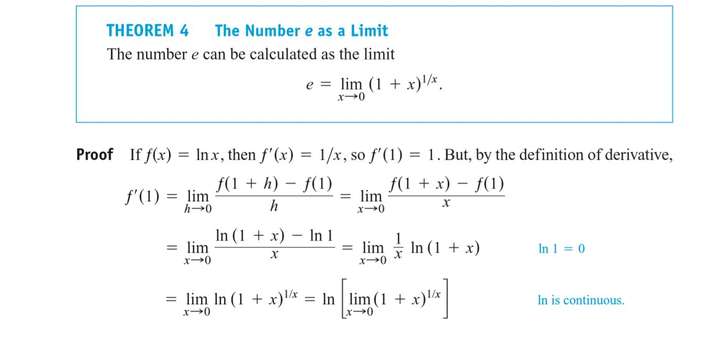
The Number e Expressed as a Limit
We have defined the number e as the number for which or the value exp (1). We see that e is an important constant for the logarithmic and exponential functions, but what is its numerical value? The next theorem shows one way to calculate e as a limit.

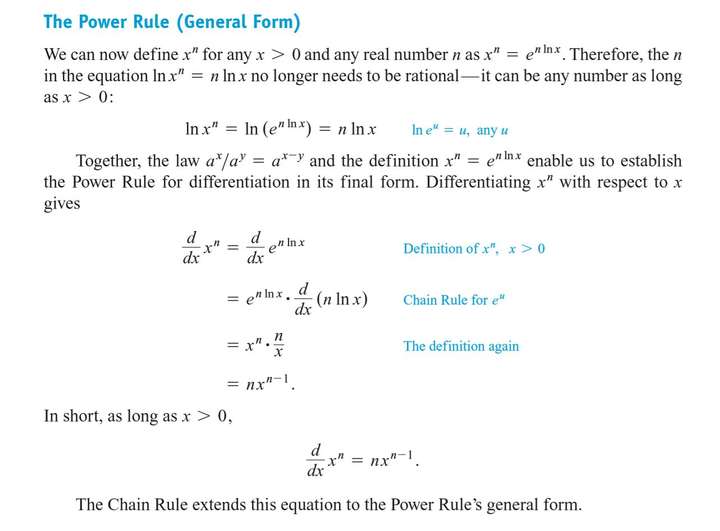
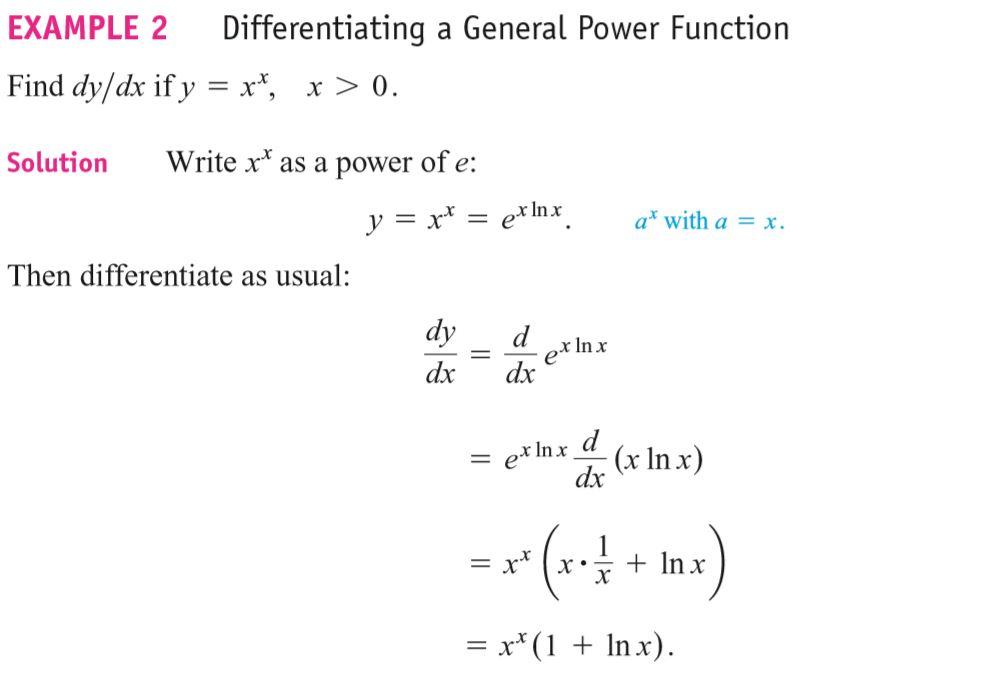


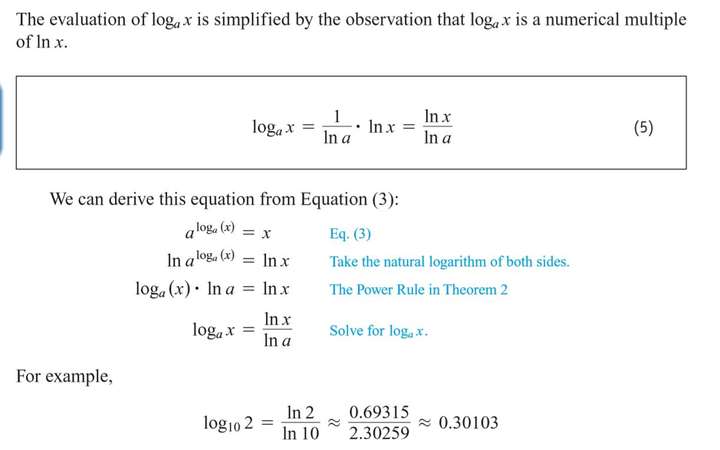

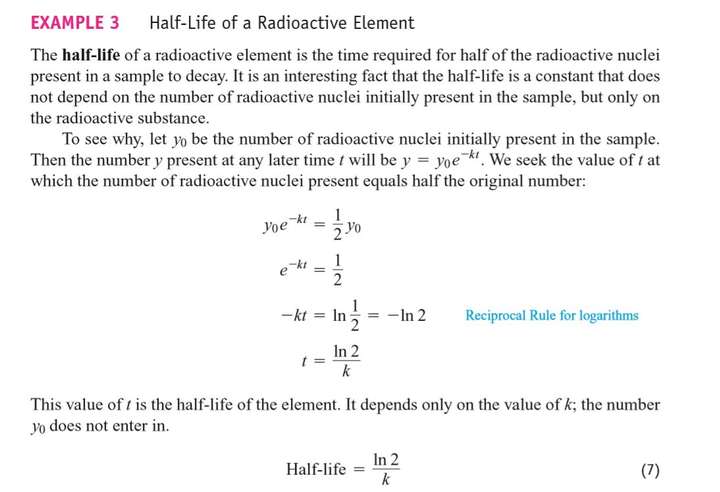
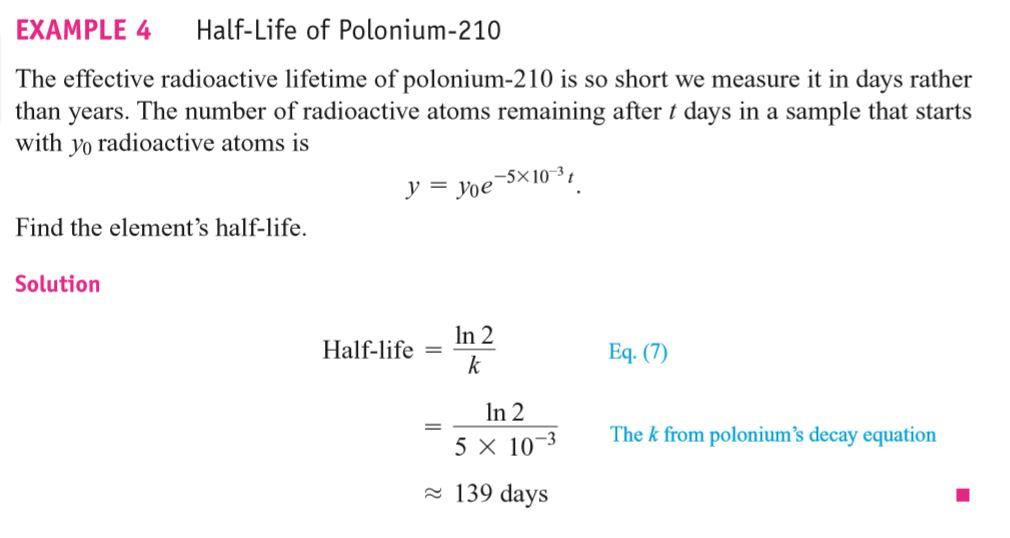
7.5 Exponential Growth and Decay
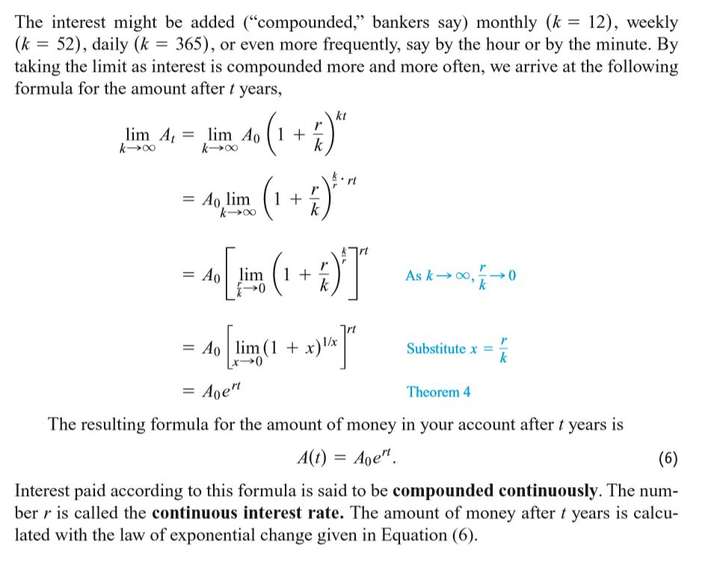
The law of Exponential Change









7.6 Relative Rates of Growth



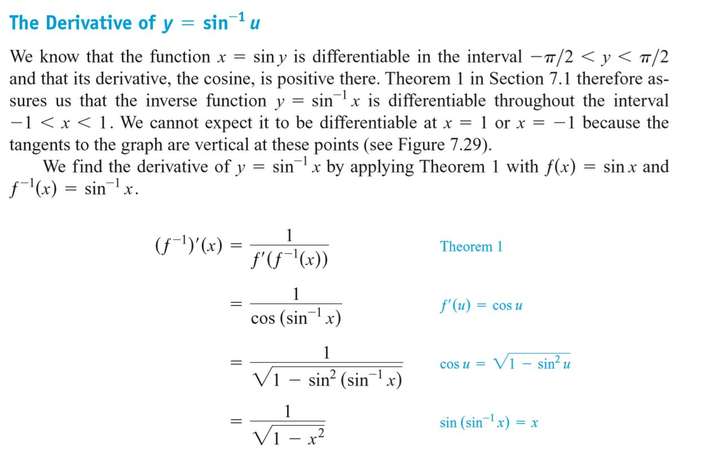
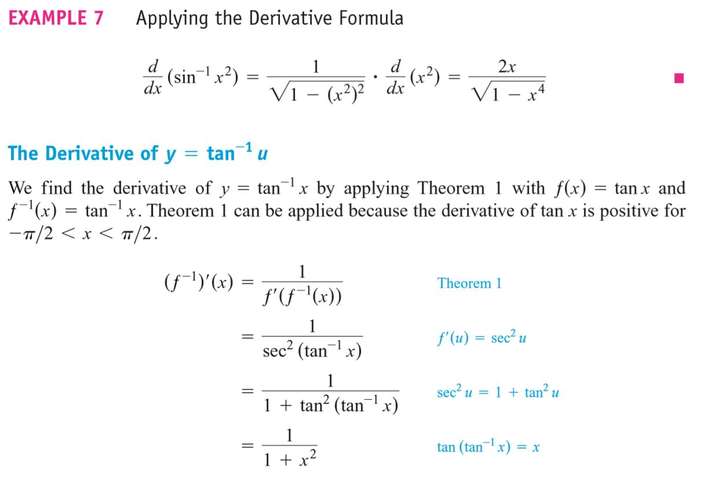
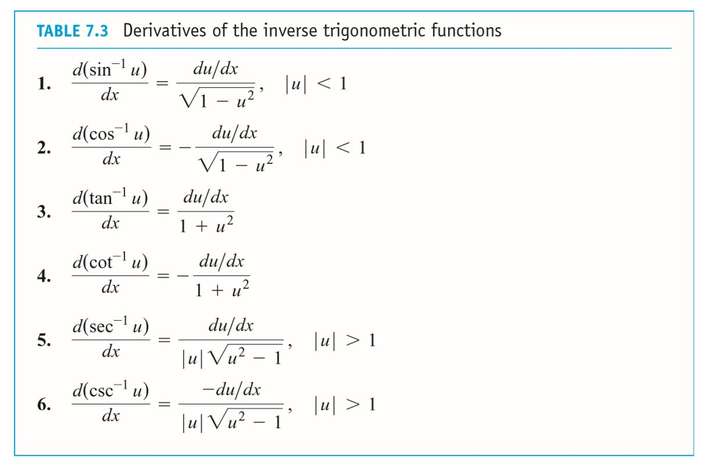
7.7 Inverse Trigonometric

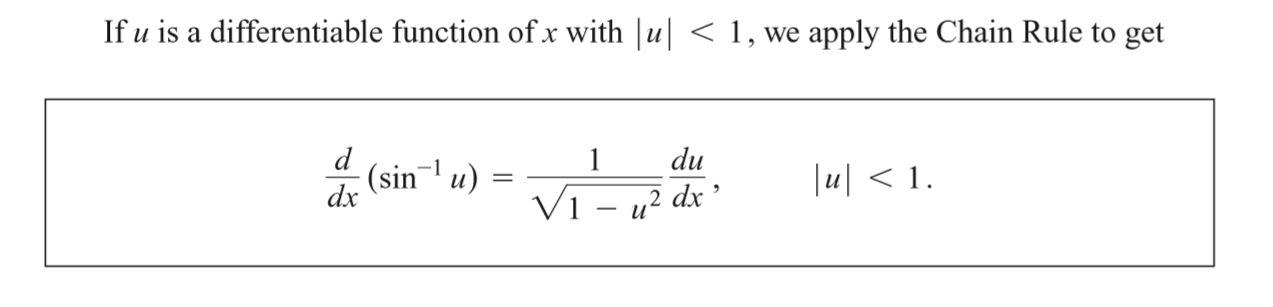


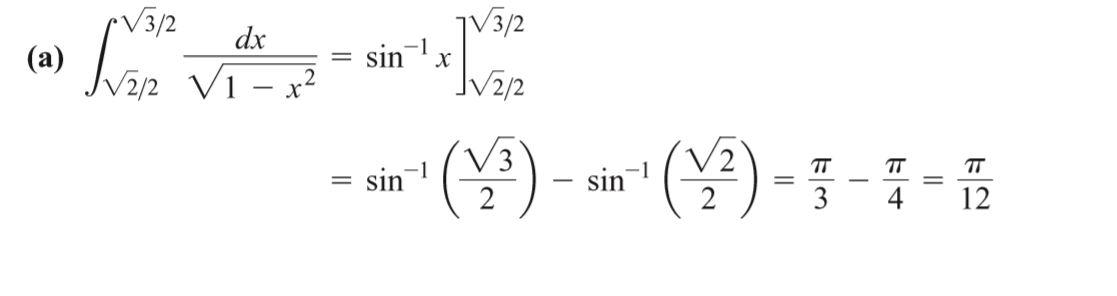

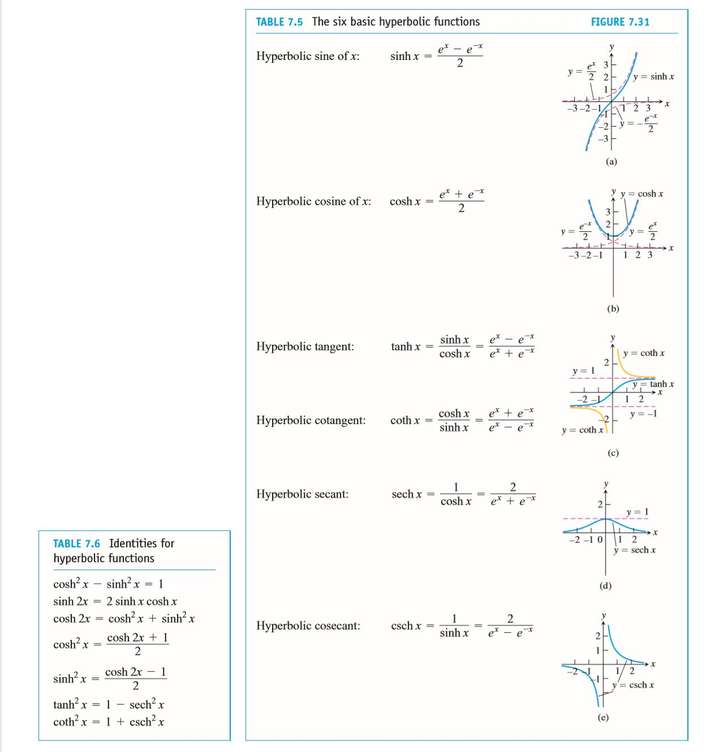
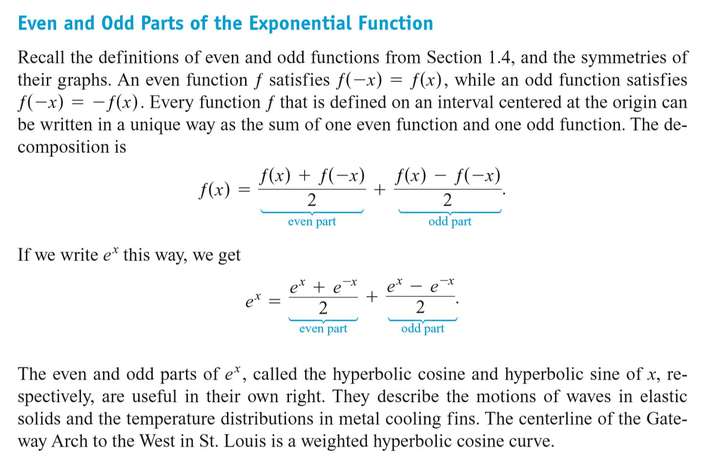
7.8 Hyperbolic Functions