String的基本特性
-
String是字符串,使用一对引号("")包装。
-
String声明是final的,不可被继承。
-
String实现了Serializable接口,表示字符串是支持序列化的;实现了Comparable接口,表示String可以比较大小。
-
String在jdk8及以前内部定义了
final char[] value用于存储字符数据,jdk9时改为byte[]。 -
String是不可变的字符序列。简称:不可变性。
-
当对字符串重新赋值时,需要重写指定内存区域赋值,不能使用原有的value进行赋值。
/** * 第一次执行, 注释掉s1 = "hello"; */ @Test public void test1() { String s1 = "abc"; String s2 = "abc"; s1 = "hello"; System.out.println(s1 == s2); // 1st. true 2nd. false System.out.println(s1); // 1st. abc 2nd. abc System.out.println(s2); // 1st. abc 2nd. hello } -
当对现有的字符串进行连续操作时,也需要重新指定内存区域赋值,不能使用原有的value进行赋值。
@Test public void test2() { String s1 = "abc"; String s2 = "abc"; s2 += "def"; System.out.println(s1); // abc System.out.println(s2); // abcdef } -
当调用String的replace()方法修改指定字符或字符串时,也需要重新指定内存区域赋值,不能使用原有的value进行赋值。
@Test public void test3() { String s1 = "abc"; String s2 = s1.replace('a', 'z'); System.out.println(s1); // abc System.out.println(s2); // zbc }
-
package com.chinda.java.base;
/**
* @author Wang Chinda
* @date 2020/5/29
* @see
* @since 1.0
*/
public class StringExer {
String str = new String("good");
char[] ch = {'t', 'e', 's', 't'};
public void change(String str, char[] ch) {
str = "test ok";
ch[0] = 'b';
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringExer e = new StringExer();
e.change(e.str, e.ch);
System.out.println(e.str); // good
System.out.println(e.ch); // best
}
}
- 通过字面量的方式(区别于new)给一个字符串赋值,此时的字符串值声明在字符串常量池中。
字符串拼接操作
- 常量与常量的拼接结果在常量池,原理是编译期优化。
- 常量池不会存在相同内容的常量。
- 只要其中有一个是变量,结果就在堆中。变量拼接的原理是StringBuilder。(jdk1.5以前是StringBuffer)
- 如果拼接的结果调用intern()方法,则主动将常量池中还有没有的字符串对象放入池中,并返回此对象地址。
package com.chinda.java.base;
import org.junit.Test;
/**
* @author Wang Chinda
* @date 2020/5/30
* @see
* @since 1.0
*/
public class StrJoin {
@Test
public void test1() {
String s1 = "javaEE";
String s2 = "hadoop";
String s3 = "javaEEhadoop";
// 编译器优化
String s4 = "javaEE" + "hadoop";
// 用变量做拼接,相当于在堆中new String()
String s5 = s1 + "hadoop";
String s6 = "javaEE" + s2;
String s7 = s1 + s2;
String s8 = s7.intern();
// 编译期优化。 相当于String s4 = "javaEEhadoop";
System.out.println("s3 == s4 --> " + (s3 == s4));
System.out.println("s3 == s5 --> " + (s3 == s5));
System.out.println("s3 == s6 --> " + (s3 == s6));
System.out.println("s3 == s7 --> " + (s3 == s7));
// 将s7放入字符串常量池,但此时常量池中已经存在该常量,直接返回该常量的地址,即s3的地址赋值给s8
System.out.println("s3 == s8 --> " + (s3 == s8));
System.out.println("s5 == s6 --> " + (s5 == s6));
System.out.println("s5 == s7 --> " + (s5 == s7));
}
}
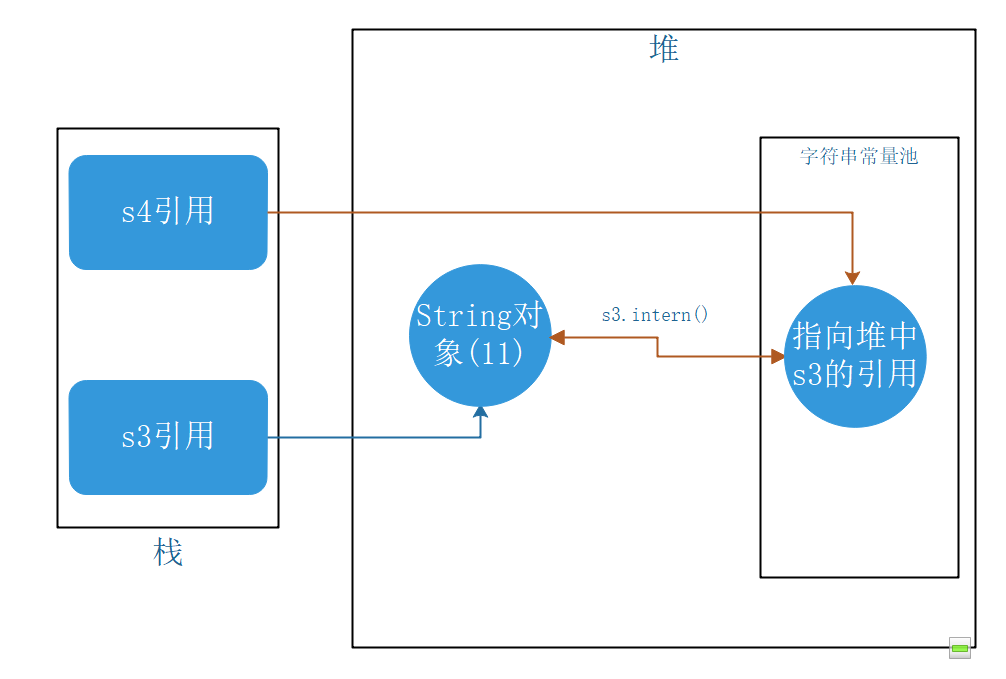
intern()在jdk1.6、jdk1.7、jdk1.8中的区别
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s3 = new String("1") + new String("1");
s3.intern();
String s4 = "11";
System.out.println("s3 == s4 --> " + (s3 == s4));
}
jdk1.6中为false,jdk1.7、jdk1.8中是true。
jdk1.6 JMM
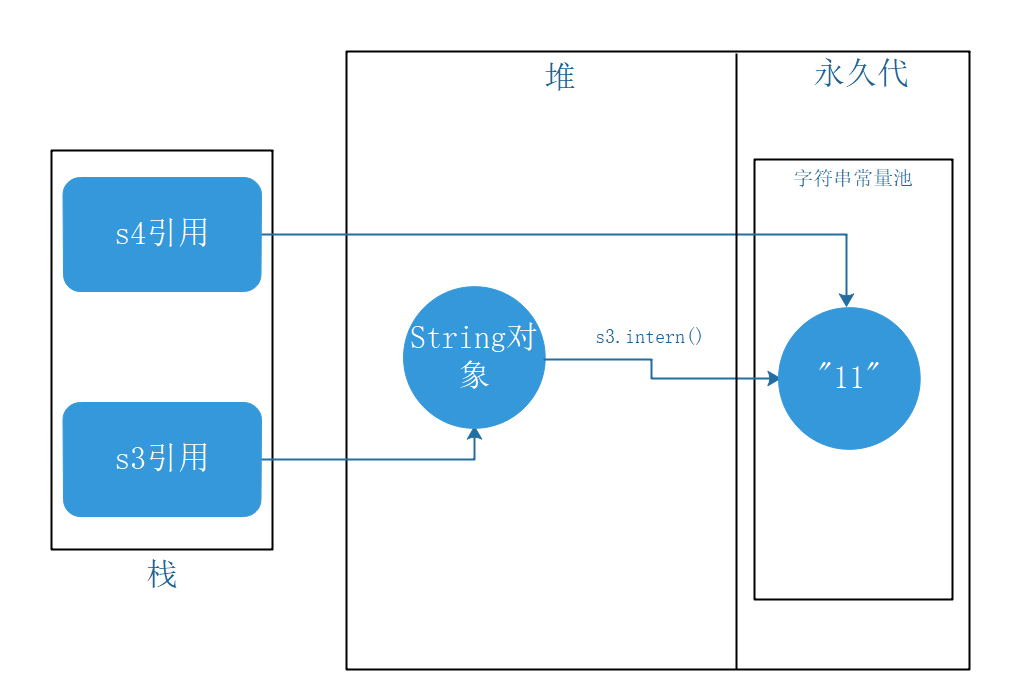
jdk1.8 JMM