1.为什么使用Epoll?
- 阻塞型IO与多路复用
- 阻塞型IO
- 多路复用
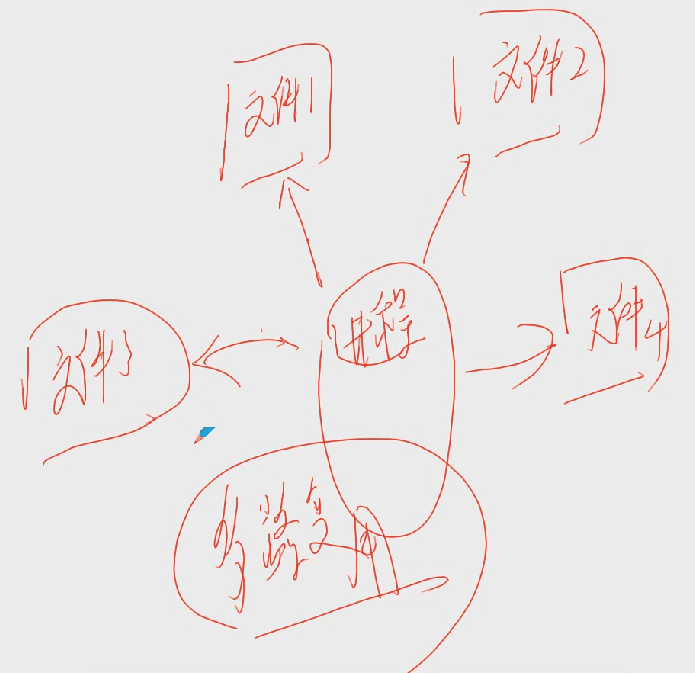 该进程对4个文件进行监控,判断4个文件是否可读,这个过程为多路复用。
该进程对4个文件进行监控,判断4个文件是否可读,这个过程为多路复用。
- 阻塞型IO
- select 与epoll的区别
1.select对监控的文件是有上限的,而epoll对监控的文件没有上限
2.当某个文件发生变话的时候,select 需要遍历的发现哪个文件造成了退出,这样子显得比较低效尤其是在数据量较大时。而epool立刻知道哪个文件发生变化,不需要遍历,省去了低效的环节。
epoll是linux 里面最优秀的多路复用机制(比如网络端 摄像头等同时做多路的监控所以采用epoll架构)
2.怎么使用Epoll
1.使用 epoll_create/epoll_create1 创建epoll监听池。
2.使用epoll_ctl 添加要监听的事件 。 成功返回0 失败返回错误码。
3.使用epoll_wait 等待事件的发生,也就是监听该事件。
3.利用epoll机制监听两个FIFO(管道)
epoll.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
int main()
{
int fd1,fd2;
int efd;
struct epoll_event event;
struct epoll_event *events;
char c;
//创建fifo
mkfifo("/tmp/fifo1",0666);
mkfifo("/tmp/fifo2",0666);
fd1 = open("/tmp/fifo1",O_RDONLY);
fd2 = open("/tmp/fifo2",O_RDONLY);
//创建监听池
efd = epoll_create1(0);
//构造监听事件,加入监听池
event.events = EPOLLIN|EPOLLET;
event.data.fd = fd1;
epoll_ctl(efd,EPOLL_CTL_ADD,fd1,&event);
event.events = EPOLLIN|EPOLLET;
event.data.fd = fd2;
epoll_ctl(efd,EPOLL_CTL_ADD,fd2,&event);
int n = 0;
events = calloc(100,sizeof(event));
n = epoll_wait(efd,events,100,-1);
int i = 0;
for(i = 0;i<n;i++)
{
if(events[i].events&EPOLLIN)
{
read(events[i].data.fd,&c,1);
printf("file %d can be read
",events[i].data.fd);
}
if(events[i].events&EPOLLOUT)
{
//处理
}
if(events[i].events&EPOLLERR)
{
//处理
}
}
free(events);
close(fd1);
close(fd2);
}
ew.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main()
{
int fd;
char c = 'c';
fd = open("/tmp/fifo1",O_WRONLY);
write(fd,&c,1);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
