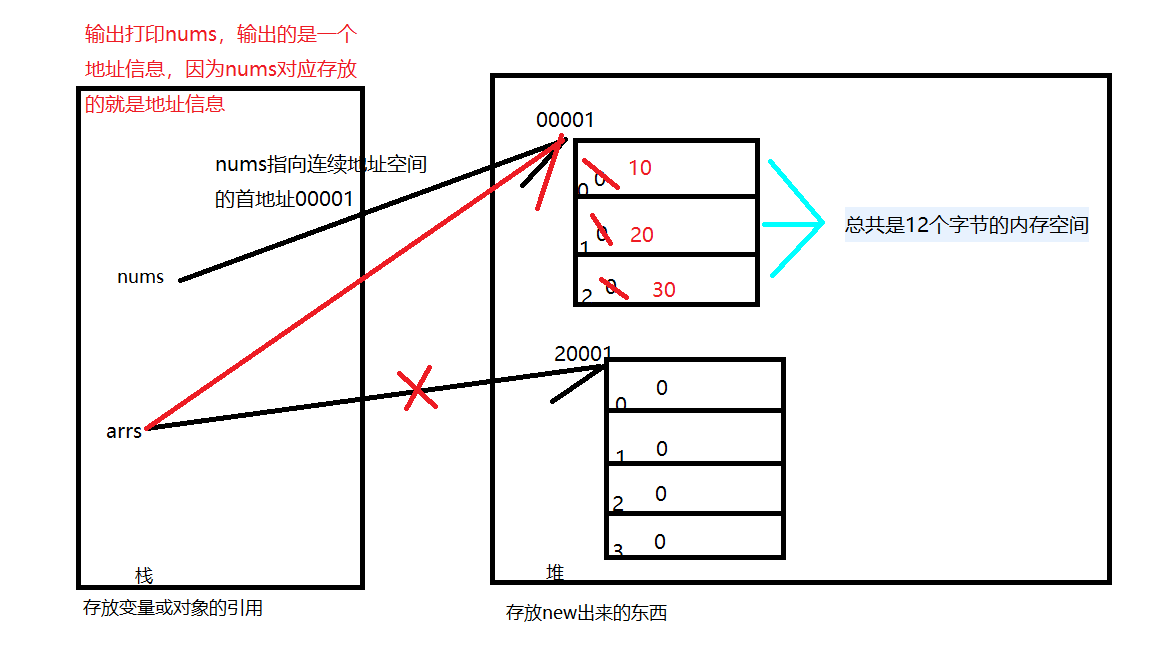
1 /** 2 * 堆和栈 3 */ 4 public class Demo2 { 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 /* 7 * 局部变量主要存放在栈内存中 8 * 在栈内存中创建了变量a的引用,然后查找栈内存中是否有3这个值,如果有,就把a指向它,如果没有,就将3放进来,然后再让a指向它 9 */ 10 int a = 3; 11 12 // 在栈内存中创建了对象的引用b,在栈内存中查找是否有3,上面已经有了,所以把b指向它 13 int b = 3; 14 15 // 查找栈内存中是否有4这个值,如果有,就把b指向它,如果没有,就将4放进来,然后再让b指向它 16 b = 4; 17 18 /* 19 * 创建数组对象 20 * nums在栈内存中 21 * 左边:是对象的引用 右边:是new出来的东西 22 * new int[3]: int:4个字节 '3':存放3个元素信息,每个元素信息占4个字节 4*3,总共是12个字节的内存空间 23 * 输出打印nums,输出的是一个地址信息 24 */ 25 int[] nums = new int[3]; 26 System.out.println(nums);// [I@5e265ba4 27 // 赋值前 28 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums));// [0, 0, 0, 0] 29 30 nums[0] = 10; 31 nums[1] = 20; 32 nums[2] = 30; 33 // 赋值后 34 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums));// [10, 20, 30] 35 36 /* 37 * 创建新的数组对象 arrs在栈内存中 38 * new int[4]: '4':存放4个元素信息,每个元素信息占4个字节 4*4,总共是16个字节的内存空间 39 */ 40 int[] arrs = new int[4]; 41 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arrs));// [0, 0, 0, 0] 42 43 // 把nums指向的首地址赋给了arrs,arrs原来的地址不存在了 44 arrs = nums; 45 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arrs));// [10, 20, 30] 46 } 47 }
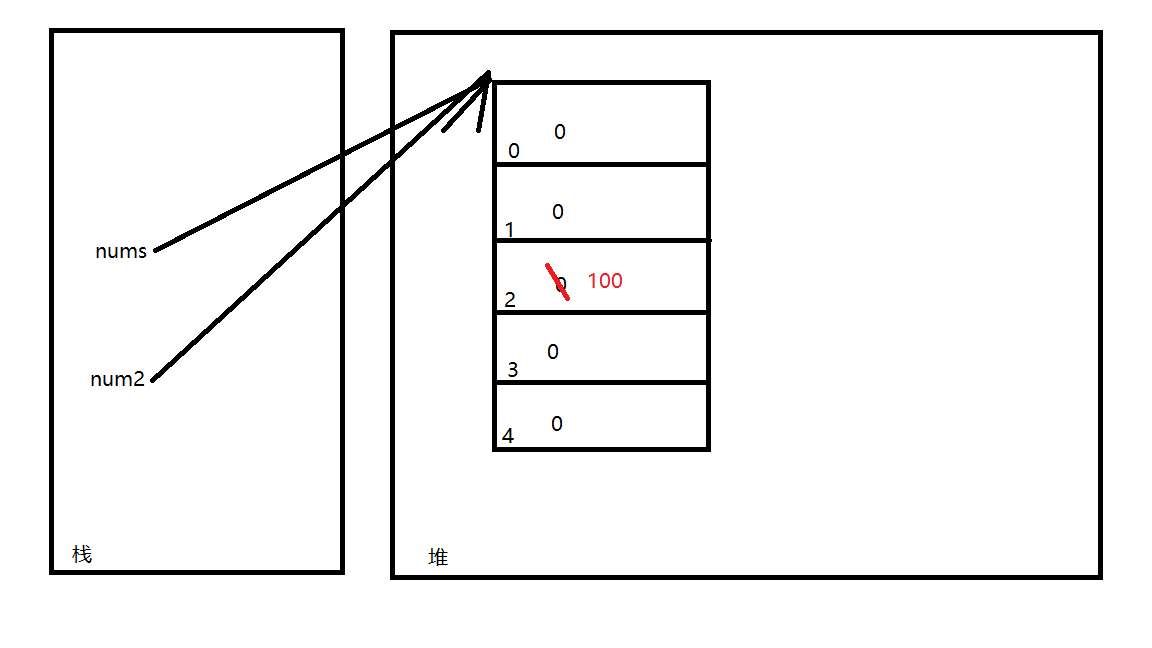
1 /** 2 * 地址传递: 只要有一个指向该地址的对象发生了变化,其他指向该地址的对象都会跟着变化 3 */ 4 public class Demo2 { 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 int[] nums = new int[5]; 7 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums));// [0, 0, 0, 0, 0] 8 9 /* 10 * 通过函数实现对nums对象下标为2的元素信息赋值 11 */ 12 insert(nums); 13 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums));// [0, 0, 100, 0, 0] 14 } 15 16 /** 17 * 给数组对象进行赋值 18 * 分析: 19 * 1、返回值类型 void 20 * 2、名称 insert 21 * 3、参数列表 int [] nums 22 */ 23 public static void insert(int[] num2) { 24 num2[2] = 100; 25 } 26 }
1 /** 2 * 值传递: 3 * 当基本数据类型作为函数的参数传递时候, 4 * 是原来信息值的拷贝,后续对拷贝后的信息进行任何更改 5 * 都不会对原来的信息值有任何影响 6 */ 7 public class Demo2 { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 /* 10 * 定义两个整数类型的变量 11 * 通过函数实现两个变量进行值信息的交换 12 * 分析: 13 * 1、定义变量 a b 14 * 2、函数的定义 15 */ 16 int a = 10, b = 20; 17 System.out.println("main方法中:a=" + a + ",b=" + b);//main方法中:a=10,b=20 18 test(a, b); 19 System.out.println("调用方法后-main方法中:a=" + a + ",b=" + b);//调用方法后-main方法中:a=10,b=20 20 } 21 22 /** 23 * 交换两个整数的值信息 24 * @param a 第一个整数 25 * @param b 第二个整数 26 * 分析: 27 * 1、返回值类型 void 28 * 2、函数名称 test 29 * 3、参数列表 int a,int b 30 */ 31 public static void test(int a, int b) { 32 System.out.println("test方法中:a=" + a + ",b=" + b);//test方法中:a=10,b=20 33 int temp = a;//临时变量存放a的值信息 34 a = b; 35 b = temp; 36 System.out.println("test交换后方法中:a=" + a + ",b=" + b);//test交换后方法中:a=20,b=10 37 } 38 }