函数扩展之默认参数
{ function add(a,b=99){ console.log(a,b); } add(1);//1 99 //参数b可以读取到之前的参数a function add2(a,b=99+a){ console.log(a,b); } add2(1);//1 100 //参数b不能读取到自身参数b function add3(a,b=99+b){ console.log(a,b); } add3(1);//报错 //参数b不能读取到之后的参数c function add4(a,b=99+c,c=2){ console.log(a,b); } add4(1);//报错 }
默认参数结合解构赋值
{ function Person({name,age=18}={}){ console.log(name,age); } Person();//undefined 18 function Person2({name,age=18}={name:"cyy"}){ console.log(name,age); } Person2();//cyy 18 function Person3({name,age=18}={name:"cyy"}){ console.log(name,age); } Person3({name:"cyy2"});//cyy2 18 }
结合扩展运算符(剩余参数)
{ function sum(){ console.log(arguments);//取得所有参数 console.log(arguments instanceof Array);//false 不是数组,是类数组 let args=Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);//类数组转数组 console.log(args);//取得所有参数 console.log(args instanceof Array);//true //使用扩展运算符,类数组转数组 let args2=[...arguments]; console.log(args2);//取得所有参数 console.log(args2 instanceof Array);//true //使用扩展运算符,类数组转数组2 let [...args3]=arguments; console.log(args3);//取得所有参数 console.log(args3 instanceof Array);//true } sum(1,2,3); }
更好的方式是:
{ //这里不算扩展运算符,算剩余参数 function sum(...args){ console.log(args);//取得所有参数 console.log(args instanceof Array);//false 不是数组,是类数组 } sum(1,2,3); }
{ //剩余参数 function op(type,...args){ console.log(type); console.log(args); } op("sum",1,2,3); }
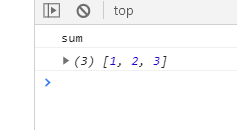
{ //剩余参数 function sum(...nums){ //reduce用法: //第一次遍历时,a是0,b是调用时传入的第一个参数1 //第二次遍历时,a是第一次遍历结束后返回的值,第二次是调用时传入的第二个参数2 return nums.reduce(function(a,b){ return a+b; },0); } console.log(sum(1,2,3));//6 }
for...of 语句创建一个循环来迭代可迭代的对象。在 ES6 中引入的 for...of 循环,以替代 for...in 和 forEach() ,并支持新的迭代协议。for...of 允许你遍历 Arrays(数组), Strings(字符串), Maps(映射), Sets(集合)等可迭代的数据结构等。
求平均数:
function avg(...num){ let sum=0; let len=num.length; for(let n of num){ sum+=n; } return sum/len; } console.log(avg(1,4,6,9));

rest(…) 参数搭配的变量是一个数组,所以可以使用数组的方法。
现有一个函数,第一项传递的参数是数组,后几项是数,先要通过函数,把后几项压入到第一项这个数组中,并输出结果。
function addArr(arr,...num){ for(let n of num){ arr.push(n); } return arr; } console.log(addArr([1,2],3,4,5));
箭头函数:
//箭头函数 const add=(a,b)=>a+b; //普通函数 function add2(a,b){ return a+b; } console.log(add(3,5)); console.log(add2(3,5));
如果函数内容一行写不下,可以用花括号
//箭头函数 const add=(a,b)=>{ a+=1; return a+b; }; //普通函数 function add2(a,b){ a+=1; return a+b; } console.log(add(3,5)); console.log(add2(3,5));

void 让函数没有返回值,或者返回undefined
如果参数只有一个,可以不用圆括号
//箭头函数 //只有一个参数arr,不用圆括号 const add=arr=>arr.pop(); console.log(add([1,2,3]));//3 pop默认弹出数组的最后一个元素 //void 使函数没有返回值 const add2=arr=>void arr.pop(); console.log(add2([1,2,3]));//3 undefined
在箭头函数中没有arguments,必须用扩展运算符来接收参数
//箭头函数没有arguments const info=()=>{ console.log(arguments); }; info(1,2,3);//报错 //扩展运算符接收参数 const info2=(...args)=>{ console.log(args); }; info2(1,2,3);//(3) [1, 2, 3]
箭头函数没有this,它的this就是自身所处环境的this,因此无法改变this指向
const person={ name:"cyy", fn1:function(){ console.log(this);//this指向person }, fn2:()=>{ console.log(this);//this指向window } } person.fn1(); person.fn2();
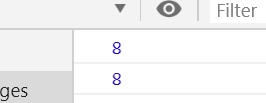
const person={ name:"cyy", fn:function(){ //模拟ajax取数据 setTimeout(function(){ console.log(this);//this指向window console.log(this.name); },100); } } person.fn(); //通过闭包 保留this特性 const person2={ name:"cyy", fn:function(){ let _this=this; //模拟ajax取数据 setTimeout(function(){ console.log(_this);//_this指向person2 console.log(_this.name); },100); } } person2.fn();

使用箭头函数解决:
//使用箭头函数 const person2={ name:"cyy", fn:function(){ //模拟ajax取数据 setTimeout(()=>{//箭头函数没有this,这里的this是fn的this console.log(this); console.log(this.name); },100); } } person2.fn();

现有一个ES5 语法的多重嵌套函数,使用箭头函数对齐进行改写
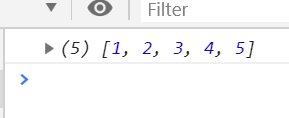
//ES5 语法的多重嵌套函数 function insert(value) { return { into: function(array) { return { after: function(afterValue) { array.splice(array.indexOf(afterValue) + 1, 0, value); return array; } }; } }; } console.log(insert(2).into([1, 3]).after(1));//(3) [1, 2, 3] //使用箭头函数改写 let insert2=(value)=>(array)=>(afterValue)=>{ // 在array的afterValue所在的索引位置+1处 // 删除0个 // 插入value array.splice(array.indexOf(afterValue) + 1, 0, value); return array; } console.log(insert2(2)([1, 3])(1));//(3) [1, 2, 3]