转载 http://blog.csdn.net/beiyetengqing/article/details/7856113
关注Trie 这种结构已经很久,Trie有一个很有趣的用途,那就是自动提示。而且,前不久在一次面试里,也需要用Trie来解答。所以,在此对这个数据结构进行总结。
Trie,又称单词查找树或键树,是一种树形结构。典型应用是用于统计和排序大量的字符串(但不仅限于字符串),所以经常被搜索引擎系统用于文本词频统计。它的优点是:最大限度地减少无谓的字符串比较,查询效率比哈希表高。
它有3个基本性质:
下面这个图就是Trie的表示,每一条边表示一个字符,如果结束,就用星号表示。在这个Trie结构里,我们有下面字符串,比如do, dork, dorm等,但是Trie里没有ba, 也没有sen,因为在a, 和n结尾,没有结束符号(星号)。
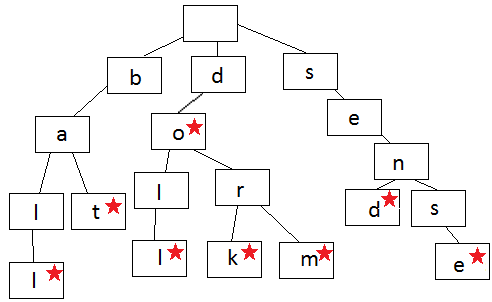
有了这样一种数据结构,我们可以用它来保存一个字典,要查询改字典里是否有相应的词,是否非常的方便呢?我们也可以做智能提示,我们把用户已经搜索的词存在Trie里,每当用户输入一个词的时候,我们可以自动提示,比如当用户输入 ba, 我们会自动提示 bat 和 baii.
现在来讨论Trie的实现。
首先,我们定义一个Abstract Trie,Trie 里存放的是一个Node。这个类里有两个操作,一个是插入,另一个是查询。具体实现放在后面。
Node 类的实现
[java] view plaincopy
- class Node {
- char content; // the character in the node
- boolean isEnd; // whether the end of the words
- int count; // the number of words sharing this character
- LinkedList<Node> childList; // the child list
- public Node(char c){
- childList = new LinkedList<Node>();
- isEnd = false;
- content = c;
- count = 0;
- }
- public Node subNode(char c){
- if(childList != null){
- for(Node eachChild : childList){
- if(eachChild.content == c){
- return eachChild;
- }
- }
- }
- return null;
- }
- }
现在我们来看这个Trie类的具体实现。
[java] view plaincopy
- public class Trie{
- private Node root;
- public Trie(){
- root = new Node(' ');
- }
- public void insert(String word){
- if(search(word) == true) return;
- Node current = root;
- for(int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++){
- Node child = current.subNode(word.charAt(i));
- if(child != null){
- current = child;
- } else {
- current.childList.add(new Node(word.charAt(i)));
- current = current.subNode(word.charAt(i));
- }
- current.count++;
- }
- // Set isEnd to indicate end of the word
- current.isEnd = true;
- }
- public boolean search(String word){
- Node current = root;
- for(int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++){
- if(current.subNode(word.charAt(i)) == null)
- return false;
- else
- current = current.subNode(word.charAt(i));
- }
- /*
- * This means that a string exists, but make sure its
- * a word by checking its 'isEnd' flag
- */
- if (current.isEnd == true) return true;
- else return false;
- }
- public void deleteWord(String word){
- if(search(word) == false) return;
- Node current = root;
- for(char c : word.toCharArray()) {
- Node child = current.subNode(c);
- if(child.count == 1) {
- current.childList.remove(child);
- return;
- } else {
- child.count--;
- current = child;
- }
- }
- current.isEnd = false;
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Trie trie = new Trie();
- trie.insert("ball");
- trie.insert("balls");
- trie.insert("sense");
- // testing deletion
- System.out.println(trie.search("balls"));
- System.out.println(trie.search("ba"));
- trie.deleteWord("balls");
- System.out.println(trie.search("balls"));
- System.out.println(trie.search("ball"));
- }
- }
时间复杂度分析:
对于insert, 如果被插入的String长度是 k, 每对一个字符进行查询,我们最多在child linkedlist里面查询26次(最多26个字母),所以,复杂度为O(26*k) = O(k). 对于 search, 复杂度是一样的。
本文代码来自:http://www.technicalypto.com/2010/04/trie-in-java.html