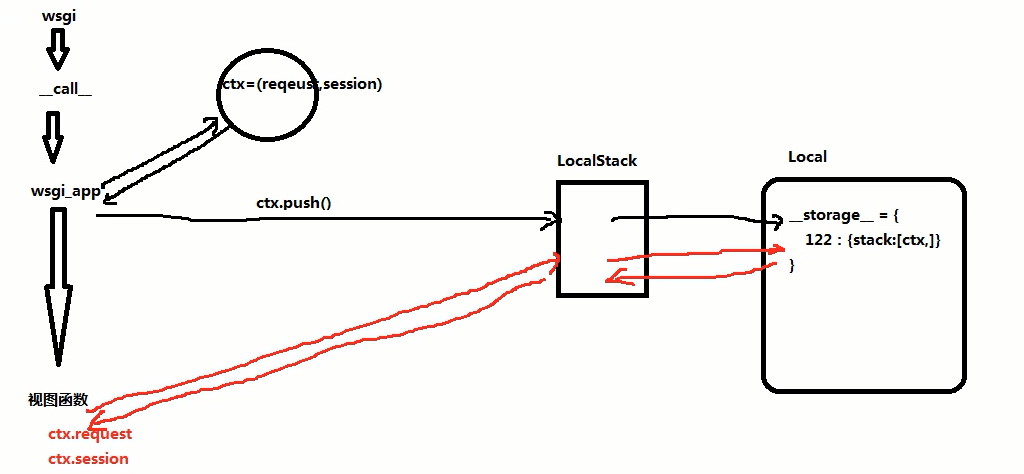
session的源码流程

将session放置在redis中
安装
pip install flask-session
使用
import redis from flask import Flask,request,session from flask.sessions import SecureCookieSessionInterface from flask_session import Session app = Flask(__name__) app.config['SESSION_TYPE'] = 'redis' app.config['SESSION_REDIS'] = redis.Redis(host='140.143.227.206',port=6379,password='1234') Session(app) @app.route('/login') def login(): session['user'] = 'alex' return 'asdfasfd' @app.route('/home') def index(): print(session.get('user')) return '...' if __name__ == '__main__': app.run()
上下文管理基础
上下文管理之基础threading.local
1.threading.local
- 实例化一个local对象
- obj.xxxx=i会触发__setattr__ 设置值
- obj.xxxx的会触发__getattr__取值
- local能为每一个线程开辟一个新的空间,让每个线程的资源相互不干扰
import threading,time from threading import local obj=local() def task(i): obj.xxxxx = i time.sleep(2) print(obj.xxxxx,i) for i in range(0,10): t=threading.Thread(target=task,args=(i,)) t.start()
2.用字典替换local
import threading,time from threading import local obj=local() DIC={} def task(i): ident = threading.get_ident() if ident in DIC: DIC[ident]['xxxx']=i else: DIC[ident]={'xxxx':i} time.sleep(2) print(DIC[ident]['xxxx'],i,ident) for i in range(0,10): t=threading.Thread(target=task,args=(i,)) t.start()
-
ident = threading.get_ident() 获取线程的唯一标识
- 将所有的数据根据线程唯一标示为key存放到字典里,那么该方法也可以避免线程资源冲突...因为DIC是一个全部变量字典
3. 重写local支持协程
import threading,time,greenlet try: get_ident=greenlet.getcurrent except Exception as e: get_ident=threading.get_ident class Local(object): DIC={} def __getattr__(self, item): ident = get_ident() print(ident) if ident in self.DIC: return self.DIC[ident].get(item) return None def __setattr__(self, key, value): ident= get_ident() if ident in self.DIC: self.DIC[ident][key]=value else: self.DIC[ident]={key:value} obj=Local() def task(i): obj.ha=i time.sleep(2) print(obj.ha) for i in range(0,10): t= threading.Thread(target=task,args=(i,)) t.start()
上下文管进阶理解
1.偏函数
# by luffycity.com import functools def index(a1,a2): return a1 + a2 # 原来的调用方式 # ret = index(1,23) # print(ret) # 偏函数,帮助开发者自动传递参数 new_func = functools.partial(index,666) ret = new_func(1) print(ret)
2.执行父类方法
class Base(object): def func(self): print('Base.func') class Foo(Base): def func(self): # 方式一:根据mro的顺序执行方法 # super(Foo,self).func() # 方式二:主动执行Base类的方法 # Base.func(self) print('Foo.func') obj = Foo() obj.func()
# print(Foo.__mro__)
3.object.__setattr__
class Foo(object): def __init__(self): # self.storage = {} # 在父类的setattr设置storage为空列表 object.__setattr__(self,'storage',{}) def __getattr__(self, item): print item def __setattr__(self, key, value): print(key,value,self.storage) obj = Foo() obj.xx = 123
- obj=Foo() 实例化对象会执行,__new__......再执行__init__方法加上object.__setattr__会执行object类的方法设置值
- obj.xx=123设置值会执行该类的__setattr__
4.Flask Local源码
- local是用来给每个线程或者协程开辟一个空间
try: from greenlet import getcurrent as get_ident except: from threading import get_ident class Local(object): __slots__ = ('__storage__', '__ident_func__') def __init__(self): # __storage__ = {1231:{'stack':[]}} object.__setattr__(self, '__storage__', {}) object.__setattr__(self, '__ident_func__', get_ident) def __getattr__(self, name): try: return self.__storage__[self.__ident_func__()][name] except KeyError: raise AttributeError(name) def __setattr__(self, name, value): ident = self.__ident_func__() storage = self.__storage__ try: storage[ident][name] = value except KeyError: storage[ident] = {name: value} def __delattr__(self, name): try: del self.__storage__[self.__ident_func__()][name] except KeyError: raise AttributeError(name)
5.LocalStack源码
- localstack 维护local的列表,维护成一个栈
class LocalStack(object): def __init__(self): self._local = Local() def push(self,value): rv = getattr(self._local, 'stack', None) # self._local.stack =>local.getattr if rv is None: self._local.stack = rv = [] # self._local.stack =>local.setattr rv.append(value) # self._local.stack.append(666) return rv def pop(self): """Removes the topmost item from the stack, will return the old value or `None` if the stack was already empty. """ stack = getattr(self._local, 'stack', None) if stack is None: return None elif len(stack) == 1: return stack[-1] else: return stack.pop() def top(self): try: return self._local.stack[-1] except (AttributeError, IndexError): return None
源码入口
app.__call__ app.wsgi_app
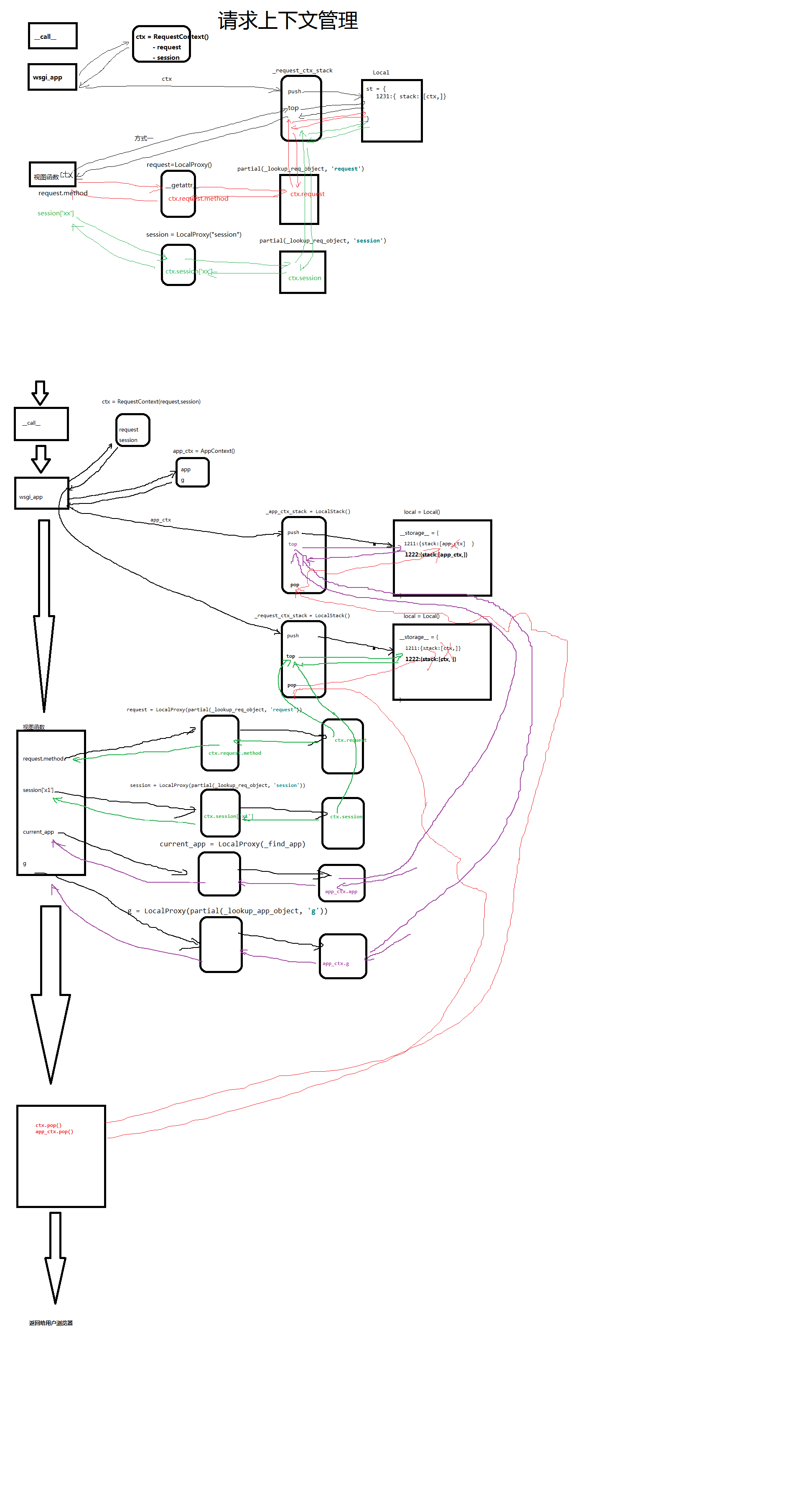
上下文管理request简易流程图
上下文管理request,session流程
- -请求到来之后会触发__call__方法,由__call__方法再次调用wsgi__app方法
- -在wsgi_app方法中:
- -首先将请求相关+空session封装到一个RequestContext对象中即:ctx
- -将ctx交给LocalStack对象,再由LocalStack将ctx添加到local中,Local结构:
- __storage__={
- 线/协程的唯一标识:{stack:[ctx,]}
- -根据请求中的cookie中提取铭文sessionid对应的值,对cookie进行加密+反序列化
- ->视图函数
- -把session中的数据再次加密序列化写入到cookie中.
- -将ctx删除
- -结果返回给用户浏览器
- -断开socket连接.
#LocalStack是全局的 单例模式 _request_ctx_stack = LocalStack() _app_ctx_stack = LocalStack() request = LocalProxy(partial(_lookup_req_object, 'request')) session = LocalProxy(partial(_lookup_req_object, 'session'))
上下文管理最终流程图