=============================================================================
=============================================================================
涉及到的知识点有:
1:List的子类(掌握)
(1)List的子类特点
(2)ArrayList类
(3)Vector类
(4)LinkedList类
(5)案例
2:泛型(掌握)
(1)泛型的概述
(2)泛型的格式
(3)泛型的好处
(4)泛型的前世今生
(5)我们在哪里使用呢?
3:增强for循环(掌握)
4:静态导入(了解)
(1)静态导入的概述
(2)静态导入的格式
(3)注意事项
5:可变参数(掌握)
(1)可变参数的概述
(2)可变参数的格式
(3)注意事项
(4)Arrays工具类中的一个方法
6:练习(掌握)
A:集合的嵌套遍历
B:产生10个1-20之间的随机数,要求随机数不能重复
C:键盘录入多个数据,以0结束,并在控制台输出最大值
7:要掌握的代码
=============================================================================
=============================================================================
1:List的子类(掌握)
(1)List的子类特点
ArrayList:
底层数据结构是数组,查询快,增删慢
线程不安全,效率高
Vector:
底层数据结构是数组,查询快,增删慢
线程安全,效率低
LinkedList:
底层数据结构是链表,查询慢,增删快
线程不安全,效率高
(2)ArrayList类
A:没有特有功能需要学习
B:案例
a:ArrayList存储字符串并遍历
b:ArrayList存储自定义对象并遍历
(3)Vector类
A:有特有功能
a:添加功能
public void addElement(E obj) -- add()
b:获取功能
public E elementAt(int index) -- get()
public Enumeration<E> elements() -- Iterator iterator()
抽象方法:
boolean hasMoreElements() -- hasNext()
Object nextElement() -- next()
JDK升级的原因:
A:提高安全
B:提高效率
C:简化书写
B:案例
a:Vector存储字符串并遍历
b:Vector存储自定义对象并遍历
(4)LinkedList类
A:有特有功能
a:添加功能
public void addFirst(Object e) 在最前面添加
public void addLast(Object e) 在最后面添加(该功能意义不大)
b:删除功能
public Object removeFirst()
public Object removeLast()
c:获取功能
public Object getFirst()
public Obejct getLast()
B:案例
a:LinkedList存储字符串并遍历
b:LinkedList存储自定义对象并遍历
(5)案例
A:去除集合中的多个字符串的重复元素
如果字符串的内容相同,即为重复元素。
法一:

1 package cn.itcast_04; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 6 /* 7 * ArrayList去除集合中字符串的重复值(字符串的内容相同) 8 * 9 * 分析: 10 * A:创建集合对象 11 * B:添加多个字符串元素(包含内容相同的) 12 * C:创建新集合 13 * D:遍历旧集合,获取得到每一个元素 14 * E:拿这个元素到新集合去找,看有没有 15 * 有:不搭理它 16 * 没有:就添加到新集合 17 * F:遍历新集合 18 */ 19 public class ArrayListDemo { 20 public static void main(String[] args) { 21 // 创建集合对象 22 ArrayList array = new ArrayList(); 23 24 // 添加多个字符串元素(包含内容相同的) 25 array.add("hello"); 26 array.add("world"); 27 array.add("java"); 28 array.add("world"); 29 array.add("java"); 30 array.add("world"); 31 array.add("world"); 32 array.add("world"); 33 array.add("world"); 34 array.add("java"); 35 array.add("world"); 36 37 // 创建新集合 38 ArrayList newArray = new ArrayList(); 39 40 // 遍历旧集合,获取得到每一个元素 41 Iterator it = array.iterator(); 42 while (it.hasNext()) { 43 String s = (String) it.next(); 44 45 // 拿这个元素到新集合去找,看有没有 46 if (!newArray.contains(s)) { 47 newArray.add(s); 48 } 49 } 50 51 // 遍历新集合 52 for (int x = 0; x < newArray.size(); x++) { 53 String s = (String) newArray.get(x); 54 System.out.println(s); 55 } 56 } 57 58 }
法二(不常用):

1 package cn.itcast_04; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 6 /* 7 * 需求:ArrayList去除集合中字符串的重复值(字符串的内容相同) 8 * 要求:不能创建新的集合,就在以前的集合上做。 9 */ 10 public class ArrayListDemo2 { 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 // 创建集合对象 13 ArrayList array = new ArrayList(); 14 15 // 添加多个字符串元素(包含内容相同的) 16 array.add("hello"); 17 array.add("world"); 18 array.add("java"); 19 array.add("world"); 20 array.add("java"); 21 array.add("world"); 22 array.add("world"); 23 array.add("world"); 24 array.add("world"); 25 array.add("java"); 26 array.add("world"); 27 28 // 由选择排序思想引入,我们就可以通过这种思想做这个题目 29 // 拿0索引的依次和后面的比较,有就把后的干掉 30 // 同理,拿1索引... 31 // 因为ArrayList底层数据结构是数组,而数组查询快,增删慢 32 for (int x = 0; x < array.size() - 1; x++) { 33 for (int y = x + 1; y < array.size(); y++) { 34 if (array.get(x).equals(array.get(y))) { 35 array.remove(y); // 因为你删一个的同时,剩下的数组会挤上去一个,而挤上的这一个没有判断 36 y--; // 所以我要再回去比较一下 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 41 // 遍历集合 42 Iterator it = array.iterator(); 43 while (it.hasNext()) { 44 String s = (String) it.next(); 45 System.out.println(s); 46 } 47 } 48 }
B:去除集合中的多个自定义对象的重复元素
如果自定义对象的成员变量值都相同,即为重复元素。

1 package cn.itcast_04; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 6 /* 7 * 需求:去除集合中自定义对象的重复值(对象的成员变量值都相同) 8 * 9 * 我们按照和字符串一样的操作,发现出问题了。 10 * 为什么呢? 11 * 我们必须思考哪里会出问题? 12 * 通过简单的分析,我们知道问题出现在了判断上。 13 * 而这个判断功能是集合自己提供的,所以我们如果想很清楚的知道它是如何判断的,就应该去看源码。 14 * contains()方法的底层依赖的是equals()方法。 15 * 而我们的学生类中没有equals()方法,这个时候,默认使用的是它父亲Object的equals()方法。 16 * Object()的equals()默认比较的是地址值,所以,它们进去了。因为new的东西,地址值都不同。 17 * 按照我们自己的需求,比较成员变量的值,重写equals()即可。 18 * 自动生成即可。 19 */ 20 public class ArrayListDemo3 { 21 public static void main(String[] args) { 22 // 创建集合对象 23 ArrayList array = new ArrayList(); 24 25 // 创建学生对象 26 Student s1 = new Student("林青霞", 27); 27 Student s2 = new Student("林志玲", 40); 28 Student s3 = new Student("凤姐", 35); 29 Student s4 = new Student("芙蓉姐姐", 18); 30 Student s5 = new Student("翠花", 16); 31 Student s6 = new Student("林青霞", 27); 32 Student s7 = new Student("林青霞", 18); 33 34 // 添加元素到集合 35 array.add(s1); 36 array.add(s2); 37 array.add(s3); 38 array.add(s4); 39 array.add(s5); 40 array.add(s6); 41 array.add(s7); 42 43 // 创建新集合 44 ArrayList newArray = new ArrayList(); 45 46 // 遍历旧集合,获取得到每一个元素 47 Iterator it = array.iterator(); 48 while (it.hasNext()) { 49 Student s = (Student) it.next(); 50 51 // 拿这个元素到新集合去找,看有没有 52 if (!newArray.contains(s)) { 53 newArray.add(s); 54 } 55 } 56 57 // 遍历新集合 58 for (int x = 0; x < newArray.size(); x++) { 59 Student s = (Student) newArray.get(x); 60 System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge()); 61 } 62 } 63 }

1 package cn.itcast_04; 2 3 public class Student { 4 private String name; 5 private int age; 6 7 public Student() { 8 super(); 9 } 10 11 public Student(String name, int age) { 12 super(); 13 this.name = name; 14 this.age = age; 15 } 16 17 public String getName() { 18 return name; 19 } 20 21 public void setName(String name) { 22 this.name = name; 23 } 24 25 public int getAge() { 26 return age; 27 } 28 29 public void setAge(int age) { 30 this.age = age; 31 } 32 33 @Override 34 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 35 if (this == obj) 36 return true; 37 if (obj == null) 38 return false; 39 if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) 40 return false; 41 Student other = (Student) obj; 42 if (age != other.age) 43 return false; 44 if (name == null) { 45 if (other.name != null) 46 return false; 47 } else if (!name.equals(other.name)) 48 return false; 49 return true; 50 } 51 52 }
C:用LinkedList模拟一个栈数据结构的集合类,并测试。
你要定义一个集合类,只不过内部可以使用LinkedList来实现(模拟)。
这样做的好处是:我们用自己的方法,让外界不知道我们用的是谁.
package cn.itcast_05; import java.util.LinkedList; /** * 自定义的栈集合 * * @author 风清扬 * @version V1.0 */ public class MyStack { private LinkedList link; public MyStack() { link = new LinkedList(); } public void add(Object obj) { link.addFirst(obj); } public Object get() { // return link.getFirst(); return link.removeFirst(); // 移除第一个元素并返回被移除的元素,其余的元素自动向上挤 } public boolean isEmpty() { return link.isEmpty(); } }
package cn.itcast_05; /* * MyStack的测试 */ public class MyStackDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建集合对象 MyStack ms = new MyStack(); // 添加元素,底层调用的是addFirst(obj); ms.add("hello"); // 第一个进来,压栈,最里面 ms.add("world"); // 第二个进来,压栈 ms.add("java"); // 第三个进来,压栈 // 改进前 // 改进后 // System.out.println(ms.get()); // java java // System.out.println(ms.get()); // java world // System.out.println(ms.get()); // java hello // NoSuchElementException // System.out.println(ms.get()); 异常 while (!ms.isEmpty()) { System.out.println(ms.get()); } } }
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
2:泛型(掌握)
(1)泛型的概述
是一种 把明确类型的工作推迟到创建对象或者调用方法的时候才去明确的 特殊的类型。也叫参数化类型,把类型当作参数一样进行传递。
(2)泛型的格式
<数据类型>
注意:该数据类型只能是引用类型。
(3)泛型的好处
A:把运行时期的问题提前到了编译期间
B:避免了强制类型转换
C:优化了程序设计,解决了黄色警告线问题,让程序更安全
(4)泛型的前世今生
A:泛型的由来
早期的Object类型可以接收任意的对象类型,但是在实际的使用中,向上转型是没有任何问题的,但是在向下转型的时候其实隐含了类型转换的问题。
也就存在这隐患,所以Java在JDK1.5以后就提供了泛型来解决这个安全问题,提高程序的安全性。
B:泛型类
把泛型定义在类上
格式:public class 类名<泛型类型1, 泛型类型2, ...>
注意:泛型类型必须是引用数据类型。因为仅仅表示一个参数,所以符合我们命名的标识符规则就行。
public class ObjectTool<T> {...}
C:泛型方法
把泛型定义在方法上
格式:public <泛型类型> 返回类型 方法名(泛型类型 泛型名)
注意:方法能接收任意类型的参数
public <T> void show(T t) {...}
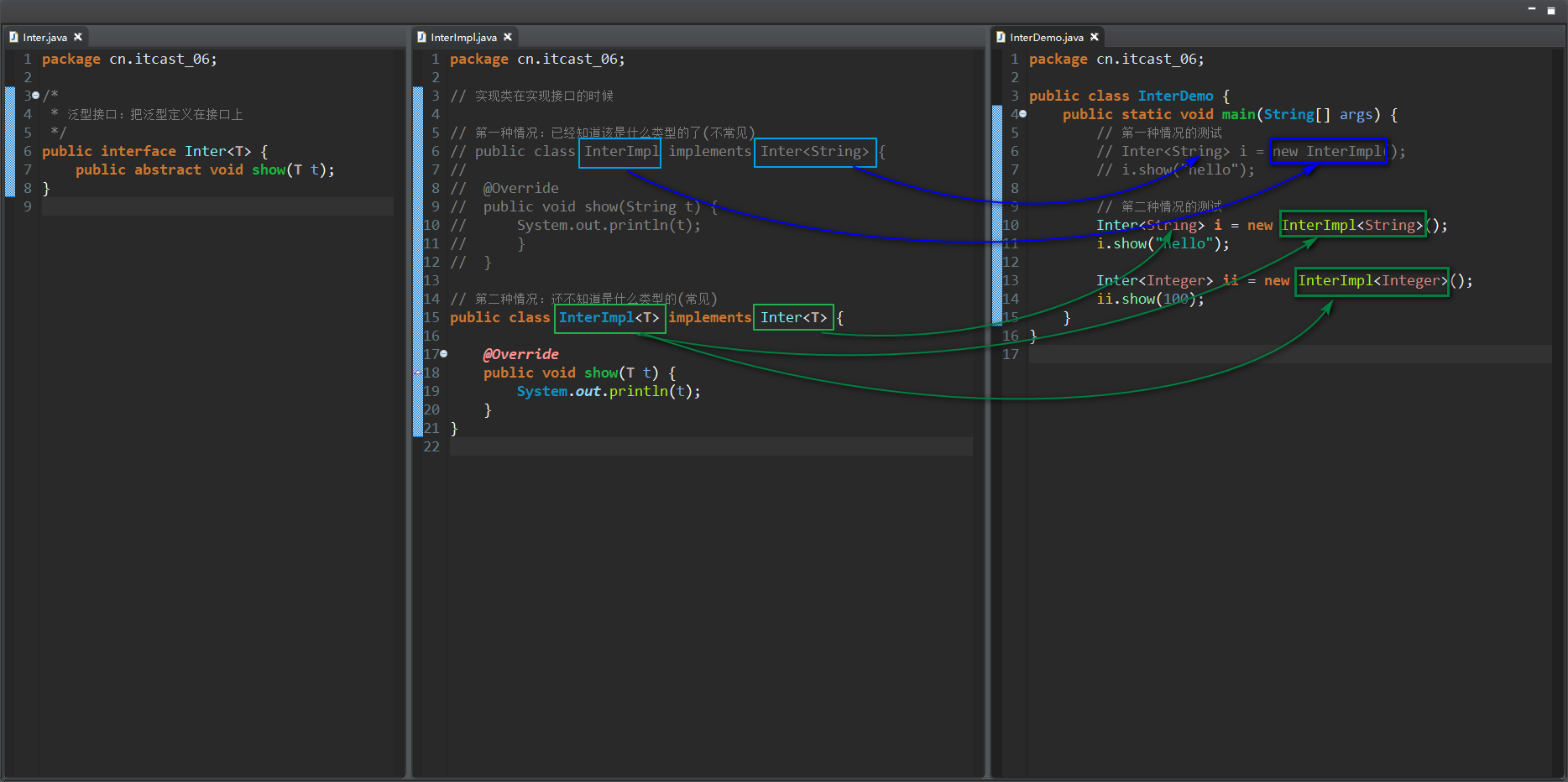
D:泛型接口
把泛型定义在接口上
格式:public interface 接口名<泛型类型1, 泛型类型2, ...>
注意:把泛型定义在接口上,该接口的实现类是实现的那一刻就知道类型的(不常见),还是以后用的时候才知道类型的(常见)。
public class InterImpl<T> implements Inter<T> {...}
E:泛型高级通配符
? 任意类型,如果没有明确,那么就是Object以及任意的Java类了(泛型如果明确地写的时候,前后必须一致)
? extends E 向下限定,E及其子类
? super E 向上限定,E及其父类

1 package cn.itcast_07; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Collection; 5 6 /* 7 * 泛型高级(通配符) 8 * ? 任意类型,如果没有明确,那么就是Object以及任意的Java类了 9 * ? extends E 向下限定,E及其子类 10 * ? super E 向上限定,E及其父类 11 */ 12 public class GenericDemo { 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 // 泛型如果明确地写的时候,前后必须一致 15 Collection<Object> c1 = new ArrayList<Object>(); 16 // Collection<Object> c2 = new ArrayList<Animal>(); // 编译报错 17 // Collection<Object> c3 = new ArrayList<Dog>(); // 编译报错 18 // Collection<Object> c4 = new ArrayList<Cat>(); // 编译报错 19 20 // ? 任意类型,如果没有明确,那么就是Object以及任意的Java类了 21 Collection<?> c5 = new ArrayList<Object>(); 22 Collection<?> c6 = new ArrayList<Animal>(); 23 Collection<?> c7 = new ArrayList<Dog>(); 24 Collection<?> c8 = new ArrayList<Cat>(); 25 26 // ? extends E 向下限定,E及其子类 27 // Collection<? extends Animal> c9 = new ArrayList<Object>(); // 编译报错 28 Collection<? extends Animal> c10 = new ArrayList<Animal>(); 29 Collection<? extends Animal> c11 = new ArrayList<Dog>(); 30 Collection<? extends Animal> c12 = new ArrayList<Cat>(); 31 32 // ? super E 向上限定,E及其父类 33 Collection<? super Animal> c13 = new ArrayList<Object>(); 34 Collection<? super Animal> c14 = new ArrayList<Animal>(); 35 // Collection<? super Animal> c15 = new ArrayList<Dog>(); // 编译报错 36 // Collection<? super Animal> c16 = new ArrayList<Cat>(); // 编译报错 37 } 38 } 39 40 class Animal { 41 } 42 43 class Dog extends Animal { 44 } 45 46 class Cat extends Animal { 47 }
(5)我们在哪里使用呢?
看API,如果类、接口、抽象类的后面跟有<E>就说要使用泛型。一般来说就是在集合中使用。
// JDK7的新特性:泛型推断。
// ArrayList<Student> array = new ArrayList<>();
// 但是我不建议这样使用。
ArrayList<Student> array = new ArrayList<Student>();
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
3:增强for循环(掌握)
(1)是for循环的一种。增强for是用来替迭代器。
(2)格式
for (元素的数据类型 变量名 : 数组或者Collection集合的对象) {
使用该变量即可,该变量其实就是数组或者集合中的元素。
}
(3)好处
简化了数组和集合的遍历。
(4)弊端
增强for循环的目标不能为null。建议在使用前,先判断是否为null。
即:对增强for的目标先进行不为null的判断,然后再使用。

1 package cn.itcast_01; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.List; 5 6 /* 7 * JDK5的新特性:自动拆装箱、泛型、增强for、静态导入、可变参数、枚举 8 * 9 * 增强for:是for循环的一种。 10 * 11 * 格式: 12 * for (元素数据类型 变量 : 数组或者Collection集合) { 13 * 使用变量即可,该变量就是元素 14 * } 15 * 16 * 好处:简化了数组和集合的遍历。 17 * 18 * 弊端: 增强for的目标不能为null。 19 * 如何解决呢?对增强for的目标先进行不为null的判断,然后再使用。 20 */ 21 public class ForDemo { 22 public static void main(String[] args) { 23 // 定义一个int数组 24 int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; 25 for (int x = 0; x < arr.length; x++) { 26 System.out.println(arr[x]); 27 } 28 System.out.println("---------------"); 29 // 增强for 30 for (int x : arr) { 31 System.out.println(x); 32 } 33 System.out.println("---------------"); 34 // 定义一个字符串数组 35 String[] strArray = { "林青霞", "风清扬", "东方不败", "刘意" }; 36 // 增强for 37 for (String s : strArray) { 38 System.out.println(s); 39 } 40 System.out.println("---------------"); 41 // 定义一个集合 42 ArrayList<String> array = new ArrayList<String>(); 43 array.add("hello"); 44 array.add("world"); 45 array.add("java"); 46 // 增强for 47 for (String s : array) { 48 System.out.println(s); 49 } 50 System.out.println("---------------"); 51 52 List<String> list = null; 53 // NullPointerException 54 // 这个s是我们从list里面获取出来的,在获取前,它肯定还要做一个判断 55 // 说白了,这就是迭代器的功能 56 if (list != null) { 57 for (String s : list) { 58 System.out.println(s); 59 } 60 } 61 62 // 增强for其实是用来替代迭代器的 63 // ConcurrentModificationException 64 // for (String s : array) { 65 // if ("world".equals(s)) { 66 // array.add("javaee"); 67 // } 68 // } 69 // System.out.println("array:" + array); 70 } 71 }
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
4:静态导入(了解)
(1)静态导入的概述
可以直接导入到方法的级别
(2)静态导入的格式
import static 包名....类名.方法名;
(3)注意事项
A:被导入的方法必须是静态的
B:如果有多个类下有同名的静态方法,就不好区分了,必须加上前缀才能导入。
所以一般我们并不使用静态导入,但是一定要能够看懂。

1 package cn.itcast_03; 2 3 /* 4 * 可变参数:定义方法的时候不知道该定义多少个参数 5 * 格式: 6 * 修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(数据类型… 变量名){ 7 * 8 * } 9 * 10 * 注意: 11 * 这里的变量其实是一个数组 12 * 如果一个方法有可变参数,并且有多个参数,那么,可变参数的位置肯定是在最后 13 */ 14 public class ArgsDemo { 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 // 2个数据求和 17 int a = 10; 18 int b = 20; 19 int result = sum(a, b); 20 System.out.println("result:" + result); // 30 21 22 // 3个数据的求和 23 int c = 30; 24 result = sum(a, b, c); 25 System.out.println("result:" + result); // 60 26 27 // 4个数据的求和 28 int d = 30; 29 result = sum(a, b, c, d); 30 System.out.println("result:" + result); // 90 31 32 // 需求:我要写一个求和的功能,到底是几个数据求和呢,我不太清楚,但是我知道在调用的时候我肯定就知道了。 33 // 为了解决这个问题,Java就提供了一个东西:可变参数 34 result = sum(a, b, c, d, 40); 35 System.out.println("result:" + result); // 130 36 37 result = sum(a, b, c, d, 40, 50); 38 System.out.println("result:" + result); // 180 39 } 40 41 public static int sum(int... a) { 42 // System.out.println(a); // [I@1f297e7 43 // return 0; 44 45 int s = 0; 46 47 for (int x : a) { 48 s += x; 49 } 50 51 return s; 52 } 53 54 // public static int sum(int a, int b, int c, int d) { 55 // return a + b + c + d; 56 // } 57 // 58 // public static int sum(int a, int b, int c) { 59 // return a + b + c; 60 // } 61 // 62 // public static int sum(int a, int b) { 63 // return a + b; 64 // } 65 }
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
5:可变参数(掌握)
(1)可变参数的概述
如果我们在写方法的时候,参数个数不明确,就应该定义可变参数。
(2)可变参数的格式
修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(数据类型… 变量名){
}
public static int sum(int... a) {
}
(3)注意事项
虽然可以把数组转成集合,但是集合的长度不能改变。
(4)Arrays工具类中的一个方法
public static <T> List<T> asList(T... a) 把数组转成集合
注意:虽然可以把数组转成集合,但是集合的长度不能改变。
因为这个集合的本质是数组。

1 package cn.itcast_03; 2 3 import java.util.Arrays; 4 import java.util.List; 5 6 /* 7 * Arrays工具类中的一个方法 8 * public static <T> List<T> asList(T... a) 把数组转成集合 9 * 10 * 注意事项: 11 * 虽然可以把数组转成集合,但是集合的长度不能改变。 12 */ 13 public class ArraysDemo { 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 // 定义一个数组 16 // String[] strArray = { "hello", "world", "java" }; 17 // List<String> list = Arrays.asList(strArray); 18 19 List<String> list = Arrays.asList("hello", "world", "java"); 20 // UnsupportedOperationException 不支持的操作异常 21 // list.add("javaee"); 22 // UnsupportedOperationException 不支持的操作异常 23 // list.remove(1); 24 list.set(1, "javaee"); // 可以修改 25 26 for (String s : list) { 27 System.out.println(s); 28 } 29 } 30 }
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
6:练习(掌握)
A:集合的嵌套遍历

1 package cn.itcast_01; 2 3 public class Student { 4 private String name; 5 private int age; 6 7 public Student() { 8 super(); 9 } 10 11 public Student(String name, int age) { 12 super(); 13 this.name = name; 14 this.age = age; 15 } 16 17 public String getName() { 18 return name; 19 } 20 21 public void setName(String name) { 22 this.name = name; 23 } 24 25 public int getAge() { 26 return age; 27 } 28 29 public void setAge(int age) { 30 this.age = age; 31 } 32 33 }

1 package cn.itcast_01; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 5 /* 6 * 集合的嵌套遍历 7 * 需求: 8 * 我们班有学生,每一个学生是不是一个对象。所以我们可以使用一个集合表示我们班级的学生。ArrayList<Student> 9 * 但是呢,我们旁边是不是还有班级,每个班级是不是也是一个ArrayList<Student>。 10 * 而我现在有多个ArrayList<Student>。也要用集合存储,怎么办呢? 11 * 就是这个样子的:ArrayList<ArrayList<Student>> 12 */ 13 public class ArrayListDemo { 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 // 创建大集合 16 ArrayList<ArrayList<Student>> bigArrayList = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Student>>(); 17 18 // 创建第一个班级的学生集合 19 ArrayList<Student> firstArrayList = new ArrayList<Student>(); 20 // 创建学生 21 Student s1 = new Student("唐僧", 30); 22 Student s2 = new Student("孙悟空", 29); 23 Student s3 = new Student("猪八戒", 28); 24 Student s4 = new Student("沙僧", 27); 25 Student s5 = new Student("白龙马", 26); 26 // 学生进班 27 firstArrayList.add(s1); 28 firstArrayList.add(s2); 29 firstArrayList.add(s3); 30 firstArrayList.add(s4); 31 firstArrayList.add(s5); 32 // 把第一个班级存储到学生系统中 33 bigArrayList.add(firstArrayList); 34 35 // 创建第二个班级的学生集合 36 ArrayList<Student> secondArrayList = new ArrayList<Student>(); 37 // 创建学生 38 Student s11 = new Student("诸葛亮", 30); 39 Student s22 = new Student("司马懿", 28); 40 Student s33 = new Student("周瑜", 26); 41 // 学生进班 42 secondArrayList.add(s11); 43 secondArrayList.add(s22); 44 secondArrayList.add(s33); 45 // 把第二个班级存储到学生系统中 46 bigArrayList.add(secondArrayList); 47 48 // 创建第三个班级的学生集合 49 ArrayList<Student> thirdArrayList = new ArrayList<Student>(); 50 // 创建学生 51 Student s111 = new Student("宋江", 40); 52 Student s222 = new Student("吴用", 35); 53 Student s333 = new Student("高俅", 30); 54 Student s444 = new Student("李师师", 22); 55 // 学生进班 56 thirdArrayList.add(s111); 57 thirdArrayList.add(s222); 58 thirdArrayList.add(s333); 59 thirdArrayList.add(s444); 60 // 把第三个班级存储到学生系统中 61 bigArrayList.add(thirdArrayList); 62 63 // 遍历集合 64 for (ArrayList<Student> array : bigArrayList) { 65 for (Student s : array) { 66 System.out.println(s.getName() + "---" + s.getAge()); 67 } 68 } 69 } 70 }
B:产生10个1-20之间的随机数,要求随机数不能重复

1 package cn.itcast_02; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Random; 5 6 /* 7 * 获取10个1-20之间的随机数,要求不能重复 8 * 9 * 用数组实现,但是数组的长度是固定的。 10 * 长度不好确定,所以我们使用集合实现。 11 * 12 * 分析: 13 * A:创建产生随机数的对象。 14 * B:创建一个存储随机数的集合。 15 * C:定义一个统计变量。从0开始。 16 * D:判断统计遍历是否小于10 17 * 是:产生一个随机数,判断该随机数在集合中是否存在。 18 * 如果不存在:就添加,统计变量++。 19 * 如果存在:就不搭理它。 20 * 否:不搭理它 21 * E:遍历集合 22 */ 23 public class RandomDemo { 24 public static void main(String[] args) { 25 // 创建产生随机数的对象。 26 Random r = new Random(); 27 28 // 创建一个存储随机数的集合。 29 ArrayList<Integer> array = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 30 31 // 定义一个统计变量。从0开始。 32 int count = 0; 33 34 // 判断统计遍历是否小于10 35 while (count < 10) { 36 // 产生一个随机数 37 int number = r.nextInt(20) + 1; 38 39 // 判断该随机数在集合中是否存在。 40 if (!array.contains(number)) { 41 // 如果不存在:就添加,统计变量++。 42 array.add(number); 43 count++; 44 } 45 } 46 47 // 遍历集合 48 for (Integer i : array) { 49 System.out.println(i); 50 } 51 } 52 }
C:键盘录入多个数据,以0结束,并在控制台输出最大值

1 package cn.itcast_03; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Arrays; 5 import java.util.Scanner; 6 7 /* 8 * 键盘录入多个数据,以0结束,要求在控制台输出这多个数据中的最大值。 9 * 10 * 分析: 11 * A:创建键盘录入数据对象 12 * B:键盘录入多个数据,我们不知道多少个,所以用集合存储 13 * C:以0结束,这个简单,只要键盘录入的数据是0,我就不继续录入数据了 14 * D:把集合转成数组 15 * E:对数组排序 16 * F:获取该数组中的最大索引的值 17 */ 18 public class ArrayListDemo { 19 public static void main(String[] args) { 20 // 创建键盘录入数据对象 21 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 22 23 // 键盘录入多个数据,我们不知道多少个,所以用集合存储 24 ArrayList<Integer> array = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 25 26 // 以0结束,这个简单,只要键盘录入的数据是0,我就不继续录入数据了 27 while (true) { 28 System.out.println("请输入数据:"); 29 int number = sc.nextInt(); 30 if (number != 0) { 31 array.add(number); 32 } else { 33 break; 34 } 35 } 36 37 // 把集合转成数组 38 // public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) 39 Integer[] i = new Integer[array.size()]; 40 // Integer[] ii = array.toArray(i); 41 array.toArray(i); 42 // System.out.println(i); // [Ljava.lang.Integer;@6cd8737 43 // System.out.println(ii); // [Ljava.lang.Integer;@6cd8737 44 45 // 对数组排序 46 // public static void sort(Object[] a) 47 Arrays.sort(i); 48 49 // 获取该数组中的最大索引的值 50 System.out.println("数组是:" + arrayToString(i) + "最大值是:" + i[i.length - 1]); 51 } 52 53 // 把数组转换成字符串 54 public static String arrayToString(Integer[] i) { 55 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 56 57 sb.append("["); 58 for (int x = 0; x < i.length; x++) { 59 if (x == i.length - 1) { 60 sb.append(i[x]); 61 } else { 62 sb.append(i[x]).append(", "); 63 } 64 } 65 sb.append("]"); 66 67 return sb.toString(); 68 } 69 }
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
7:要掌握的代码
集合存储元素,加入泛型,并可以使用增强for遍历。
=============================================================================
