大家好,我是辰哥~
本文带大家学习正则表达式,并通过python代码举例讲解常用的正则表达式
最后实战爬取小说网页:重点在于爬取的网页通过正则表达式进行解析。
正则表达式语法
Python的re模块(正则表达式)提供各种正则表达式的匹配操作。在绝大多数情况下能够有效地实现对复杂字符串的分析并取出相关信息。在讲解如何实际应用正则表达式之前,先教大家学习并掌握正则表达式的基本语法(匹配规则)。
正则表达式匹配过程如下:
(1)将定义好的正则表达式和字符串进行比较。
(2)如果每一个字符串都能匹配,则成功;一旦有匹配不成功的字符则匹配失败。
正则表达式规则
常见规则
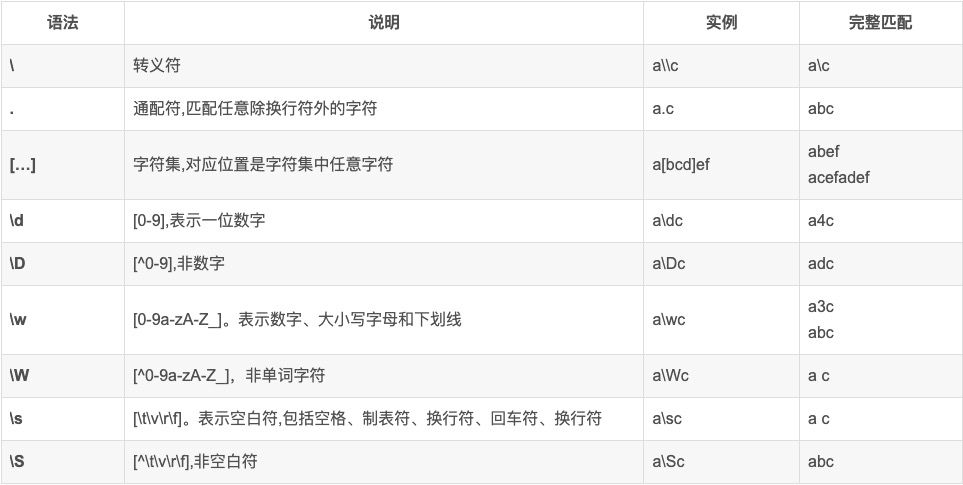
数量词匹配规则
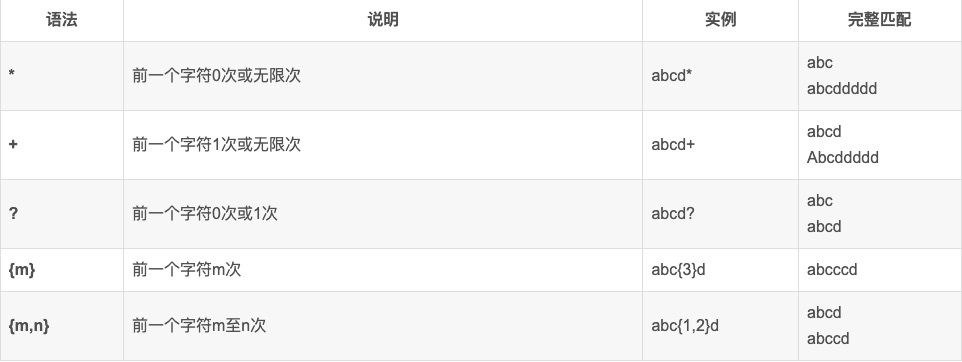
边界匹配规则
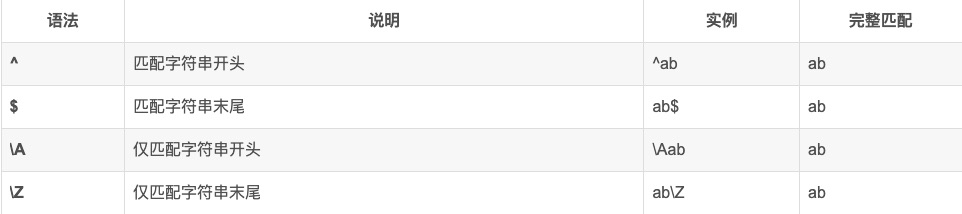
Re模块
Python中使用Re库去定义的正则表达式,常用的方法列举如下:
lpattern对象
re.compile(string[,flag])
l匹配所用函数
re.match(pattern, string[, flags])
re.search(pattern, string[, flags])
re.split(pattern, string[, maxsplit])
re.findall(pattern, string[, flags])
re.finditer(pattern, string[, flags])
re.sub(pattern, repl, string[, count])
re.subn(pattern, repl, string[, count])
其中pattern对象是由我们传入字符串对象,通过compile方法生成。利用这个对象来进行下一步的匹配。针对上述列举的各种正则表达式匹配规则和函数,下面通过Python代码进行举例讲解。
(1) re.match(pattern, string[, flags])
match函数将会从String(待匹配的字符串)的开头开始,尝试匹配pattern,一直向后匹配。如果中途匹配pattern成功,则终止匹配,返回匹配结果。如果无法匹配或者到字符串末尾还未匹配到,则返回None。
举例:
#导入re模块
import re
pattern = re.compile(r'python')
# 使用re.match匹配文本,获得匹配结果,无法匹配时将返回None
result1 = re.match(pattern,'python')
result2 = re.match(pattern,'pythonn CQC!')
result3 = re.match(pattern,'pthon CQC!')
print(result1)
print(result2)
print(result3)
"""
结果:
<_sre.SRE_Match object; span=(0, 6), match='python'>
<_sre.SRE_Match object; span=(0, 6), match='python'>
None
"""
(2) re.search(pattern, string[, flags])
Search函数会扫描整个string字符串查找匹配,存在的话返回匹配结果,不存在则返回None。
举例:
import re
pattern = re.compile(r'python')
#从“hello pythonnnnn!”中匹配“python”
result1 = re.search(pattern,'hello pythonnnnn!')
#从“hello pyhon!”中匹配“python”
result2 = re.search(pattern,'hello pyhon!')
print(result1)
print(result2)
"""
结果:
<_sre.SRE_Match object; span=(6, 12), match='python'>
None
"""
(3) re.split(pattern, string[, maxsplit])
split函数可以按照pattern匹配模式将string字符串分割后返回列表,其中maxsplit参数可以指定最大分割次数,不指定则将字符串全部分割。
举例:
import re
#以一位或者多位数字作为分割间隔
pattern = re.compile(r'd+')
print(re.split(pattern,'python1java2php3js'))
#只分割两次
print(re.split(pattern,'python1java2php3js',maxsplit=2))
"""
结果:
['python', 'java', 'php', 'js']
['python', 'java', 'php3js']
"""
(4) re.findall(pattern, string[, flags])
findall函数作用是搜索整个字符串,以列表形式返回全部能匹配的子串。
举例:
import re
pattern = re.compile(r'd+')
print(re.findall(pattern,'python1java2php3js2245'))
"""
结果:
['1', '2', '3', '2245']
"""
(5) re.finditer(pattern, string[, flags])
finditer函数作用是搜索整个字符串,返回一个符合匹配结果(Match对象)的迭代器。
举例:
import re
#以一位或者多位数字作为搜索条件
pattern = re.compile(r'd+')
#搜索结果得到一个集合,通过循环对集合遍历输出
for item in re.finditer(pattern,'python1java2php3js2245'):
print(item.group())
"""
结果:
1
2
3
2245
"""
(6) re.sub(pattern, repl, string[, count])
先看两个例子,然后再解释这个sub函数的作用。
举例:
import re
pattern1 = re.compile(r'music')
#例1中“i love the music”里的music替换成python
print(re.sub(pattern1, 'python', 'i love the music'))
pattern2 = re.compile(r'(d+)')
#例2中“数字123 和9”被python替换。
print(re.sub(pattern2, 'python', 'My number is 123 and my favorite number is 9'))
"""
结果:
i love the python
My number is python and my favorite number is python
"""
(7) re.subn(pattern, repl, string[, count])
subn可以指定替换次数,不指定则默认替换全部。
举例:
import re
#以一位或者多位数字作为替换条件
pattern1 = re.compile(r'(d+)')
#用“python”替换数字(一位或者多位),最后返回替换结果和替换次数
print(re.subn(pattern1, 'python', 'My number is 123 and my favorite number is 9'))
pattern2 = re.compile(r'(d+)')
print(re.subn(pattern2, 'python', 'My number is 123 and my favorite number is 9',1))
"""
结果:
('My number is python and my favorite number is python', 2)
('My number is python and my favorite number is 9', 1)
"""
实战
需求:提取小说章节正文和标题
本节通过实战案例来讲解正则表达式的应用。案例目的是:提取小说章节内容。步骤是先采集到每一章小说正文内容网页源码,然后通过正则表达式将里面的正文提取出来。
这里爬取小说 第一章 北灵院,用正则表达式提取小说章节正文和标题
目标链接:http://book.chenlove.cn/book/12242/39a44ff6dd27f.html
页面如下:
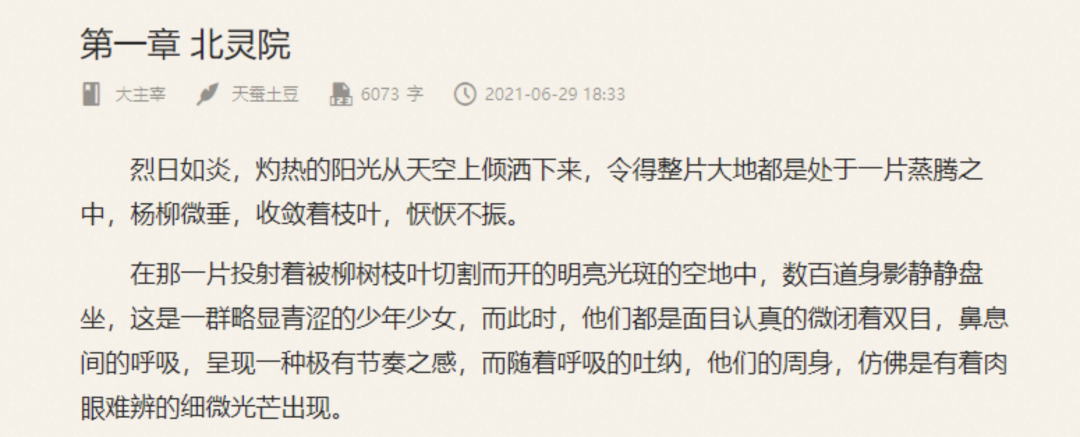
分析网页源码:

可以看到章节标题在h3标签中,其class为j_chapterName;正文内容在p标签中,清楚这些之后,下面开始编写代码请求网页源码,并编写正则表达式去提取标题和正文。
完整代码如下:
import requests
import re
import json
# 设置代理服务器
headers = {
'User_Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/89.0.4389.114 Safari/537.36'
}
#请求连接
url = "http://book.chenlove.cn/book/12242/39a44ff6dd27f.html"
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
if response.status_code == 200:
# 转化为utf-8格式,不加这条语句,输出爬取的信息为乱码
response.encoding = 'utf8'
#获取到源码
html = response.text
# 正则表达式解析小说章节标题
pattern1 = re.compile('<h3>(.+)</h3>')
title = re.findall(pattern1, html)[0]
#正则表达式解析小说章节正文内容
text = re.findall(r"<p>(.*?)</p>", html,re.S)[2:-1][0].split("</div>")[0]
# 打印输出
print(title)
print(text)
"""
结果:
第一章 北灵院
烈日如炎,灼热的阳光从天空上倾洒下来,令得整片大地都是处于一片蒸腾之中,杨柳微垂,......
"""
可以看到第一章的标题和正文已经成功提取出来了,因为正文内容很长,这里仅展示部分。
最后
本文汇总正则表达式常用的基本语法,并结合Python进行举例演示
最后实战讲解正则表达式在爬虫中的应用。