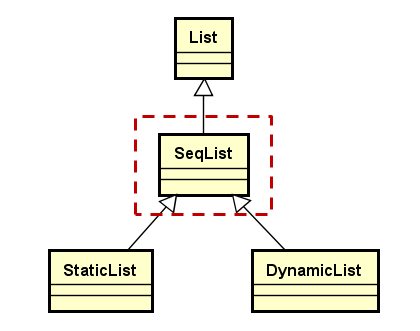
顺序存储结构SeqList类的抽象实现,该类继承于线性表抽象类List类
// 线性表抽象类
template<typename T>
class List : public Object
{
public:
virtual bool insert(int i, const T& e) = 0;
virtual bool remove(int i) = 0;
virtual bool set(int i, const T& e) = 0;
virtual bool get(int i, T& e) const = 0;
virtual int length() const = 0;
virtual void clear() =0;
};
顺序存储结构的抽象类SeqList的设计要点:
- 抽象类模板,存储空间的位置和大小由子类完成
- 实现顺序存储结构线性表的关键操作(增、删、改、查等)
- 提供数组操作符,方便快速获取元素
类模板如下:
template<typename T>
class SeqList : public List<T>
{
protected:
T* m_array; // 线性表的存储空间,具体值在子类中实现
int m_length; // 当前线性表的长度
public:
bool insert(int i, const T& e);
bool remove(int i);
bool set(int i, const T& e);
bool get(int i, T& e) const;
int length() const;
void clear();
// 顺序存储线性表的数组访问方式
T& operator[] (int i);
T operator[] (int i) const;
// 顺序存储空间的容量
virtual int capacity() const = 0;
};
SeqList继承于List,需要将List中的virtual函数一一实现
下面对SeqList的关键操作进行具体实现:
template<typename T>
class SeqList : public List<T>
{
protected:
T* m_array; // 线性表的存储空间,具体值在子类中实现
int m_length; // 当前线性表的长度
public:
bool insert(int i, const T& e)
{
bool ret = ((i >= 0) && ( i<= m_length));
ret = ret && ((m_length+1) <= capacity());
if (ret)
{
for(int p = m_length - 1; p >= i; p--)
{
m_array[p+1] = m_array[p];
}
m_array[i] = e;
m_length++;
}
return ret;
}
bool remove(int i)
{
bool ret = ((i >= 0) && ( i< m_length));
if (ret)
{
for(int p = i; p < m_length-1; p++)
{
m_array[p] = m_array[p+1];
}
m_length--;
}
return ret;
}
bool set(int i, const T& e)
{
bool ret = ((i >= 0) && ( i< m_length));
if (ret)
{
m_array[i] = e;
}
return ret;
}
bool get(int i, T& e) const
{
bool ret = ((i >= 0) && ( i< m_length));
if (ret)
{
e = m_array[i]; // 不直接返回值是因为有可能目标位置i不合法,get()的返回值用来表示当前获取值是否成功
}
return ret;
}
int length() const
{
return m_length;
}
void clear()
{
m_length = 0; // 清空一个线性表意味着这个线性表没有任何元素
}
// 顺序存储线性表的数组访问方式
T& operator[] (int i)
{
if((0 <= i) && (i < m_length))
{
return m_array[i]; // 目标位置合法,返回对应的数据元素
}
else
{
// 不合法,抛异常
// 意味着越界
THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Parameter i is invalid...");
}
}
// 函数体一摸一样,考虑代码复用
// T operator[] (int i) const
// {
// if((0 <= i) && (i < m_length))
// {
// return m_array[i]; // 目标位置合法,返回对应的数据元素
// }
// else
// {
// // 不合法,抛异常
// // 意味着越界
// THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Parameter i is invalid...");
// }
// }
T operator[] (int i) const
{
// 思路,去除对象的const属性,调用上面的非const的操作符
return (const_cast<SeqList<T>&>(*this))[i];
}
// 顺序存储空间的容量
// 顺序存储空间的具体指定是在子类中完成的,capacity要放在子类中完成
virtual int capacity() const = 0;
};