day1 变量、运算符与数据类型
目录
1.注释
2.运算符
3.变量和赋值
4.数据类型与转换
5.print()函数
6.练习
一、注释
单行注释:#
多行注释 :''' ''' 或者是 """ """ ,在单引号或者双引号之间的内容被注释,常用语多内容多行注释
print('hi') #hi ''' 第一天 首次 打卡 ''' print('hi')
二、运算符
首先说一下运算符的优先级
- 一元运算符优于二元运算符。例如
3 ** -2等价于3 ** (-2)。 - 先算术运算,后移位运算,最后位运算。例如
1 << 3 + 2 & 7等价于(1 << (3 + 2)) & 7。 - 逻辑运算最后结合。例如
3 < 4 and 4 < 5等价于(3 < 4) and (4 < 5)
一元运算符有1个操作数。例bai如,递增运算du符"++"就是一元运zhi算符,二元运算符有2个操作数。例如,除dao法运算符"/"有2个操作数
1.算术运算符
| 操作符 | 名称 | 例子 |
| + | 加 | 1+1 |
| - | 减 | 2-1 |
| * | 乘 | 3*4 |
| / | 除 | 3/4 |
| // | 地板除(即是支取整数位) | 3//4 |
| % | 取余 | 3%4 |
| ** | 幂 | 2**3 |
#算术运算符 print(1+1) #2 print(2-1) #1 print(3*4) #12 print(3/4) #0.75 print(3//4) #0 print(3%4) #3 print(2**3) #8
2.比较运算符:返回的是布尔型,True或者False
| 操作符 | 名称 | 例子 |
| > | 大于 | 2>1 |
| >= | 大于或等于 | 2>=4 |
| < | 小于 | 1<2 |
| <= | 小于或等于 | 5<=2 |
| == | 等于(注意:=是赋值) | 3==4 |
| != | 不等于 | 3!=5 |
#比较运算符 print(2 > 1) # True print(2 >= 4) # False print(1 < 2) # True print(5 <= 2) # False print(3 == 4) # False print(3 != 5) # True
3.逻辑运算符:返回的也是布尔型,True或者False
| 操作符 | 名称 | 例子 |
| and | 且 | (3>2) and (3<5) |
| or | 或(只要一个正确就为正) | (1>3) or (9<2) |
| not | 非 | not (2>1) |
#逻辑运算符 print((3 > 2) and (3 < 5)) # True print((1 > 3) or (9 < 2)) # False print(not (2 > 1)) # False
4.位运算符
#位运算符
print('~4={}, 4 & 5={}, 4 | 5={}, 4 ^ 5={}, 4 << 2={}, 4 >> 2={}'.format(~4,4 & 5,4 | 5,4 ^ 5,4 << 2,4 >> 2))#~4=-5, 4 & 5=4, 4 | 5=5, 4 ^ 5=1, 4 << 2=16, 4 >> 2=1
先说一下二进制的原码反码和补码
原码:就是用二进制表示(注意,最高位(第一位)是符号位)
00 00 00 11 -> 3 10 00 00 11 -> -3
反码:正数的反码就是原码,负数的反码是符号位不变,其余位取反(对应正数按位取反)
00 00 00 11 -> 3 11 11 11 00 -> -3
补码:正数的补码就是原码,负数的补码是反码+1
00 00 00 11 -> 3 11 11 11 01 -> -3
符号位:最高位为符号位,0表示正数,1表示负数。在位运算中符号位也参与运算
| 操作符 | 描述 | 例子 |
| & | 按位与运算符:参与运算的两个值,如果两个相应位都为1,则该位的结果为1,否则为0 | (a & b) 输出结果 12 ,二进制解释: 0000 1100 |
| | | 按位或运算符:只要对应的二个二进位有一个为1时,结果位就为1。 | (a | b) 输出结果 61 ,二进制解释: 0011 1101 |
| ^ | 按位异或运算符:当两对应的二进位相异时,结果为1 | (a ^ b) 输出结果 49 ,二进制解释: 0011 0001 |
| ~ | 按位取反运算符:对数据的每个二进制位取反,即把1变为0,把0变为1 。~x 类似于 -x-1 | (~a ) 输出结果 -61 ,二进制解释: 1100 0011,在一个有符号二进制数的补码形式。 |
| << | 左移动运算符:运算数的各二进位全部左移若干位,由 << 右边的数字指定了移动的位数,高位丢弃,低位补0。 | a << 2 输出结果 240 ,二进制解释: 1111 0000 |
| >> | 右移动运算符:把">>"左边的运算数的各二进位全部右移若干位,>> 右边的数字指定了移动的位数 | a >> 2 输出结果 15 ,二进制解释: 0000 1111 |
#位运算 a = 60 # 60 = 0011 1100 b = 13 # 13 = 0000 1101 c = 0 c = a & b; # 12 = 0000 1100 print( "1 - c 的值为:", c) c = a | b; # 61 = 0011 1101 print( "2 - c 的值为:", c) c = a ^ b; # 49 = 0011 0001 print( "3 - c 的值为:", c) c = ~a; # -61 = 1100 0011 print ("4 - c 的值为:", c) c = a << 2; # 240 = 1111 0000 print ("5 - c 的值为:", c) c = a >> 2; # 15 = 0000 1111 print( "6 - c 的值为:", c) #输出: 1 - c 的值为: 12 2 - c 的值为: 61 3 - c 的值为: 49 4 - c 的值为: -61 5 - c 的值为: 240 6 - c 的值为: 15
5.三元运算符
6.其他运算符
| 操作符 | 名称 | 例子 |
| in | 在 (返回布尔型) | 'A' in ['A', 'B', 'C'] |
| not in | 不在(返回布尔型) | 'h' not in ['A', 'B', 'C'] |
| is | 是(返回布尔型) | "hello" is "hello" |
| is not | 不是(返回布尔型) | "hello" is not "hello" |
#in ,not in ,is ,is not l=list('abc') l1=list('abc') print(l,'a' in l,'a' not in l,'a' is l,l is l,l is l1,l is not l1) #['a', 'b', 'c'] True False False True False True #比较is,is not 和 ==,!= print(l==l1,l is l1,l!=l1,l is not l1) #True False False True
注意:
- is, is not 对比的是两个变量的内存地址
- ==, != 对比的是两个变量的值
- 比较的两个变量,指向的都是地址不可变的类型(str等),那么is,is not 和 ==,!= 是完全等价的。
- 对比的两个变量,指向的是地址可变的类型(list,dict等),则两者是有区别的
三、变量和赋值
在变量使用之前,要先赋值
变量名可以包括字母、数字、下划线,但是不能以数字开头
变量名是大小写敏感的,整个python都是
#变量和赋值 a=1 1_a=1 #SyntaxError: invalid token _a=1
四、数据类型与转换
1.int整型
type()可以看出变量或者值属于什么数据类型,dir()可以看该对象有什么属性和方法
#int a=10 type(a) type(10) dir(int)
b='10'
int(b)
2.浮点型 float
可以理解为有小数点的数字
可以用decimal.getcontext().prec 或者 round 来调节精度
#float import decimal from decimal import Decimal #getcontext().prec 来调整精度 decimal.getcontext().prec = 4 c = Decimal(1) / Decimal(3) print(c) #用round round(1/3,2) #0.33 #转换为float型 float(10) #10.0
3.布尔型
布尔 (boolean) 型变量只能取两个值,True 和 False。当把布尔型变量用在数字运算中,用 1 和 0 代表 True 和 False
除了直接给变量赋值 True 和 False,还可以用 bool(X) 来创建变量,其中 X 可以是
(1)基本变量(整型、浮点型、布尔型)
(2)容器类型:字符串、元组、列表、字典和集合
bool 作用在基本类型变量:X 只要不是整型 0、浮点型 0.0,bool(X) 就是 True,其余就是 False
bool 作用在容器类型变量:X 只要不是空的变量,bool(X) 就是 True,其余就是 False
#布尔型 print(True + True) # 2 print(True + False) # 1 print(True * False) # 0 print(type(0), bool(0), bool(1)) # <class 'int'> False True print(type(10.31), bool(0.00), bool(10.31)) # <class 'float'> False True print(type(True), bool(False), bool(True)) # <class 'bool'> False True print(type(''), bool(''), bool('python')) # <class 'str'> False True print(type(()), bool(()), bool((10,))) # <class 'tuple'> False True print(type([]), bool([]), bool([1, 2])) # <class 'list'> False True print(type({}), bool({}), bool({'a': 1, 'b': 2})) # <class 'dict'> False True print(type(set()), bool(set()), bool({1, 2})) # <class 'set'> False True
4.获取数据类型
type() 获取类型信息
isinstance(object, classinfo) 判断一个对象是否是一个已知的类型
类型转换
- 转换为整型
int(x, base=10) - 转换为字符串
str(object='') - 转换为浮点型
float(x)
#数据类型和转换 #type() print(type(1)) # <class 'int'> print(type(5.2)) # <class 'float'> print(type(True)) # <class 'bool'> print(type('5.2')) # <class 'str'> #isinstance print(isinstance(1, int)) # True print(isinstance(5.2, float)) # True print(isinstance(True, bool)) # True print(isinstance('5.2', str)) # True #类型转换 print(int('520')) # 520 print(int(520.52)) # 520 print(float('520.52')) # 520.52 print(float(520)) # 520.0 print(str(10 + 10)) # 20 print(str(10.1 + 5.2)) # 15.3
五、print()函数
#参数 print(*objects, sep=' ', end=' ', file=sys.stdout, flush=False)
- 将对象以字符串表示的方式格式化输出到流文件对象file里。其中所有非关键字参数都按
str()方式进行转换为字符串输出; - 关键字参数
sep是实现分隔符,比如多个参数输出时想要输出中间的分隔字符; - 关键字参数
end是输出结束时的字符,默认是换行符 - 关键字参数
file是定义流输出的文件,可以是标准的系统输出sys.stdout,也可以重定义为别的文件; - 关键字参数
flush是立即把内容输出到流文件,不作缓存
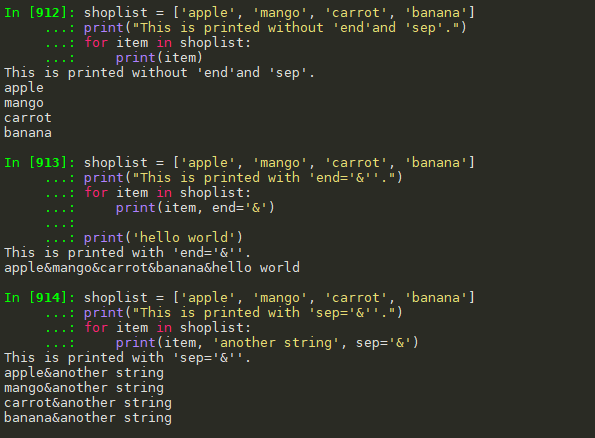
#print #没有参数时,每次输出后都会换行 shoplist = ['apple', 'mango', 'carrot', 'banana'] print("This is printed without 'end'and 'sep'.") for item in shoplist: print(item) #每次输出结束都用end设置的参数&结尾,并没有默认换行 shoplist = ['apple', 'mango', 'carrot', 'banana'] print("This is printed with 'end='&''.") for item in shoplist: print(item, end='&') print('hello world') #item值与'another string'两个值之间用sep设置的参数&分割。由于end参数没有设置,因此默认是输出解释后换行,即end参数的默认值为 shoplist = ['apple', 'mango', 'carrot', 'banana'] print("This is printed with 'sep='&''.") for item in shoplist: print(item, 'another string', sep='&')
附上全部代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Created on Tue Jul 21 10:52:00 2020 @author: Admin """ print('hi') #hi ''' 第一天 首次 打卡 ''' print('hi') #算术运算符 print(1+1) #2 print(2-1) #1 print(3*4) #12 print(3/4) #0.75 print(3//4) #0 print(3%4) #3 print(2**3) #8 #比较运算符 print(2 > 1) # True print(2 >= 4) # False print(1 < 2) # True print(5 <= 2) # False print(3 == 4) # False print(3 != 5) # True #逻辑运算符 print((3 > 2) and (3 < 5)) # True print((1 > 3) or (9 < 2)) # False print(not (2 > 1)) # False #位运算符 print('~4={}, 4 & 5={}, 4 | 5={}, 4 ^ 5={}, 4 << 2={}, 4 >> 2={}'.format(~4,4 & 5,4 | 5,4 ^ 5,4 << 2,4 >> 2)) #in ,not in ,is ,is not l=list('abc') l1=list('abc') print(l,'a' in l,'a' not in l,'a' is l,l is l,l is l1,l is not l1) #['a', 'b', 'c'] True False False True False True #比较is,is not 和 ==,!= print(l==l1,l is l1,l!=l1,l is not l1) #True False False True #变量和赋值 a=1 1_a=1 #SyntaxError: invalid token _a=1 #int a=10 type(a) type(10) dir(int) b='10' int(b) #float import decimal from decimal import Decimal #getcontext().prec 来调整精度 decimal.getcontext().prec = 4 c = Decimal(1) / Decimal(3) print(c) #用round round(1/3,2) #0.33 #转换为float型 float(10) #10.0 #布尔型 print(True + True) # 2 print(True + False) # 1 print(True * False) # 0 print(type(0), bool(0), bool(1)) # <class 'int'> False True print(type(10.31), bool(0.00), bool(10.31)) # <class 'float'> False True print(type(True), bool(False), bool(True)) # <class 'bool'> False True print(type(''), bool(''), bool('python')) # <class 'str'> False True print(type(()), bool(()), bool((10,))) # <class 'tuple'> False True print(type([]), bool([]), bool([1, 2])) # <class 'list'> False True print(type({}), bool({}), bool({'a': 1, 'b': 2})) # <class 'dict'> False True print(type(set()), bool(set()), bool({1, 2})) # <class 'set'> False True #数据类型和转换 #type() print(type(1)) # <class 'int'> print(type(5.2)) # <class 'float'> print(type(True)) # <class 'bool'> print(type('5.2')) # <class 'str'> #isinstance print(isinstance(1, int)) # True print(isinstance(5.2, float)) # True print(isinstance(True, bool)) # True print(isinstance('5.2', str)) # True #类型转换 print(int('520')) # 520 print(int(520.52)) # 520 print(float('520.52')) # 520.52 print(float(520)) # 520.0 print(str(10 + 10)) # 20 print(str(10.1 + 5.2)) # 15.3 #print #没有参数时,每次输出后都会换行 shoplist = ['apple', 'mango', 'carrot', 'banana'] print("This is printed without 'end'and 'sep'.") for item in shoplist: print(item) #每次输出结束都用end设置的参数&结尾,并没有默认换行 shoplist = ['apple', 'mango', 'carrot', 'banana'] print("This is printed with 'end='&''.") for item in shoplist: print(item, end='&') print('hello world') #item值与'another string'两个值之间用sep设置的参数&分割。由于end参数没有设置,因此默认是输出解释后换行,即end参数的默认值为 shoplist = ['apple', 'mango', 'carrot', 'banana'] print("This is printed with 'sep='&''.") for item in shoplist: print(item, 'another string', sep='&') #位运算 a = 60 # 60 = 0011 1100 b = 13 # 13 = 0000 1101 c = 0 c = a & b; # 12 = 0000 1100 print( "1 - c 的值为:", c) c = a | b; # 61 = 0011 1101 print( "2 - c 的值为:", c) c = a ^ b; # 49 = 0011 0001 print( "3 - c 的值为:", c) c = ~a; # -61 = 1100 0011 print ("4 - c 的值为:", c) c = a << 2; # 240 = 1111 0000 print ("5 - c 的值为:", c) c = a >> 2; # 15 = 0000 1111 print( "6 - c 的值为:", c)