单生产和消费模式
在Java中,负责产生数据的模块的是生产者,负责使用数据的模块是消费者,生产者消费者解决数据的平衡问题,即先有数据才能使用,没有数据时消费者需要等待。
例如:有一个饭店,它有一个厨师和一个服务员,服务员必须等厨师把菜做好了,通知到服务员才能上菜,然后返回继续等待,厨师代表生产者,服务员代表消费者,两个任务在被消费和生产同时运行。
public class Text17 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ValueOP valueOP=new ValueOP();
//测试生产-消费
ProductThread productThread=new ProductThread(valueOP);
ConsumerThread consumerThread=new ConsumerThread(valueOP);
productThread.start();
consumerThread.start();
}
}
//定义线程类模拟生产者
class ProductThread extends Thread
{
private ValueOP obj;
public ProductThread(ValueOP obj)
{
this.obj=obj;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true)
{
try {
obj.SetValue();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
class ConsumerThread extends Thread
{
private ValueOP obj;
public ConsumerThread(ValueOP obj)
{
this.obj=obj;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true)
{
try {
obj.GetValue();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//SetValue用来设置值,如果不为空就不设置值,如果GetValue为空,就等待不读取,这样前一个设置后一个读取
class ValueOP
{
public String value="";
//修改值方法
public void SetValue() throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (this)
{
//如果不是空字符串就等待
if(!value.equalsIgnoreCase(""))
{
this.wait();
}
//如果是空串就设置value值
String value=System.currentTimeMillis()+"-"+System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("set设置的是"+value);
this.value=value;
this.notify();
}
}
//读取字段
public void GetValue() throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (this)
{
//如果是空字符串就等待
if(value.equalsIgnoreCase(""))
{
this.wait();
}
//不是空串就读取,并赋值为空
System.out.println("get的值是:"+value);
this.value="";
this.notify();
}
}
}

这样生产与消费交替运行
多生产和消费模式
一个饭店有多个厨师和服务员,当厨师们做菜过快了,导致服务员上菜速度跟不上,导致菜堆积在窗口,这时候要让厨师停止生产,等待服务员把菜上完,再继续做菜。如果服务员们上菜速度太快了,厨师没有做完,多名服务员又想上菜,这时候要等待厨师做菜。
public class Text17 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ValueOP valueOP=new ValueOP();
//测试生产-消费
ProductThread productThread=new ProductThread(valueOP);
ProductThread productThread2=new ProductThread(valueOP);
ConsumerThread consumerThread=new ConsumerThread(valueOP);
ConsumerThread consumerThread2=new ConsumerThread(valueOP);
productThread.start();
productThread2.start();;
consumerThread.start();
consumerThread2.start();
}
}
//定义线程类模拟生产者
class ProductThread extends Thread
{
private ValueOP obj;
public ProductThread(ValueOP obj)
{
this.obj=obj;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true)
{
try {
obj.SetValue();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
class ConsumerThread extends Thread
{
private ValueOP obj;
public ConsumerThread(ValueOP obj)
{
this.obj=obj;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true)
{
try {
obj.GetValue();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//SetValue用来设置值,如果不为空就不设置值,如果GetValue为空,就等待不读取,这样前一个设置后一个读取
class ValueOP
{
public String value="";
//修改值方法
public void SetValue() throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (this)
{
//如果不是空字符串就等待
while (!value.equalsIgnoreCase(""))
{
this.wait();
}
//如果是空串就设置value值
String value=System.currentTimeMillis()+"-"+System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("set设置的是"+value);
this.value=value;
this.notifyAll();
}
}
//读取字段
public void GetValue() throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (this)
{
//如果是空字符串就等待
while (value.equalsIgnoreCase(""))
{
this.wait();
}
//不是空串就读取,并赋值为空
System.out.println("get的值是:"+value);
this.value="";
this.notifyAll();
}
}
}
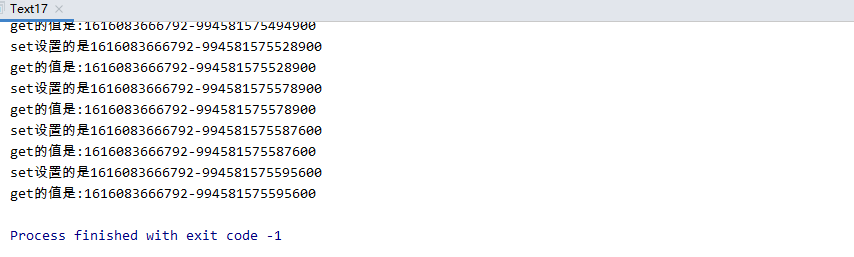
在多生产消费的环境notify不能保证是唤醒消费者,如果生产者唤醒生产者就会出现假死情况。
通过管道实现线程通信
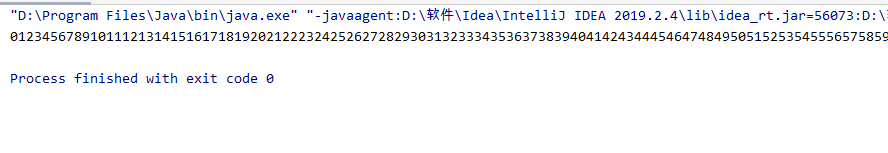
在java.io包中的pipeStream管道流用于在线程之间传送数据,一个线程发送数据到输出管道,另一个线程从输入管道读取数据,相关的类包括:pidedInputStream和pipedoutStream,pipedReader和pepedWriter
import java.awt.print.PrinterIOException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PipedInputStream;
import java.io.PipedOutputStream;
public class TextWrite {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
PipedInputStream inputStream=new PipedInputStream();
PipedOutputStream outputStream=new PipedOutputStream();
inputStream.connect(outputStream);
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
WriteData(outputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
ReadData(inputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
//定义方法向管道流中写入数据
public static void WriteData(PipedOutputStream outputStream) throws IOException {
for (int i = 0; i <100 ; i++) {
String data=""+i;
outputStream.write(data.getBytes());//把字节数组写入到输出管道中
}
outputStream.close();
}
//从管道流中读取数据
public static void ReadData(PipedInputStream inputStream) throws IOException {
byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];
int len=inputStream.read(bytes);//返回读到的字节数,没有读到返回-1
while (len != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, len));
len=inputStream.read(bytes);//继续从管道读取数据
}
inputStream.close();
}
}