作为分布式应用,Spark的数据存储在不同机器上。这就涉及到数据的传输,元数据的管理等内容。而且由于Spark可以利用内存和磁盘作为存储介质,这还涉及到了内存和磁盘的数据管理。
Spark存储体系架构
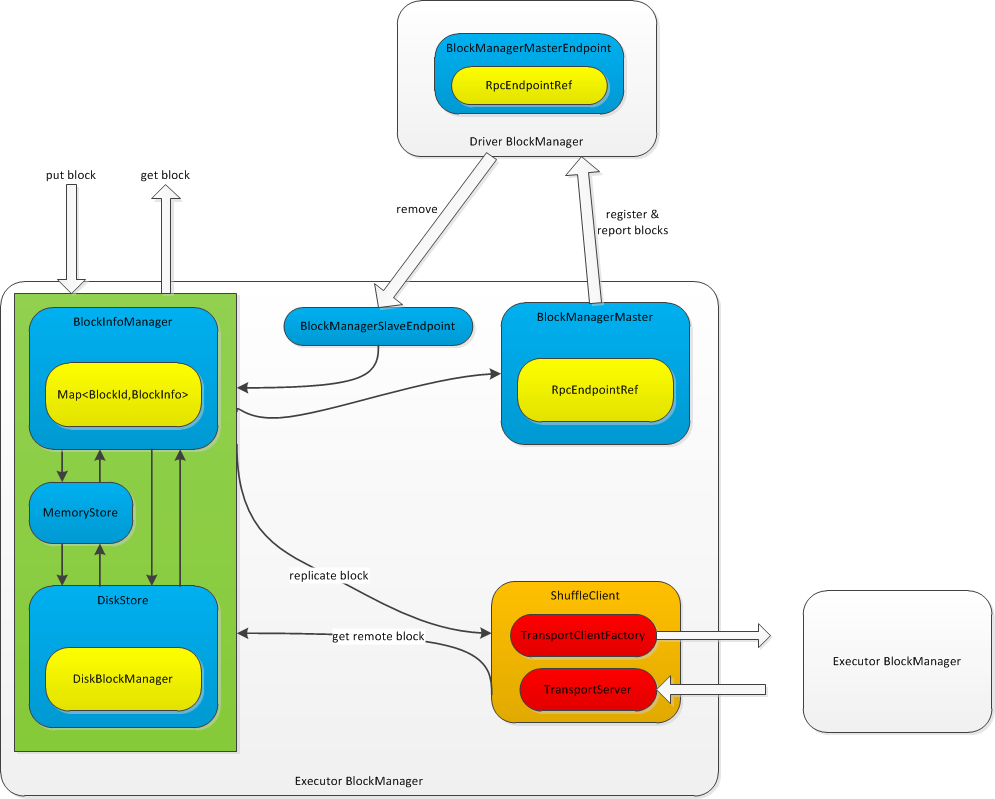
Spark存储(主要由BlockManager来完成)主要完成了写入数据块,如果需要备份数据块,则将数据块写入其他节点;读取数据块,如果当前节点不含有数据块,则从其他节点获取数据块;向Driver节点注册自身的BlockManager,以及上报其所管理的数据块信息。
Spark使用BlockInfoManager来管理当前节点所管理的数据块的元数据,维护了BlockId(数据块的唯一标识)到BlockInfo(数据块元数据)的映射关系。使用内存(MemoryStore)和磁盘(DiskStore)来存储数据块。
Spark使用BlockManagerMaster使Executor的BlockManager与Driver进行通信,向Driver注册自己,并上报数据块信息。Driver通过Executor BlockManager的BlockManagerSlaveEndpoint向Executor发出删除数据块/Rdd/Shuffle/Broadcast等数据。
Spark使用ShuffleClient来实现不同Executor BlockManager之间的通信。ShuffleClient中包含了一个TransportServer和一个用来创建client的TransportClientFactory,作为服务器和客户端实现Executor BlockManager之间的双向通信。
Spark设置了多种存储级别:
| 存储级别 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| DISK_ONLY | 只使用磁盘存储 |
| DISK_ONLY_2 | 只使用磁盘存储,并且有一个备份 |
| MEMORY_ONLY | 只使用内存储存储 |
| MEMORY_ONLY_2 | 只使用内存存储,并有一个备份 |
| MEMORY_ONLY_SER | 只使用内存存储序列化数据 |
| MEMORY_ONLY_SER_2 | 只使用内存存储序列化数据,并有一个备份 |
| MEMORY_AND_DISK | 优先内存存储,内存不足则使用磁盘 |
| MEMORY_AND_DISK_2 | 优先内存存储,内存不足使用磁盘,并有一个备份 |
| MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER | 优先内存存储序列化数据,内存不足使用磁盘 |
| MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER_2 | 优先内存存储序列化数据,内存不足使用磁盘,并有一个备份 |
| OFF_HEAP | 使用堆外存储(同MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER,只是使用堆外内存) |
put block(写入数据块):在写数据块的时候,根据存储级别的不同,如果存储级别要求存储序列化/非序列化的数据,而输入的数据块是非序列化/序列化的,则要首先序列化/反序列化;如果支持内存存储,则将数据块保存到内存中,如果设置了MEMORY_AND_DISK之类的存储级别,当内存不足时,会将数据块写入磁盘。如果不支持内存存储,只支持磁盘存储,则直接将数据块写入磁盘。如果需要备份数据块,则将数据块同步的写入其他节点。
get block(获取数据块):获取数据块时,如果请求序列化的数据而存储级别是非序列化,则优先从磁盘中获取数据,如果磁盘获取不到,则根据存储级别尝试从内存获取数据并将其序列化;如果存储级别就是序列化数据,则首先尝试从内存获取数据,如果获取不到,则根据存储级别从磁盘获取数据。如果请求的是非序列化的数据,如果存储级别包括内存,则首先尝试从内存获取,如果获取不到,则根据存储级别再尝试从磁盘获取并反序列化数据;如果存储级别只包括磁盘,则直接从磁盘获取并反序列化数据。
register & register block(注册BlockManager&上报数据块信息):Executor的BlockManager在初始化时需要向Driver注册,并定时上报其所管理的数据块信息。
remove(删除数据块):Driver向Executor BlockManager下发删除数据块/Rdd/Shuffle/Broadcast等数据的指令,Executor BlockManager接收指令并在本地执行删除操作。
BlockManager 块管理器
Spark中使用BlockManager块管理器来管理当前节点内存和磁盘的数据块,Driver和Executor节点都会创建块管理器。块管理器负责数据的读写请求,删除等操作,并向Driver节点注册,汇报其所管理的数据块元数据信息(如果是Driver节点的块管理器,则整个注册过程无需网络通信,如果是Executor节点的块管理器注册,则需要与Driver节点进行网络通信)。当节点需要的数据块不在本地时,块管理器会首先通过Driver节点获取到持有所需数据块的节点,然后直接与该节点进行通信,完成数据的传输。其中涉及到的通信(不论是网络通信还是本地通信),都是通过Spark的RPC框架实现的(RPC框架相关内容见Spark RPC笔记)。
BlockManager主要功能有
- 向Driver注册当前的BlockManger
- 向Driver上报所管理的数据块信息
- 从本地获取序列化/非序列化数据块的方法
- 保存数据块到本地
- 从Driver获取集群中持有某个数据块的节点信息
- 从其他节点获取数据块的方法
- 注册任务,获取/释放数据块上的锁
- 将所持有的数据块复制到其他节点
BlockManagerMaster
BlockManagerMaster是BlockManager的组件,BlockManager通过其来与Driver进行通信,完成向Driver注册BlockManager,从Driver获取数据块的位置信息,定时向Driver同步BlockManager所管理的数据块信息,响应Driver发来的删除数据块的请求等。
在创建BlockManagerMaster时,会传入类型为RpcEndpointRef的driverEndpoint,是BlockManagerMaster与Driver通信的rpdEndpoint的引用,通过Spark的RPC框架(RPC框架相关内容见Spark RPC笔记)最终netty通过调用rpcEndpointRef中的driver地址实现BlockManagerMaster与Driver之间的通信。
Driver和Executor节点都会创建自己的BlockManagerMaster,区别是Driver自身BlockManager中的BlockManagerMaster与Driver通信时,不产生网络通信。而Executor节点中的BlockManagerMaster与Driver通信时,会产生网络通信。
BlockManagerMasterEndpoint
BlockManagerMasterEndpoint是RpcEndpoint的一个具体实现类,就是上文中BlockManagerMaster所持有的RpcEndpointRef的具体指向类,是Driver的BlockManager处理来自Executor请求,以及向Executor发送请求的逻辑。来自Executor的请求/向Executor发送的请求与BlockManagerMaster发送和响应的相同,主要为注册Executor的BlockManager,返回所保存的数据块的位置信息,接收并更新Executor发送过来的数据块信息,向Executor发送删除数据块的请求等。
在BlockManagerMasterEndpoint中维护了注册的BlockManager,BlockManager和Executor的映射关系,数据块所在的位置等信息。这些都可以看做是存储相关的元数据信息。Driver节点通过保存这些元数据来管理整个集群的存储。
源码分析
- BlockManagerMasterEndpoint存储的元数据
// Mapping from block manager id to the block manager's information.
private val blockManagerInfo = new mutable.HashMap[BlockManagerId, BlockManagerInfo]
// Mapping from executor ID to block manager ID.
private val blockManagerIdByExecutor = new mutable.HashMap[String, BlockManagerId]
// Mapping from block id to the set of block managers that have the block.
private val blockLocations = new JHashMap[BlockId, mutable.HashSet[BlockManagerId]]
- 根据来自Executor不同的请求,调用相关函数并回调请求回调函数
override def receiveAndReply(context: RpcCallContext): PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
case RegisterBlockManager(blockManagerId, maxMemSize, slaveEndpoint) =>
register(blockManagerId, maxMemSize, slaveEndpoint)
context.reply(true)
case _updateBlockInfo @
UpdateBlockInfo(blockManagerId, blockId, storageLevel, deserializedSize, size) =>
context.reply(updateBlockInfo(blockManagerId, blockId, storageLevel, deserializedSize, size))
listenerBus.post(SparkListenerBlockUpdated(BlockUpdatedInfo(_updateBlockInfo)))
case GetLocations(blockId) =>
context.reply(getLocations(blockId))
case GetLocationsMultipleBlockIds(blockIds) =>
context.reply(getLocationsMultipleBlockIds(blockIds))
case GetPeers(blockManagerId) =>
context.reply(getPeers(blockManagerId))
case GetExecutorEndpointRef(executorId) =>
context.reply(getExecutorEndpointRef(executorId))
case GetMemoryStatus =>
context.reply(memoryStatus)
case GetStorageStatus =>
context.reply(storageStatus)
case GetBlockStatus(blockId, askSlaves) =>
context.reply(blockStatus(blockId, askSlaves))
case GetMatchingBlockIds(filter, askSlaves) =>
context.reply(getMatchingBlockIds(filter, askSlaves))
case RemoveRdd(rddId) =>
context.reply(removeRdd(rddId))
case RemoveShuffle(shuffleId) =>
context.reply(removeShuffle(shuffleId))
case RemoveBroadcast(broadcastId, removeFromDriver) =>
context.reply(removeBroadcast(broadcastId, removeFromDriver))
case RemoveBlock(blockId) =>
removeBlockFromWorkers(blockId)
context.reply(true)
case RemoveExecutor(execId) =>
removeExecutor(execId)
context.reply(true)
case StopBlockManagerMaster =>
context.reply(true)
stop()
case BlockManagerHeartbeat(blockManagerId) =>
context.reply(heartbeatReceived(blockManagerId))
case HasCachedBlocks(executorId) =>
blockManagerIdByExecutor.get(executorId) match {
case Some(bm) =>
if (blockManagerInfo.contains(bm)) {
val bmInfo = blockManagerInfo(bm)
context.reply(bmInfo.cachedBlocks.nonEmpty)
} else {
context.reply(false)
}
case None => context.reply(false)
}
}
- 向Executor节点发送各种删除请求,如
private def removeBlockManager(blockManagerId: BlockManagerId) {
val info = blockManagerInfo(blockManagerId)
// Remove the block manager from blockManagerIdByExecutor.
blockManagerIdByExecutor -= blockManagerId.executorId
// Remove it from blockManagerInfo and remove all the blocks.
blockManagerInfo.remove(blockManagerId)
val iterator = info.blocks.keySet.iterator
while (iterator.hasNext) {
val blockId = iterator.next
val locations = blockLocations.get(blockId)
locations -= blockManagerId
if (locations.size == 0) {
blockLocations.remove(blockId)
}
}
listenerBus.post(SparkListenerBlockManagerRemoved(System.currentTimeMillis(), blockManagerId))
logInfo(s"Removing block manager $blockManagerId")
}
BlockManagerSlaveEndpoint
BlockManagerSlaveEndpoint是RpcEndpoint的一个具体实现类,是BlockManager的组件,当向Driver注册BlockManager时,会带上BlockManagerSlaveEndpoint信息。BlockManagerSlaveEndpoint保存了Executor的地址,Driver可以通过调用相关BlockManager的BlockManagerSlaveEndpoint来向BlockManager发送删除指令。
源码分析
- 处理来自Driver的删除请求,并返回删除结果的逻辑
override def receiveAndReply(context: RpcCallContext): PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
case RemoveBlock(blockId) =>
doAsync[Boolean]("removing block " + blockId, context) {
blockManager.removeBlock(blockId)
true
}
case RemoveRdd(rddId) =>
doAsync[Int]("removing RDD " + rddId, context) {
blockManager.removeRdd(rddId)
}
case RemoveShuffle(shuffleId) =>
doAsync[Boolean]("removing shuffle " + shuffleId, context) {
if (mapOutputTracker != null) {
mapOutputTracker.unregisterShuffle(shuffleId)
}
SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager.unregisterShuffle(shuffleId)
}
case RemoveBroadcast(broadcastId, _) =>
doAsync[Int]("removing broadcast " + broadcastId, context) {
blockManager.removeBroadcast(broadcastId, tellMaster = true)
}
case GetBlockStatus(blockId, _) =>
context.reply(blockManager.getStatus(blockId))
case GetMatchingBlockIds(filter, _) =>
context.reply(blockManager.getMatchingBlockIds(filter))
case TriggerThreadDump =>
context.reply(Utils.getThreadDump())
}
private def doAsync[T](actionMessage: String, context: RpcCallContext)(body: => T) {
val future = Future {
logDebug(actionMessage)
body
}
future.onSuccess { case response =>
logDebug("Done " + actionMessage + ", response is " + response)
context.reply(response)
logDebug("Sent response: " + response + " to " + context.senderAddress)
}
future.onFailure { case t: Throwable =>
logError("Error in " + actionMessage, t)
context.sendFailure(t)
}
}
BlockTransferService
BlockTransferService用来实现BlockManager与其他Executor的BlockManager的相互通信,来获取/上传数据块。BlockTransferService是一个抽象类,NettyBlockTransferService是他的实现类,通过netty实现网络通信。
创建NettyBlockTransferService后,在调用NettyBlockTransferService其他方法之前需要调用init方法,来创建netty传输相关的TransportServer,TransportClientFactory,NettyBlockRpcServer。其中TransportServer用来接收其他Executor BlockManager发来的请求,TransportClientFactory用来创建client向其他Executor BlockManager发送请求,NettyBlockRpcServer用来执行响应请求的具体逻辑。
源码分析
- 初始化NettyBlockTransferService
// 创建rpcHandler,server,client,来发送和接收block
override def init(blockDataManager: BlockDataManager): Unit = {
// 创建实际负责处理请求的rpcHandler
val rpcHandler = new NettyBlockRpcServer(conf.getAppId, serializer, blockDataManager)
var serverBootstrap: Option[TransportServerBootstrap] = None
var clientBootstrap: Option[TransportClientBootstrap] = None
// 如果需要认证,则在实际初始化TransportServer和TransportClientFactory之前需要执行bootstrap方法
if (authEnabled) {
serverBootstrap = Some(new SaslServerBootstrap(transportConf, securityManager))
clientBootstrap = Some(new SaslClientBootstrap(transportConf, conf.getAppId, securityManager,
securityManager.isSaslEncryptionEnabled()))
}
transportContext = new TransportContext(transportConf, rpcHandler)
clientFactory = transportContext.createClientFactory(clientBootstrap.toSeq.asJava)
server = createServer(serverBootstrap.toList)
appId = conf.getAppId
logInfo(s"Server created on ${hostName}:${server.getPort}")
}
- 从其他Executor获取数据块
override def fetchBlocks(
host: String,
port: Int,
execId: String,
blockIds: Array[String],
listener: BlockFetchingListener): Unit = {
logTrace(s"Fetch blocks from $host:$port (executor id $execId)")
try {
// 调用shuffle包中的方法从远端获取数据
val blockFetchStarter = new RetryingBlockFetcher.BlockFetchStarter {
override def createAndStart(blockIds: Array[String], listener: BlockFetchingListener) {
val client = clientFactory.createClient(host, port)
new OneForOneBlockFetcher(client, appId, execId, blockIds.toArray, listener).start()
}
}
val maxRetries = transportConf.maxIORetries()
if (maxRetries > 0) {
// Note this Fetcher will correctly handle maxRetries == 0; we avoid it just in case there's
// a bug in this code. We should remove the if statement once we're sure of the stability.
new RetryingBlockFetcher(transportConf, blockFetchStarter, blockIds, listener).start()
} else {
blockFetchStarter.createAndStart(blockIds, listener)
}
} catch {
case e: Exception =>
logError("Exception while beginning fetchBlocks", e)
blockIds.foreach(listener.onBlockFetchFailure(_, e))
}
}
- 响应其他Executor的请求,将数据块返回给请求的Executor
override def uploadBlock(
hostname: String,
port: Int,
execId: String,
blockId: BlockId,
blockData: ManagedBuffer,
level: StorageLevel,
classTag: ClassTag[_]): Future[Unit] = {
val result = Promise[Unit]()
val client = clientFactory.createClient(hostname, port)
// StorageLevel and ClassTag are serialized as bytes using our JavaSerializer.
// Everything else is encoded using our binary protocol.
val metadata = JavaUtils.bufferToArray(serializer.newInstance().serialize((level, classTag)))
// Convert or copy nio buffer into array in order to serialize it.
val array = JavaUtils.bufferToArray(blockData.nioByteBuffer())
client.sendRpc(new UploadBlock(appId, execId, blockId.toString, metadata, array).toByteBuffer,
new RpcResponseCallback {
override def onSuccess(response: ByteBuffer): Unit = {
logTrace(s"Successfully uploaded block $blockId")
result.success((): Unit)
}
override def onFailure(e: Throwable): Unit = {
logError(s"Error while uploading block $blockId", e)
result.failure(e)
}
})
result.future
}
- NettyBlockRpcServer
// TODO
BlockInfoManager
BlockInfoManager主要维护了BlockManager所管理的所有数据块元数据以及对申请数据块读写的任务提供数据块读写锁。Spark中的数据块除了实际存储数据的Block之外,还有两个数据结构,BlockId和BlockInfo分别用来为数据块提供全局唯一的标记,以及记录数据块的元数据。
BlockId
BlockId用来全局标示一个数据块,对于存储在文件中的数据块,文件名通常就是BlockId的name。针对不同类型的数据块(如Shuffle Block,Broadcast Block,TaskResult Block等),都有特定的BlockId与之对应。不同类型的BlockId区别是他们的name前缀不一样。
BlockInfo
BlockInfo主要用来保存数据块的元数据信息,如数据块大小,当前数据块被加读锁的次数,数据块当前是否被某个任务持有写锁。
源码分析
- BlockInfoManager维护的数据结构
/**
* blockId -> blockInfo维护blockId和block元数据的映射关系
* 添加和删除infos中数据需要首先获取写锁
*/
@GuardedBy("this")
private[this] val infos = new mutable.HashMap[BlockId, BlockInfo]
/**
* taskAttemptId -> blockIds
* 记录任务已经获取到写锁的数据块
*/
@GuardedBy("this")
private[this] val writeLocksByTask =
new mutable.HashMap[TaskAttemptId, mutable.Set[BlockId]]
with mutable.MultiMap[TaskAttemptId, BlockId]
/**
* taskAttempId -> blockIds
* 记录任务已经获取到读锁的数据块集合,维护了每个数据块已经被锁的次数(这里的读锁是可重入的)
*/
@GuardedBy("this")
private[this] val readLocksByTask =
new mutable.HashMap[TaskAttemptId, ConcurrentHashMultiset[BlockId]]
- 获取数据块写锁
/**
*
* 获取一个块的写锁,并返回块的元数据
*
* 如果另一个任务已经获取了块的读锁或写锁,则当前任务需要阻塞直到锁被释放,或如果配置了blocking=false
* 则立刻返回
*/
def lockForWriting(
blockId: BlockId,
blocking: Boolean = true): Option[BlockInfo] = synchronized {
logTrace(s"Task $currentTaskAttemptId trying to acquire write lock for $blockId")
do {
infos.get(blockId) match {
case None => return None
case Some(info) =>
// 块上没有写锁,也没有读锁
if (info.writerTask == BlockInfo.NO_WRITER && info.readerCount == 0) {
// 获取当前数据块的写锁
info.writerTask = currentTaskAttemptId
// 将数据块加入当前任务所持有的写锁的数据块集合
writeLocksByTask.addBinding(currentTaskAttemptId, blockId)
logTrace(s"Task $currentTaskAttemptId acquired write lock for $blockId")
return Some(info)
}
}
// 如果是阻塞调用,则一直等待直到成功获取写锁
if (blocking) {
wait()
}
} while (blocking)
None
}
- 获取数据块读锁
/**
* 获取一个数据块的读锁并返回数据块元数据
*
* 如果另外的任务已经获取了数据块的读锁,则读锁会直接返回给当前调用的任务,并将读锁的引用+1
*
* 如果另外的任务已经获取了数据块的写锁,则当前调用的任务会被阻塞直到写锁被释放,或者如果配置了
* blocking=false,则立刻返回
*
* 一个任务可以多次获取数据块的读锁,每次获取的读锁需要单独释放
*/
def lockForReading(
blockId: BlockId,
blocking: Boolean = true): Option[BlockInfo] = synchronized {
logTrace(s"Task $currentTaskAttemptId trying to acquire read lock for $blockId")
do {
infos.get(blockId) match {
case None => return None
case Some(info) =>
// 如果当前数据块没有写锁,则将数据块读锁引用+1,将当前数据块添加到当前任务所持有读锁的数据块集合
if (info.writerTask == BlockInfo.NO_WRITER) {
info.readerCount += 1
readLocksByTask(currentTaskAttemptId).add(blockId)
logTrace(s"Task $currentTaskAttemptId acquired read lock for $blockId")
return Some(info)
}
}
// 到这里说明当前数据块有写锁,如果blocking=true,则阻塞一直到成功获取读锁
if (blocking) {
wait()
}
} while (blocking)
None
}
- 释放所持有的数据块的锁
/**
* 释放数据块上的锁
*/
def unlock(blockId: BlockId): Unit = synchronized {
logTrace(s"Task $currentTaskAttemptId releasing lock for $blockId")
val info = get(blockId).getOrElse {
throw new IllegalStateException(s"Block $blockId not found")
}
// 释放任务持有的写锁
if (info.writerTask != BlockInfo.NO_WRITER) {
// 将数据块上的写锁释放
info.writerTask = BlockInfo.NO_WRITER
// 将数据块移出当前任务所持有写锁的数据块集合
writeLocksByTask.removeBinding(currentTaskAttemptId, blockId)
} else {
// 释放读锁
assert(info.readerCount > 0, s"Block $blockId is not locked for reading")
// 将数据块上读锁的引用-1
info.readerCount -= 1
// 将数据块从当前任务所持有读锁的数据块列表中移出一个
val countsForTask = readLocksByTask(currentTaskAttemptId)
val newPinCountForTask: Int = countsForTask.remove(blockId, 1) - 1
assert(newPinCountForTask >= 0,
s"Task $currentTaskAttemptId release lock on block $blockId more times than it acquired it")
}
notifyAll()
}
MemoryStore
MemoryStore用来将数据块以序列化/非序列化的形式保存到内存中,以及从内存中获取数据块。当内存空间不足时,MemoryStore会将内存中的数据块迁移到磁盘中。
具体见 Spark内存管理
DiskStore
DiskStore用来将数据块存储到磁盘上,以及从磁盘上获取数据块。如果数据块的存储级别配置了磁盘,则当内存不足时,Spark会将数据块从内存移动到磁盘上。
在新建DiskStore时,会传入DiskBlockManager实例,DiskBlockManager主要用来创建和维护逻辑数据块和磁盘实际存储的物理位置的映射关系。
源码分析
- 将数据块保存到磁盘
/**
* 向磁盘写入数据块
* 首先通过diskManager获取到数据块存放到磁盘的路径,然后通过调用传入的writeFunc方法将数据块写入磁盘
*/
def put(blockId: BlockId)(writeFunc: FileOutputStream => Unit): Unit = {
if (contains(blockId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(s"Block $blockId is already present in the disk store")
}
logDebug(s"Attempting to put block $blockId")
val startTime = System.currentTimeMillis
val file = diskManager.getFile(blockId)
val fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file)
var threwException: Boolean = true
try {
writeFunc(fileOutputStream)
threwException = false
} finally {
try {
Closeables.close(fileOutputStream, threwException)
} finally {
if (threwException) {
remove(blockId)
}
}
}
val finishTime = System.currentTimeMillis
logDebug("Block %s stored as %s file on disk in %d ms".format(
file.getName,
Utils.bytesToString(file.length()),
finishTime - startTime))
}
- 从磁盘获取数据块
def getBytes(blockId: BlockId): ChunkedByteBuffer = {
val file = diskManager.getFile(blockId.name)
val channel = new RandomAccessFile(file, "r").getChannel
Utils.tryWithSafeFinally {
// 判断文件大小是否小于minMemoryMapBytes(启用mmap的最小文件大小,默认是2m)。如果低于minMemoryMapBytes
// 文件将直接通过NIO读取,否则将通过内存映射方式读取
// 一般来说,对于接近或低于操作系统页大小的文件进行内存映射会有较高的开销,所以此处对小文件的读取进行了优化
if (file.length < minMemoryMapBytes) {
val buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(file.length.toInt)
channel.position(0)
while (buf.remaining() != 0) {
if (channel.read(buf) == -1) {
throw new IOException("Reached EOF before filling buffer
" +
s"offset=0
file=${file.getAbsolutePath}
buf.remaining=${buf.remaining}")
}
}
buf.flip()
new ChunkedByteBuffer(buf)
} else {
new ChunkedByteBuffer(channel.map(MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, file.length))
}
} {
channel.close()
}
}
DiskBlockManager
DiskBlockManager用来创建并维护逻辑数据块和磁盘实际存储的物理位置的映射关系。数据块会被保存到以BlockId为名字的文件中。数据块文件会被hash到spark.local.dir所配置的目录。