20135328陈都信息安全系统设计基础第十二周学习总结
标签(空格分隔):20135328陈都
第十二周(11.23-11.29):
一、学习目标
- 掌握进程控制
- 掌握信号处理的方法
- 掌握管道和fifo进行进程间通信的方法
二、学习资源
编译、运行、阅读、理解process.tar.gz压缩包中的代码
exec1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
char *arglist[3];
arglist[0] = "ls";
arglist[1] = "-l";
arglist[2] = 0 ;//NULL
printf("* * * About to exec ls -l
");
execvp( "ls" , arglist );,
printf("* * * ls is done. bye");
return 0;
}
exec3
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
char *arglist[3];
char*myenv[3];
myenv[0] = "PATH=:/bin:";
myenv[1] = NULL;
arglist[0] = "ls";
arglist[1] = "-l";
arglist[2] = 0 ;
printf("* * * About to exec ls -l
");
execlp("ls", "ls", "-l", NULL);
printf("* * * ls is done. bye
");
}
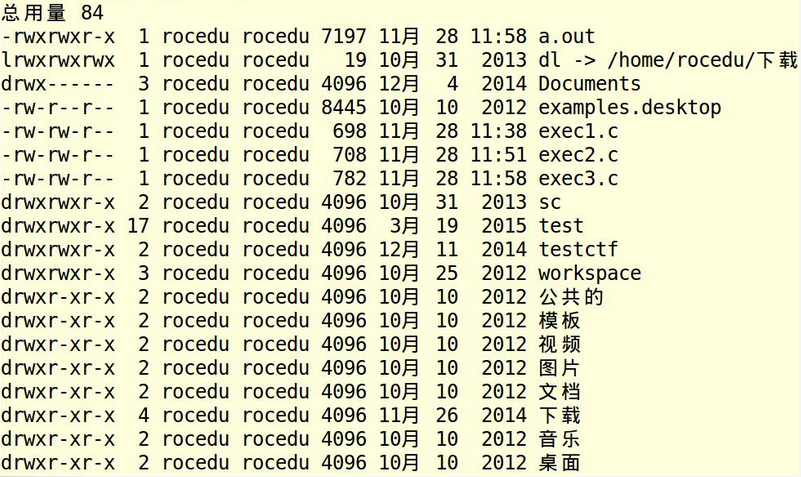
forkdemo1
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main()
{
int ret_from_fork, mypid;
mypid = getpid();
printf("Before: my pid is %d
", mypid);
ret_from_fork = fork();
sleep(1);
printf("After: my pid is %d, fork() said %d
",
getpid(), ret_from_fork);
return 0;
}
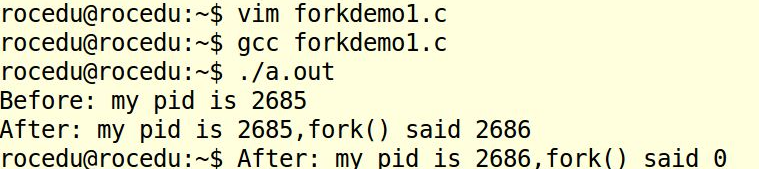
forkdemo2
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
printf("before:my pid is %d
", getpid() );
fork();
fork();
printf("aftre:my pid is %d
", getpid() );
return 0;
}
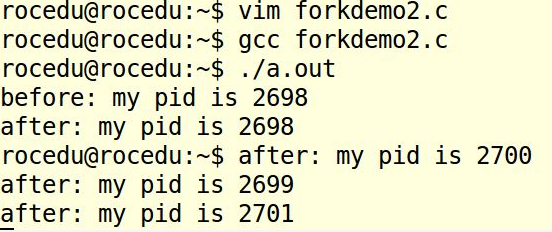
forkdemo3
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
int fork_rv;
printf("Before: my pid is %d
", getpid());
fork_rv = fork(); /* create new process */
if ( fork_rv == -1 ) /* check for error */
perror("fork");
else if ( fork_rv == 0 ){
printf("I am the child. my pid=%d
", getpid());
exit(0);
}
else{
printf("I am the parent. my child is %d
", fork_rv);
exit(0);
}
return 0;
}

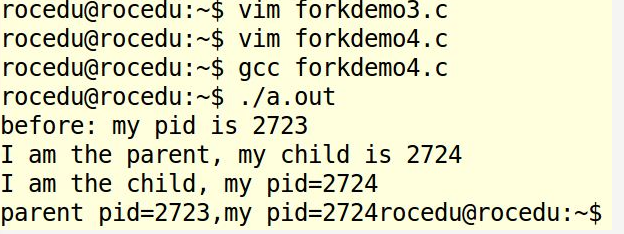
forkdemo4
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
int fork_rv;
printf("Before: my pid is %d
", getpid());
fork_rv = fork(); /* create new process */
if ( fork_rv == -1 ) /* check for error */
perror("fork");
else if ( fork_rv == 0 ){
printf("I am the child. my pid=%d
", getpid());
printf("parent pid= %d, my pid=%d
", getppid(), getpid());
exit(0);
}
else{
printf("I am the parent. my child is %d
", fork_rv);
sleep(10);
exit(0);
}
return 0;
}
。
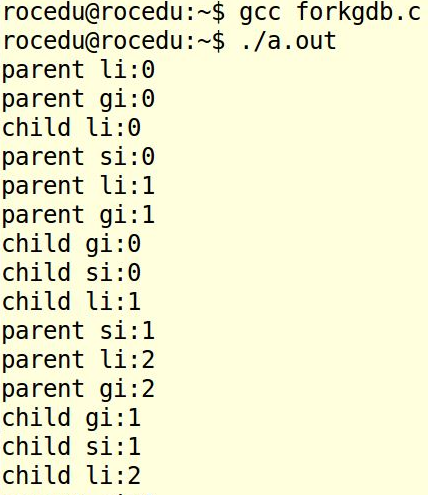
forkgdb
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int gi=0;
int main()
{
int li=0;
static int si=0;
int i=0;
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid == -1){
exit(-1);
}
else if(pid == 0){
for(i=0; i<5; i++){
printf("child li:%d
", li++);
sleep(1);
printf("child gi:%d
", gi++);
printf("child si:%d
", si++);
}
exit(0);
}
else{
for(i=0; i<5; i++){
printf("parent li:%d
", li++);
printf("parent gi:%d
", gi++);
sleep(1);
printf("parent si:%d
", si++);
}
exit(0);
}
return 0;
}
psh1
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define MAXARGS 20
#define ARGLEN 100
int execute( char *arglist[] )
{
execvp(arglist[0], arglist);
perror("execvp failed");
exit(1);
}
char * makestring( char *buf )
{
char *cp;
buf[strlen(buf)-1] = '�';
cp = malloc( strlen(buf)+1 );
if ( cp == NULL ){
fprintf(stderr,"no memory
");
exit(1);
}
strcpy(cp, buf);
return cp;
}
int main()
{
char *arglist[MAXARGS+1];
int numargs;
char argbuf[ARGLEN];
numargs = 0;
while ( numargs < MAXARGS )
{
printf("Arg[%d]? ", numargs);
if ( fgets(argbuf, ARGLEN, stdin) && *argbuf != '
' )
arglist[numargs++] = makestring(argbuf);
else
{
if ( numargs > 0 ){
arglist[numargs]=NULL;
execute( arglist );
numargs = 0;
}
}
}
return 0;
}

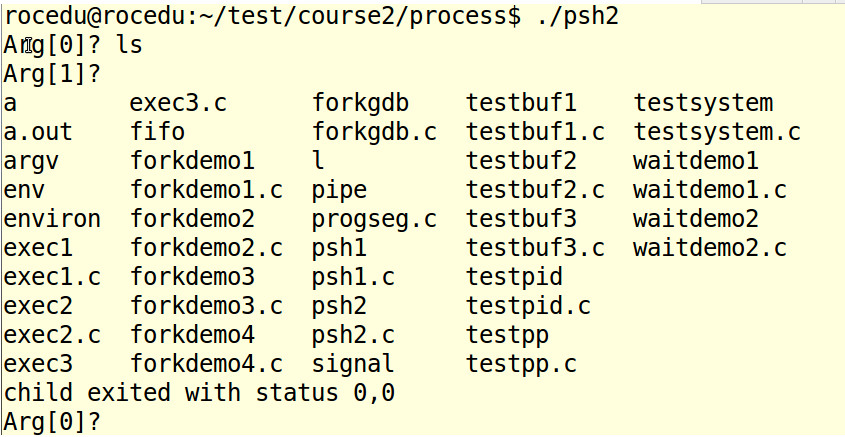
psh2
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#define MAXARGS 20
#define ARGLEN 100
char *makestring( char *buf )
{
char *cp;
buf[strlen(buf)-1] = '�';
cp = malloc( strlen(buf)+1 );
if ( cp == NULL ){
fprintf(stderr,"no memory
");
exit(1);
}
strcpy(cp, buf);
return cp;
}
void execute( char *arglist[] )
{
int pid,exitstatus;
pid = fork();
switch( pid ){
case -1:
perror("fork failed");
exit(1);
case 0:
execvp(arglist[0], arglist);
perror("execvp failed");
exit(1);
default:
while( wait(&exitstatus) != pid )
;
printf("child exited with status %d,%d
",
exitstatus>>8, exitstatus&0377);
}
}
int main()
{
char *arglist[MAXARGS+1];
int numargs;
char argbuf[ARGLEN];
numargs = 0;
while ( numargs < MAXARGS )
{
printf("Arg[%d]? ", numargs);
if ( fgets(argbuf, ARGLEN, stdin) && *argbuf != '
' )
arglist[numargs++] = makestring(argbuf);
else
{
if ( numargs > 0 ){
arglist[numargs]=NULL;
execute( arglist );
numargs = 0;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
testbuf1
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
printf("hello");
fflush(stdout);
while(1);
}
效果是先输出hello,然后换行。之后不退出。

testbuf2
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("hello
");
while(1);
}
程序输出hello,无法退出。

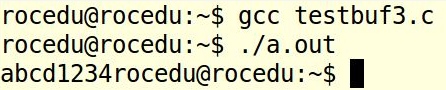
testbuf3
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
fprintf(stdout, "1234", 5);
fprintf(stderr, "abcd", 4);
}
将内容格式化输出到标准错误、输出流中。结果如图:
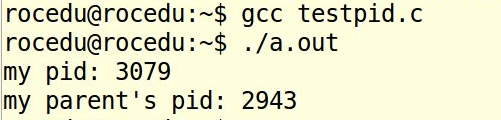
testpid
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int main()
{
printf("my pid: %d
", getpid());
printf("my parent's pid: %d
", getppid());
return 0;
}
输出当前进程pid和当前进程的父进程的pid。
testpp
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
char **pp;
pp[0] = malloc(20);
return 0;
}

testsystem
代码如下:
#include <stdlib.h>
int main ( int argc, char *argv[] )
{
system(argv[1]);
system(argv[2]);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
} /* --------
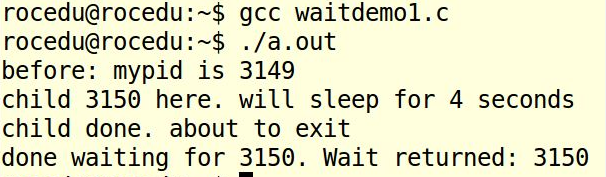
waitdemo1
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define DELAY 4
void child_code(int delay)
{
printf("child %d here. will sleep for %d seconds
", getpid(), delay);
sleep(delay);
printf("child done. about to exit
");
exit(17);
}
void parent_code(int childpid)
{
int wait_rv=0; /* return value from wait() */
wait_rv = wait(NULL);
printf("done waiting for %d. Wait returned: %d
",
childpid, wait_rv);
}
int main()
{
int newpid;
printf("before: mypid is %d
", getpid());
if ( (newpid = fork()) == -1 )
perror("fork");
else if ( newpid == 0 )
child_code(DELAY);
else
parent_code(newpid);
return 0;
}
如果有子进程,则终止子进程,成功返回子进程pid。
waitdemo2
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define DELAY 10
void child_code(int delay)
{
printf("child %d here. will sleep for %d seconds
", getpid(), delay);
sleep(delay);
printf("child done. about to exit
");
exit(27);
}
void parent_code(int childpid)
{
int wait_rv;
int child_status;
int high_8, low_7, bit_7;
wait_rv = wait(&child_status);
printf("done waiting for %d. Wait returned: %d
", childpid, wait_rv);
high_8 = child_status >> 8; /* 1111 1111 0000 0000 */
low_7 = child_status & 0x7F; /* 0000 0000 0111 1111 */
bit_7 = child_status & 0x80; /* 0000 0000 1000 0000 */
printf("status: exit=%d, sig=%d, core=%d
", high_8, low_7, bit_7);
}
int main()
{
int newpid;
printf("before: mypid is %d
", getpid());
if ( (newpid = fork()) == -1 )
perror("fork");
else if ( newpid == 0 )
child_code(DELAY);
else
parent_code(newpid);
}

。
参考资料
- 《进程间通信-命名管道FIFO》(http://blog.csdn.net/xiajun07061225/article/details/8471777)
- 《linux i/o重定向与管道编程》
(http://blog.csdn.net/fulianzhou/article/details/48895327) - 教材:第八章,详细学习指导:http://group.cnblogs.com/topic/73069.html
- 闫佳歆同学的博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/20135202yjx/p/5003653.html