一、实现生产者消费者模型
1.使用sychronized和wait notify实现
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { AtomicInteger a=new AtomicInteger(5);//原子类整型 final int MAX_SIZE=10;//最大长度 Thread pro = new Thread(new Runnable() {//消费者线程 @Override public void run() { while(true){ synchronized (a){ while(a.get()==0){ try { a.wait();//注意是锁住对象的wait 不能直接wait } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"消费"+a.get()); a.getAndDecrement();//消费者消费 a.notifyAll();//注意是锁住对象的notify } } } }, "消费者"); Thread cus = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { while (true){ synchronized (a) { while(a.get()==MAX_SIZE){ try { a.wait();//锁住对象 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } a.getAndIncrement();//生产者生产 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"生产"+a.get()); a.notifyAll();//锁住对象 } } } }, "生产者"); pro.start(); cus.start(); }
2.lock和condition实现
public static void main(String[] args) { ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();//锁 Condition empty = lock.newCondition();//空情况 Condition full = lock.newCondition();//满情况 AtomicInteger num=new AtomicInteger(5); Thread cus = new Thread(new Runnable() {//消费者 @Override public void run() { while (true) { lock.lock();//要在try块外 上锁(确定一定上锁 try里上锁 遇到异常跳出就不会锁住了) try { while (num.get() == 0) { empty.await();//此时为空 空情况等待 } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "消费了" + num); num.getAndDecrement(); full.signal();//此时已经消费了1个 所以把通知满情况等待的线程 } catch (InterruptedException e) { } finally { lock.unlock();//要在finally里 解锁 } } } }, "消费者"); Thread pro=new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { while (true) { lock.lock(); try { while (num.get() == 10) { full.await();//此时已满 满情况等待 } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "生产了" + num); num.getAndIncrement(); empty.signal();//生产了一个 通知空情况等待的线程 } catch (InterruptedException e) { } finally { lock.unlock(); } } } },"生产者"); cus.start(); pro.start(); }
3.阻塞队列
public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer>(10);//阻塞队列 容量为10 Thread cus=new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { while (true){ try { Integer take = blockingQueue.take();//拿走阻塞队列的数据 System.out.println("消费者 拿走了"+take); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } },"消费者"); Thread pro=new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { while (true){ Random random = new Random(); int tmp=random.nextInt(10); blockingQueue.offer(tmp);//提供数据 System.out.println("生产者生产了 +"+tmp); } } },"生产者"); pro.start(); cus.start(); }
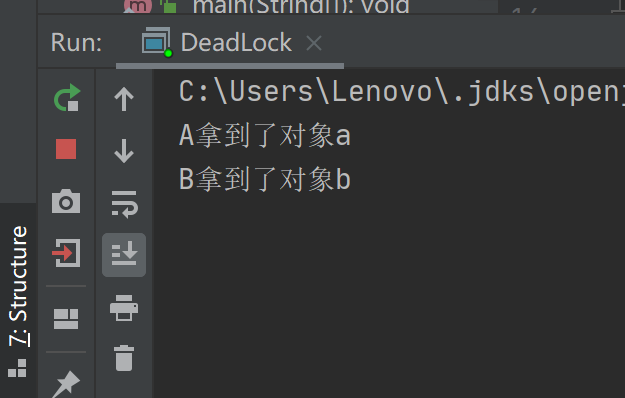
二、写一个死锁的例子
public static void main(String[] args) { Object a=new Object(); Object b = new Object(); Thread A = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { synchronized (a) { try { Thread.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "拿到了对象a"); synchronized (b) { System.out.println("死锁 无法进入到这里"); } } } }, "A"); Thread B = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { synchronized (b) { try { Thread.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "拿到了对象b"); synchronized (a) { System.out.println("发生了死锁 无法进入这里"); } } } }, "B"); A.start(); B.start(); }
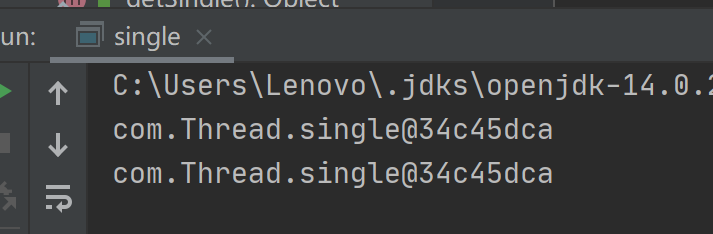
三、双检锁单例模式
public class single { static volatile single instance;//使用volatile保证 public static Object getSingle(){ if(instance==null){ synchronized (single.class){//锁类而不是锁对象 if(instance==null){ instance=new single(); } } } return instance; } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(getSingle());//测试1 System.out.println(getSingle());//测试2 } }
为什么使用volatile?或者不加volatile会出现什么问题?
当线程A在初始化instance,执行new single()方法时。线程B访问到了一个未实例化完整的instance 但是也是不为空 就会将不完整的返回。
原理:实例化对象三步骤:1内存开辟空间 2实例化对象 3指向内存空间。
由于2 3没有依赖关系 所以会被JMM重排序为 1 3 2。这时候instance是不完整的。
四、三个线程交替打印ABC
public class abc { static int count=0;//利用count来计数 和3取余 0=A 1=B 2=C public static void main(String[] args) { ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();//可重入锁 Condition Acon = lock.newCondition();//等待/通知A Condition Bcon = lock.newCondition();//等待/通知B Condition Ccon = lock.newCondition();//等待/通知C Thread A = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { while (true){//如果要改成 输出10次 将这里的while改为for 10次就行 lock.lock(); try { while(count%3!=0) Acon.await();//当前取余值不为0 等待唤醒 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": A"); count++; Bcon.signal();//唤醒B 该B执行了打印了 } catch (Exception e) { } finally { lock.unlock(); } } } }, "1"); Thread B = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { while (true){ lock.lock(); try { while(count%3!=1) Bcon.await(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": B"); count++; Ccon.signal(); } catch (Exception e) { } finally { lock.unlock(); } } } }, "2"); Thread C = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { while (true){ lock.lock(); try { while(count%3!=2) Ccon.await(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": C"); count++; Acon.signal(); } catch (Exception e) { } finally { lock.unlock(); } } } }, "3"); A.start(); B.start(); C.start(); } }
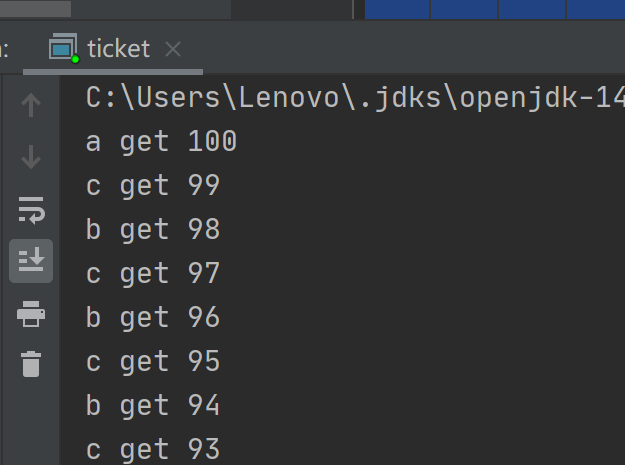
五、多服务器抢票
/** * @Description: * @Author: cckong * @Date: */ public class ticket { private static int ticket=100; static Object server=new Object(); static Runnable runnable = new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { synchronized (server){ while (ticket>0){ server.notifyAll(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" get "+ticket); ticket--; try { server.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }; public static void main(String[] args) { new Thread(runnable,"a").start(); new Thread(runnable,"b").start(); new Thread(runnable,"c").start(); } }