先声明:Statement在本文中简写为stmt PreparedStatement简写为psmt
在进行批量更新的时候 我吹爆addbatch
不是好用 是真好用啊
数据库的处理速度是非常惊人的 单次吞吐量很大 执行效率极高
addBatch()把若干sql语句装载到一起,然后一次送到数据库执行,执行需要很短的时间
而executeUpdate() 是一条一条发往数据库执行的 时间都消耗在数据库连接的传输上面
返回一个数组:
包含批中每个命令的一个元素的更新计数所组成的数组(数组中的每个元素为:成功处理了命令后,执行命令所影响数据库中行数的更新计数)。数组的元素根据将命令添加到批中的顺序排序
{ public static void main(String[] args) { ResultSet rs = null; Statement stmt = null; Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement pstm=null; try { //1.注册驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); //2.建立连接 conn = (Connection) DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=FALSE" ,"root",""); //3.处理结果集 // stmt = conn.createStatement(); // rs = stmt.executeQuery("select * from tablename1"); // // // while (rs.next()) { // int age = rs.getInt("age"); // //// 输出查到的记录的各个字段的值 // System.out.println( " " + age); // } //预编译语句 // String sql="select * from tablename1 where age = ?"; // pstm=conn.prepareStatement(sql); // pstm.setInt(1,21); // rs=pstm.executeQuery(); // while (rs.next()) { // int age = rs.getInt("age"); // //// 输出查到的记录的各个字段的值 // System.out.println( " " + age); // } //addbatch方法 执行一组sql语句 String sql1="insert into tablename1(age) values(30)"; String sql2="insert into tablename1(age) values(32)"; String sql3="insert into tablename1(age) values(34)"; stmt = conn.createStatement(); stmt.addBatch(sql1); stmt.addBatch(sql2); stmt.addBatch(sql3); //执行命令所影响数据库中行数的更新计数 int[] upRowS=stmt.executeBatch(); for(int tmp:upRowS) System.out.println(tmp); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { //4.关闭资源 if (rs != null) { rs.close(); rs = null; } if (stmt != null) { stmt.close(); stmt = null; } if (conn != null) { conn.close(); conn = null; } } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }

(看过上一篇的应该看到我刚才数据库里age只有一个21的值 执行过后有四个。

在刚才的程序上我们用的stmt 在psmt里面有点不同
psmt里面重写了addBatch方法 取消了里面的参数
分享一波失败案例(不能每次都新建pstm 这样不就和stmt一样了吗 自己蠢了。。。)
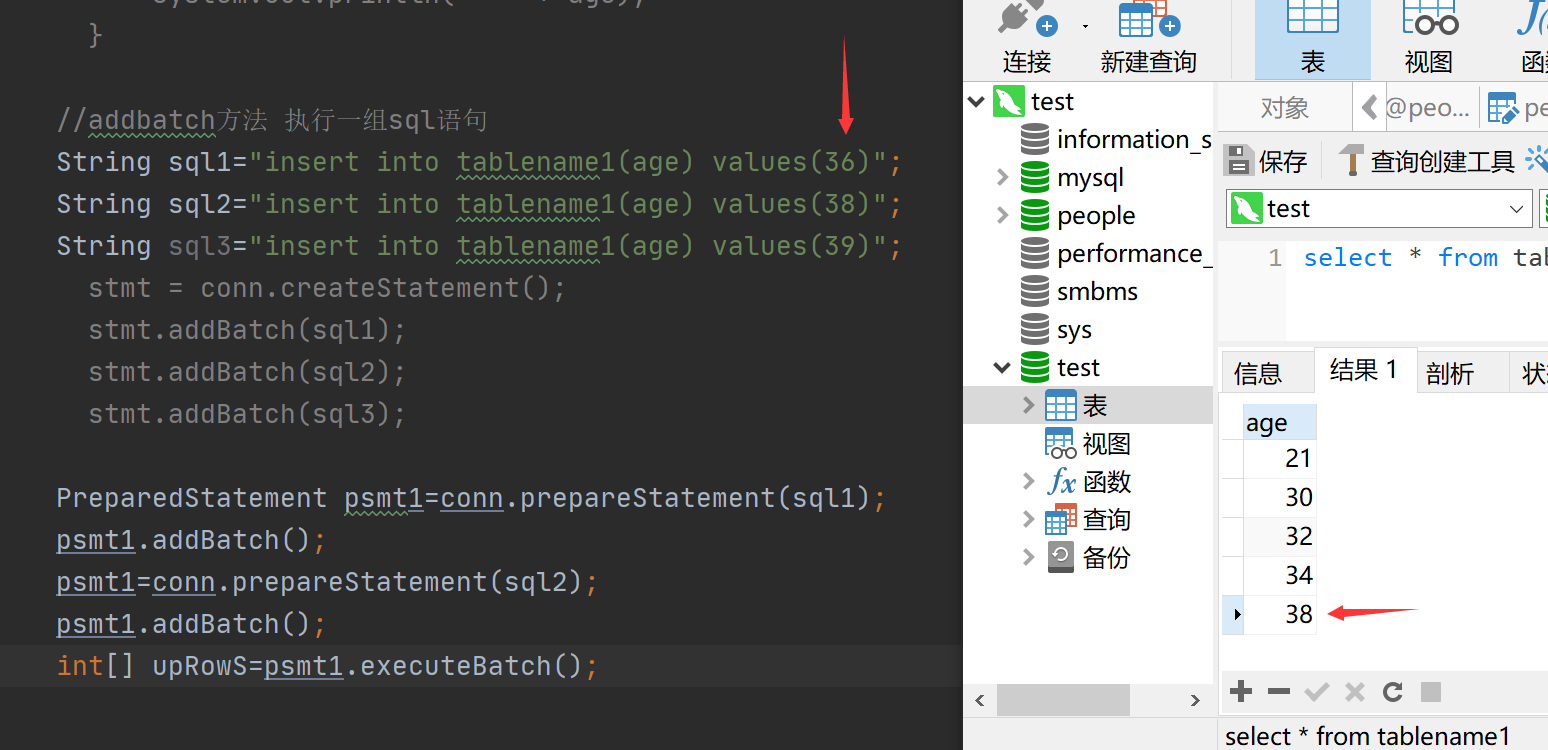
成功案例:每次赋值一次 就addBatch一次
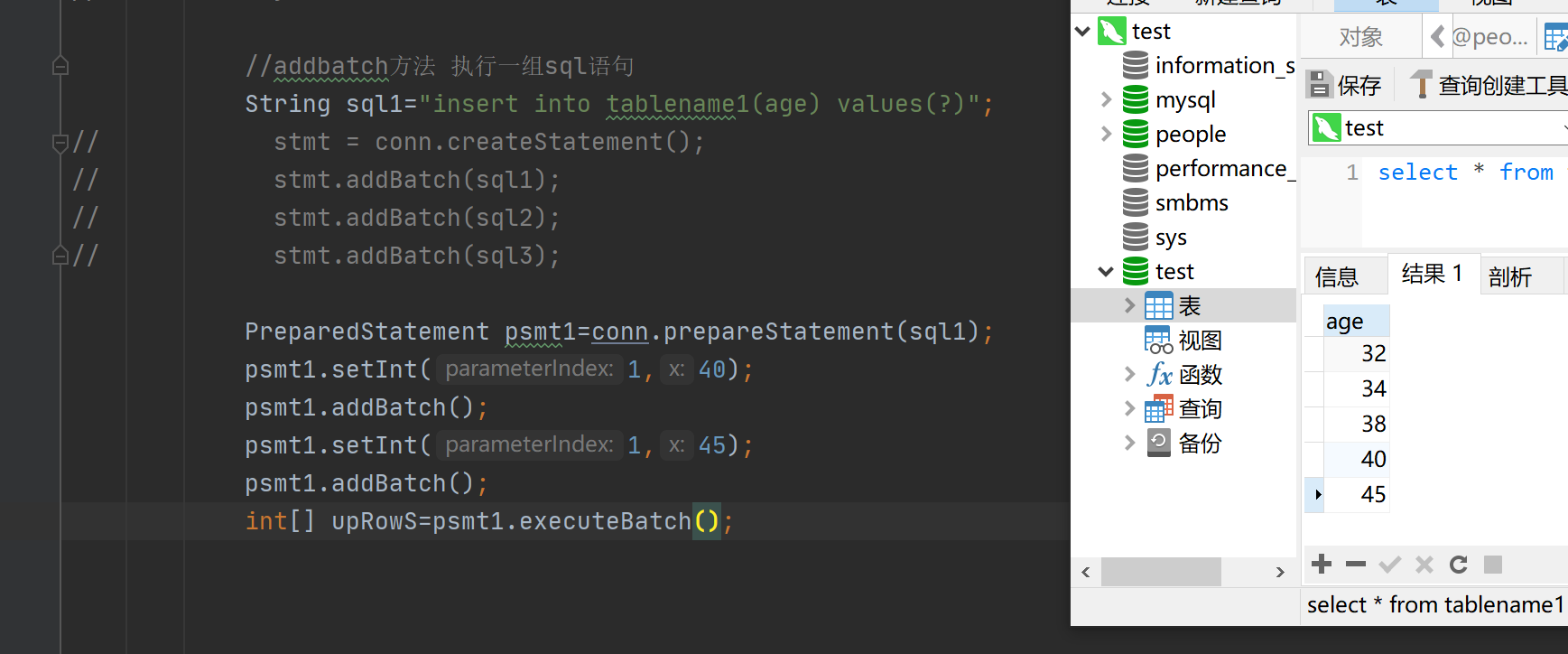
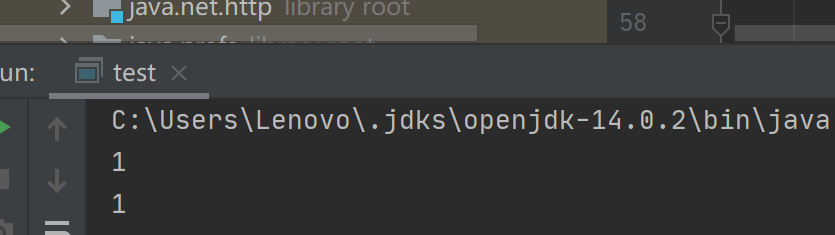
upRows也正常显示了
关键代码如下:
//addbatch方法 执行一组sql语句 String sql1="insert into tablename1(age) values(?)"; // stmt = conn.createStatement(); // stmt.addBatch(sql1); // stmt.addBatch(sql2); // stmt.addBatch(sql3); PreparedStatement psmt1=conn.prepareStatement(sql1); psmt1.setInt(1,40); psmt1.addBatch(); psmt1.setInt(1,45); psmt1.addBatch(); int[] upRowS=psmt1.executeBatch(); //执行命令所影响数据库中行数的更新计数 // int[] upRowS=stmt.executeBatch(); for(int tmp:upRowS) System.out.println(tmp);