1. 读取数据集
def load_data(filename,dataType): return np.loadtxt(filename,delimiter=",",dtype = dataType) def read_data(): data = load_data("data2.txt",np.float64) X = data[:,0:-1] y = data[:,-1] return X,y
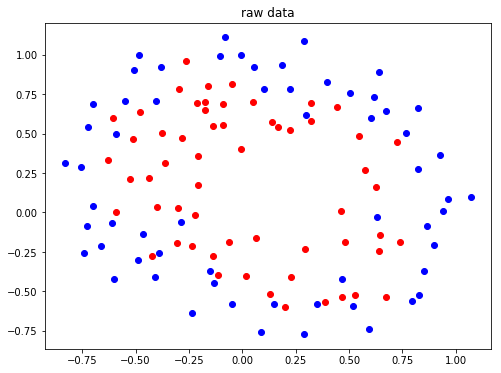
2. 查看原始数据的分布
def plot_data(x,y): pos = np.where(y==1) # 找到标签为1的位置 neg = np.where(y==0) #找到标签为0的位置 plt.figure(figsize=(8,6)) plt.plot(x[pos,0],x[pos,1],'ro') plt.plot(x[neg,0],x[neg,1],'bo') plt.title("raw data") plt.show() X,y = read_data() plot_data(X,y)
结果:
3. 将数据映射为多项式
由原图数据分布可知,数据的分布是非线性的,这里将数据变为多项式的形式,使其变得可分类。
映射为二次方的形式: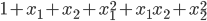
def mapFeature(x1,x2): degree = 2; #映射的最高次方 out = np.ones((x1.shape[0],1)) # 映射后的结果数组(取代X) for i in np.arange(1,degree+1): for j in range(i+1): temp = x1 ** (i-j) * (x2**j) out = np.hstack((out,temp.reshape(-1,1))) return out
4. 定义交叉熵损失函数
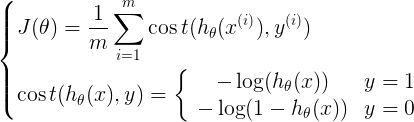
可以综合起来为: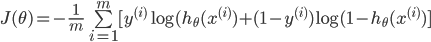
其中: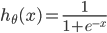
为了防止过拟合,加入正则化技术: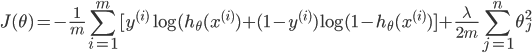
注意j是重1开始的,因为theta(0)为一个常数项,X中最前面一列会加上1列1,所以乘积还是theta(0),feature没有关系,没有必要正则化
def sigmoid(x): return 1.0 / (1.0+np.exp(-x)) def CrossEntropy_loss(initial_theta,X,y,inital_lambda): #定义交叉熵损失函数 m = len(y) h = sigmoid(np.dot(X,initial_theta)) theta1 = initial_theta.copy() # 因为正则化j=1从1开始,不包含0,所以复制一份,前theta(0)值为0 theta1[0] = 0 temp = np.dot(np.transpose(theta1),theta1) loss = (-np.dot(np.transpose(y),np.log(h)) - np.dot(np.transpose(1-y),np.log(1-h)) + temp*inital_lambda/2) / m return loss
5. 计算梯度
对上述的交叉熵损失函数求偏导:
利用梯度下降法进行优化:
def gradientDescent(initial_theta,X,y,initial_lambda,lr,num_iters): m = len(y) theta1 = initial_theta.copy() theta1[0] = 0 J_history = np.zeros((num_iters,1)) for i in range(num_iters): h = sigmoid(np.dot(X,theta1)) grad = np.dot(np.transpose(X),h-y)/m + initial_lambda * theta1/m theta1 = theta1 - lr*grad #print(theta1) J_history[i] = CrossEntropy_loss(theta1,X,y,initial_lambda) return theta1,J_history
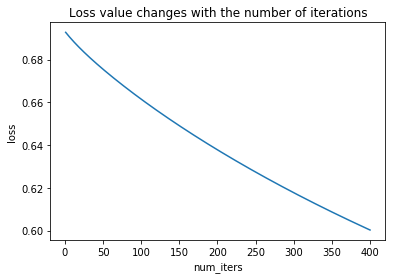
6. 绘制损失值随迭代次数的变化曲线
def plotLoss(J_history,num_iters):
x = np.arange(1,num_iters+1)
plt.plot(x,J_history)
plt.xlabel("num_iters")
plt.ylabel("loss")
plt.title("Loss value changes with the number of iterations")
plt.show()
7. 绘制决策边界
def plotDecisionBoundary(theta,x,y): pos = np.where(y==1) #找到标签为1的位置 neg = np.where(y==0) #找到标签为2的位置 plt.figure(figsize=(8,6)) plt.plot(x[pos,0],x[pos,1],'ro') plt.plot(x[neg,0],x[neg,1],'bo') plt.title("Decision Boundary") #生成和原数据类似的数据 u = np.linspace(-1,1.5,50) v = np.linspace(-1,1.5,50) z = np.zeros((len(u),len(v))) #利用训练好的参数做预测 for i in range(len(u)): for j in range(len(v)): z[i,j] = np.dot(mapFeature(u[i].reshape(1,-1),v[j].reshape(1,-1)),theta) z = np.transpose(z) plt.contour(u,v,z,[0,0.01],linewidth=2.0) # 画等高线,范围在[0,0.01],即近似为决策边界 plt.legend() plt.show()
8.主函数
if __name__ == "__main__": #数据的加载 x,y = read_data() X = mapFeature(x[:,0],x[:,1]) Y = y.reshape((-1,1)) #参数的初始化 num_iters = 400 lr = 0.1 initial_theta = np.zeros((X.shape[1],1)) #初始化参数theta initial_lambda = 0.1 #初始化正则化系数 #迭代优化 theta,loss = gradientDescent(initial_theta,X,Y,initial_lambda,lr,num_iters) plotLoss(loss,num_iters) plotDecisionBoundary(theta,x,y)
9.结果