Fox Ciel is playing a mobile puzzle game called "Two Dots". The basic levels are played on a board of size n × m cells, like this:
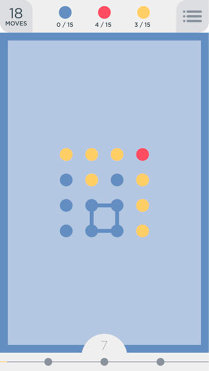
Each cell contains a dot that has some color. We will use different uppercase Latin characters to express different colors.
The key of this game is to find a cycle that contain dots of same color. Consider 4 blue dots on the picture forming a circle as an example. Formally, we call a sequence of dots d1, d2, ..., dk a cycle if and only if it meets the following condition:
- These k dots are different: if i ≠ j then di is different from dj.
- k is at least 4.
- All dots belong to the same color.
- For all 1 ≤ i ≤ k - 1: di and di + 1 are adjacent. Also, dk and d1 should also be adjacent. Cells x and y are called adjacent if they share an edge.
Determine if there exists a cycle on the field.
The first line contains two integers n and m (2 ≤ n, m ≤ 50): the number of rows and columns of the board.
Then n lines follow, each line contains a string consisting of m characters, expressing colors of dots in each line. Each character is an uppercase Latin letter.
Output "Yes" if there exists a cycle, and "No" otherwise.
3 4
AAAA
ABCA
AAAA
Yes
3 4
AAAA
ABCA
AADA
No
4 4
YYYR
BYBY
BBBY
BBBY
Yes
7 6
AAAAAB
ABBBAB
ABAAAB
ABABBB
ABAAAB
ABBBAB
AAAAAB
Yes
2 13
ABCDEFGHIJKLM
NOPQRSTUVWXYZ
No
In first sample test all 'A' form a cycle.
In second sample there is no such cycle.
The third sample is displayed on the picture above ('Y' = Yellow, 'B' = Blue, 'R' = Red).
题意:找同一种颜色的环
这题麻烦的地方在于走过的路被标记了,那怎么判断有环呢?
其实记录步数就可以了,bfs和dfs道理是一样的
bfs做法:
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define ll long long struct node { int x,y; }; bool v[55][55]; int book[55][55]; char a[55][55]; int d[4][2]={{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}}; queue<node>q; int main() { int n,m; cin>>n>>m; memset(v,0,sizeof(v)); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) { cin>>a[i][j]; } } bool f=0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) { if(!v[i][j]) { memset(book,0,sizeof(book)); v[i][j]=1; while(!q.empty()) q.pop(); node b; b.x=i; b.y=j; book[i][j]=1; q.push(b); while(!q.empty()) { node b=q.front(); q.pop(); for(int k=0;k<4;k++) { int xx=b.x+d[k][0]; int yy=b.y+d[k][1]; if(xx<1||yy<1||xx>n||yy>m||a[xx][yy]!=a[i][j]) continue; v[xx][yy]=1; node c; c.x=xx; c.y=yy; if(book[xx][yy]>=book[b.x][b.y])//如果当前走过去格子有步数且的步数比当前这个格子还要大,说明已经走过了,形成了环。 { f=1;break; } if(book[xx][yy])continue; q.push(c); book[xx][yy]=book[b.x][b.y]+1;//保存路的步数 } if(f) break; } if(f) break; } if(f) break; } if(f) break; } if(f) cout<<"Yes"; else cout<<"No"; return 0; }
dfs也是同样道理:
#include<iostream> #include<string> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<cstdio> using namespace std; char a[55][55]; bool book[55][55]; int v[55][55]; int z[55]; int n,m; int d[4][2]={{-1,0},{1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}}; bool f=0; int si,sj; void dfs(char c,int x,int y) { for(int i=0;i<4;i++) { int xx=x+d[i][0]; int yy=y+d[i][1]; if(xx<1||yy<1||xx>n||yy>m) continue; if(v[xx][yy]!=0&&v[x][y]-v[xx][yy]>1)//走过去的格子已经有值了且比现在走的格子还大不止1,大1可能是之前走过来的 { f=1; return; } if(a[xx][yy]==c&&v[xx][yy]==0) { v[xx][yy]=v[x][y]+1; book[xx][yy]=1; dfs(c,xx,yy); if(f) return; v[xx][yy]=0; } } } int main() { scanf("%d %d",&n,&m); memset(z,0,sizeof(z)); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) { cin>>a[i][j]; } } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) { if(!book[i][j]) { z[a[i][j]-'A']=1; memset(v,0,sizeof(v)); book[i][j]=1; si=i; sj=j; v[i][j]=1; dfs(a[i][j],i,j); if(f) break; } } if(f) break; } if(f) cout<<"Yes"; else cout<<"No"; return 0; }