1.前言
习惯了spring注解风格,方便好用,现在用vert.x框架,怎么使用spring注解呢?
2.maven安装依赖包
<!--spring注解依赖包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.1.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
3.注册bean有两个方法:xml注册,注解注册
方法1:xml注册
新建一个xml配置文件

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!-- 默认单例,,加上scope="prototype"为多例--> <bean name="eatService" class="xue.myVertX.service.serviceImpl.EatServiceImpl" scope="prototype"/> </beans>
接口和他的实现类在springMVC里该怎么写还是怎么写,不变,这里旧省略了
使用方法:

package xue.myVertX; import io.vertx.core.AbstractVerticle; import io.vertx.core.Vertx; import io.vertx.core.http.HttpMethod; import io.vertx.core.http.HttpServer; import io.vertx.ext.web.Router; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import xue.myVertX.likeController.IndexHandle; import xue.myVertX.service.serviceImpl.EatServiceImpl; /** * 简单的路由使用 */ public class SimpleRouter extends AbstractVerticle { @Override public void start() throws Exception { //读取bean配置文件,注册所有bean,获取上下文对象 //方法1: //xml文件手动注册bean方法 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-context.xml"); // 创建HttpServer HttpServer server = vertx.createHttpServer(); // 创建路由对象 Router router = Router.router(vertx); // 监听/index地址 ,就像spring注解@RequestMapping注册虚拟路径,然后调用controller方法 router.route("/index").handler(new IndexHandle(context)); // 把请求交给路由处理--------------------(1) //旧版写法 server.requestHandler(router::accept); //新版写法,需要版本在4以上才可以 // server.requestHandler(router); server.listen(8080); } public static void main(String[] args) { Vertx.vertx().deployVerticle(new SimpleRouter()); } }

package xue.myVertX.likeController; import io.vertx.core.Handler; import io.vertx.ext.web.RoutingContext; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import xue.myVertX.service.EatService; import xue.myVertX.service.serviceImpl.EatServiceImpl; /** * 这个类就像spring注解controller, */ public class IndexHandle implements Handler<RoutingContext> { private EatService eatService; public IndexHandle(final ApplicationContext context) { //读取全局bean配置文件,实例bean对象 //方法1,配合xml手动注册,可不写注解 eatService = (EatService) context.getBean("eatService"); } @Override public void handle(RoutingContext routingContext) { // //获取参数,其实就是类似于request // String user = routingContext.request().getParam("user"); // String pass = routingContext.request().getParam("pass"); // routingContext.response() // .putHeader("Content-type", "text/html;charset=utf-8") // .end("接收到的用户名为:" + user + " 接收到的密码为:" + pass); // // String str =eatService.eatApply(); System.out.println("可以吃啥?"+str); routingContext.response().putHeader("Content-type", "text/html;charset=utf-8").end(str); } }
方法2:注解注册
在实现类添加注解

使用方法

package xue.myVertX; import io.vertx.core.AbstractVerticle; import io.vertx.core.Vertx; import io.vertx.core.http.HttpMethod; import io.vertx.core.http.HttpServer; import io.vertx.ext.web.Router; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import xue.myVertX.likeController.IndexHandle; import xue.myVertX.service.serviceImpl.EatServiceImpl; /** * 简单的路由使用 */ public class SimpleRouter extends AbstractVerticle { @Override public void start() throws Exception { //读取bean配置文件,注册所有bean,获取上下文对象 //方法1: //xml文件手动注册bean方法 // ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-context.xml"); // //方法2: //使用注解自动注册 ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(EatServiceImpl.class); // 创建HttpServer HttpServer server = vertx.createHttpServer(); // 创建路由对象 Router router = Router.router(vertx); // 监听/index地址 ,就像spring注解@RequestMapping注册虚拟路径,然后调用controller方法 router.route("/index").handler(new IndexHandle(context)); // 把请求交给路由处理--------------------(1) //旧版写法 server.requestHandler(router::accept); //新版写法,需要版本在4以上才可以 // server.requestHandler(router); server.listen(8080); } public static void main(String[] args) { Vertx.vertx().deployVerticle(new SimpleRouter()); } }

package xue.myVertX.likeController; import io.vertx.core.Handler; import io.vertx.ext.web.RoutingContext; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import xue.myVertX.service.EatService; import xue.myVertX.service.serviceImpl.EatServiceImpl; /** * 这个类就像spring注解controller, */ public class IndexHandle implements Handler<RoutingContext> { private EatService eatService; public IndexHandle(final ApplicationContext context) { //读取全局bean配置文件,实例bean对象 //方法1,配合xml手动注册,可不写注解 // eatService = (EatService) context.getBean("eatService"); //方法2,使用注解,需要在实现类加@Service才可以被调用,参数为实现类的名字 eatService = context.getBean(EatServiceImpl.class); } @Override public void handle(RoutingContext routingContext) { // //获取参数,其实就是类似于request // String user = routingContext.request().getParam("user"); // String pass = routingContext.request().getParam("pass"); // routingContext.response() // .putHeader("Content-type", "text/html;charset=utf-8") // .end("接收到的用户名为:" + user + " 接收到的密码为:" + pass); // // String str =eatService.eatApply(); System.out.println("可以吃啥?"+str); routingContext.response().putHeader("Content-type", "text/html;charset=utf-8").end(str); } }
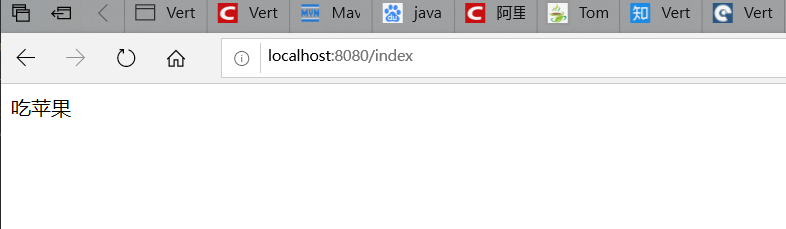
3.测试结果
网页
控制台打印

