目录:
- HashMap结构
- HashMap方法简述
HashMap结构
在Java7中我们可以更具HashMap的table属性及Entry内部类观察出,其底层是基于数组实现,并在发生Hash冲突的时候用链表解决,将相同hash值的key组层一个链表维护。
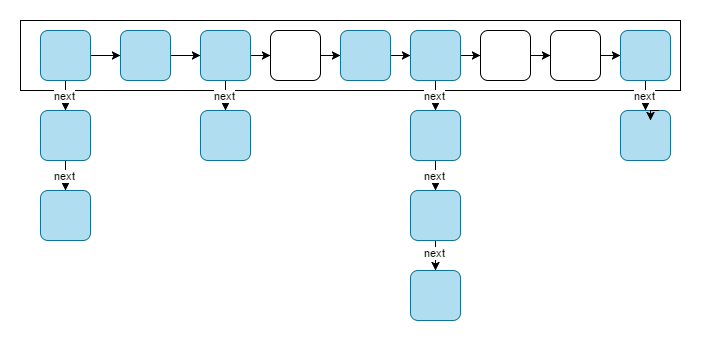
1 transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE; 2 3 static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { 4 final K key; 5 V value; 6 Entry<K,V> next; 7 int hash; 8 }
还有几个属性需要注意下:
- capacity:数组容量,始终保持2^n次倍,可以扩容,扩容后大小为当前数组的2倍。
- loadFactory:负载因子,默认为0.75。
- threshold:扩容阀值,等于capacity * loadFactory。
HashMap方法简述
java.util.HashMap#put:添加一个键值对到map中。
1 public V put(K key, V value) { 2 // 若数组为空,也就是添加第一个元素时,初始化数组容量 3 if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) { 4 inflateTable(threshold); 5 } 6 // 若key为null,则会把这个entry放到table[0]中 7 if (key == null) 8 return putForNullKey(value); 9 // 1、求key的hash值 10 int hash = hash(key); 11 // 2、找到对应的数组下标 12 int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); 13 // 3、遍历整个map的链表,若有重复的key值则覆盖 14 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { 15 Object k; 16 if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { 17 V oldValue = e.value; 18 e.value = value; 19 e.recordAccess(this); 20 return oldValue; 21 } 22 } 23 24 modCount++; 25 // 4、不存在的key值将次添加到链表中 26 addEntry(hash, key, value, i); 27 return null; 28 }
可以看到一个key value对添加到map中有很多个步骤,接下来我们一步步的分析。
1、inflateTable(threshold):初始化数组容量。
1 private void inflateTable(int toSize) { 2 // toSize从上层函数的threshold可以看出,其值默认为16,或者是你自己初始化的大小 3 // roundUpToPowerOf2会保证数组大小一定是2的n次方,假如你是new HashMap(20),那么capacity的值就位32 4 int capacity = roundUpToPowerOf2(toSize); 5 6 // 计算扩容阀值:capacity * loadFactor 7 threshold = (int) Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1); 8 table = new Entry[capacity]; 9 initHashSeedAsNeeded(capacity); 10 }
这里有一个保持数组容量为2^n的要求,同意的Java8 HashMap和ConcurrentHashMap也是这样,只不过实现略有不同而已。
那为什么要这么做呢,其实啊某些东西的特殊要求要么就是需要满足既定的条件才能实现,要么就是这样要求能更加快捷的达到目的;而我们这个就属于后者,这样写能提高HashMap计算数组下标的效率。
因为模运算(%)的效率不如位运算(&),而sun公司的大佬又发现了hash & (capacity - 1) == hash % capacity。所以就有了这一要求
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44933374/article/details/98469424
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
2、indexFor(hash, table.length):利用hash值计算数据放入的下标。
1 static int indexFor(int h, int length) { 2 // assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2"; 3 return h & (length-1); 4 }
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
3、addEntry(hash, key, value, i):添加节点到链表中。
1 void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { 2 // HashMap大小已到阀值,且当前数组位置也已经有元素了;所以要扩容了 3 if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) { 4 // 扩容 5 resize(2 * table.length); 6 // 扩容后重新计算hash值 7 hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0; 8 // 重新计算扩容后的下标 9 bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length); 10 } 11 12 // 将新值放入链表表头,然后增加HashMap大小 13 createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex); 14 } 15 16 void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { 17 Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex]; 18 table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e); 19 size++; 20 }
4、resize(2 * table.length):扩容。
1 void resize(int newCapacity) { 2 Entry[] oldTable = table; 3 int oldCapacity = oldTable.length; 4 if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { 5 threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; 6 return; 7 } 8 9 // 新的数组 10 Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity]; 11 // 将原来数组中的值迁到新的且更大的数组中 12 transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity)); 13 table = newTable; 14 threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1); 15 }
代码比较简单,不多讲。
java.util.HashMap#get:根据key获取value。
1 public V get(Object key) { 2 if (key == null) 3 return getForNullKey(); 4 Entry<K,V> entry = getEntry(key); 5 6 return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue(); 7 } 8 9 final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) { 10 if (size == 0) { 11 return null; 12 } 13 14 int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key); 15 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)]; 16 e != null; 17 e = e.next) { 18 Object k; 19 if (e.hash == hash && 20 ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 21 return e; 22 } 23 return null; 24 }
相对于put,get则更简单;根据key计算hash值,找到对应数组下标后遍历改数组的链表,直到找到==或equals的key。
虽然说不难,但想要看懂代码还是需要有链表基础的,哈哈。