Trie
In computer science, a trie, also called digital tree and sometimes radix tree or prefix tree (as they can be searched by prefixes), is an ordered tree data structure that is used to store a dynamic set or associative array where the keys are usually strings. Unlike a binary search tree, no node in the tree stores the key associated with that node; instead, its position in the tree defines the key with which it is associated. All the descendants of a node have a common prefix of the string associated with that node, and the root is associated with the empty string. Values are normally not associated with every node, only with leaves and some inner nodes that correspond to keys of interest.
 .
. 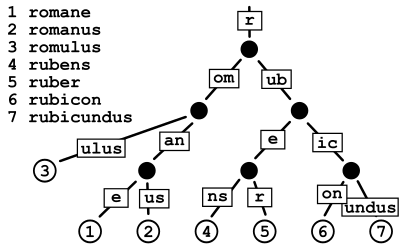
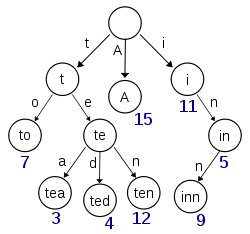
A trie for keys "A", "to", "tea", "ted", "ten", "i", "in", and "inn" An example of a radix tree
Radix Tree
In computer science, a radix tree (also patricia trie, radix trieor compact prefix tree) is a data structure that represents a space-optimized trie in which each node with only one child is merged with its parent.
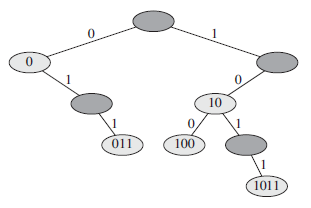
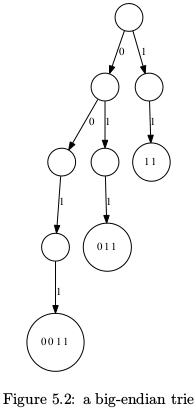
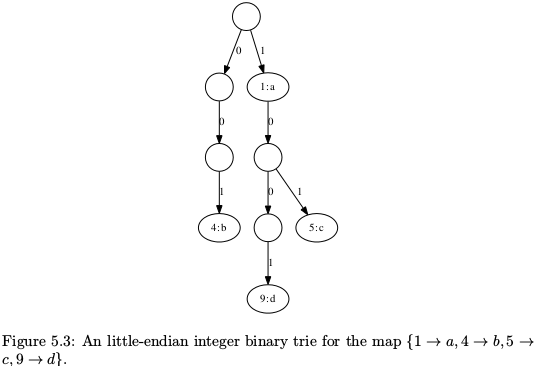

Integer Trie
Trie树可以存储位串(stirngs of bits),因为整数可以用二进制表示,故Trie树可以存储整数.如Figure 5.2所示,串0011,011,11表示不同的位串,但却表示同一个整数3,这就是问题所在!解决方法就是使用小端整数(右边的权重高),这样3是(11)2,2是(01)2.
python实现Figure 5.3:

#!/usr/bin/python #-*- coding:utf-8 -*- class Node: def __init__(self): self.left = self.right = None self.value = None def TrieInsert(t, key,value = None): if t is None: t = Node() p = t while key != 0: if key & 1==0: if p.left is None: p.left = Node() p = p.left else: if p.right is None: p.right = Node() p = p.right key =key>>1 p.value = value return t def Lookup(t,key): while key != 0 and (t is not None): if key & 1 == 0: t = t.left else: t = t.right key = key>>1 if t is not None: return t.value else: return None def main(): t = Node() TrieInsert(t, 1, 'a') TrieInsert(t, 4 ,'b') TrieInsert(t, 5, 'c') TrieInsert(t, 9, 'd') print Lookup(t,9) if __name__ == "__main__": main()
Integer Patricia(practical algorithm)
Figure5.3比较浪费空间,一种改进的办法是路径压缩--将没有对应关键字的结点压缩到一起.如Figure 5.4(暂时搞不懂,以后再补充吧)
Alphabetic Trie
Trie树也可以存储字符串.

#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> typedef struct Node{ struct Node* children[26]; int* data; }Node; Node* create_node(){ Node* t = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)); int i; for(i=0;i<26;i++){ t->children[i] = NULL; } t->data = NULL; return t; } Node* insert(Node* t, const char* key, int* value){ int c; Node* p; if(!t){ t = create_node(); } for(p = t; *key; ++key, p = p->children[c] ){ c = *key - 'a'; if(!p->children[c]){ p->children[c] = create_node(); } } p->data = value; return t; } int* lookup(Node* t, const char* key){ while(*key && t && t->children[*key-'a']){ t = t->children[*key++ - 'a']; } return (*key || !t) ? NULL: t->data; } int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { Node *t = create_node(); char* ch[3]= {"we","hello","were"}; int v[3] ={1,2,3}; int i; for(i=0;i<3;i++){ insert(t, ch[i],v+i); } printf("%d ", *lookup(t, ch[1]) ); return 0; }
Alphabetic Partricia
