更确切的说,是用存储过程对比myisam和innodb的写入效率;
1,创建两张表
create table testmyisam( id int unsigned primary key auto_increment, `name` varchar(20) not null )engine=myisam; create table testinnodb( id int unsigned primary key auto_increment, `name` varchar(20) not null )engine=innodb;
2,分别创建存储过程
drop procedure if exists ptestmyisam; delimiter ;; create procedure ptestmyisam() begin declare pid int ; set pid = 1000000; while pid>0 do insert into testmyisam(name) values(concat("fuzhu", pid)); set pid = pid-1; end while; end ;; delimiter ; drop procedure if exists ptestInndb; delimiter ;; create procedure ptestInndb() begin declare pid int ; set pid = 1000000; while pid>0 do insert into testinnodb(name) values(concat("fuzhu", pid)); set pid = pid-1; end while; end ;; delimiter ;
3,分别调用
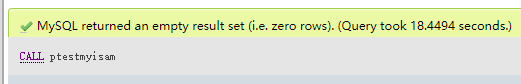
call ptestmyisam();
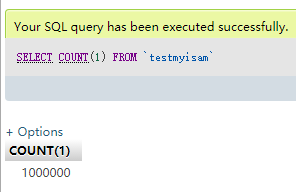
结果:
call ptestInndb();
结果:
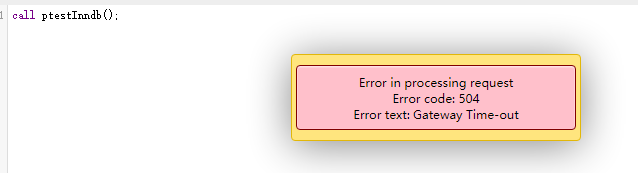
执行大约三十秒后,页面报错。。。。
但是执行
SHOW PROCESSLIST

会发现该存储过程仍在继续执行。。。
SELECT COUNT(1) FROM `testinnodb`
也能发现数据仍在增加,三十秒提示504时,数据库大约插入了2万条。。
即便是把innodb的autocommit设置为0,执行结果也差不多。。