201871010106-丁宣元 《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十一周学习总结
正文开头:
|
项目 |
内容 |
|
这个作业属于哪个课程 |
https://home.cnblogs.com/u/nwnu-daizh/ |
|
这个作业的要求在哪里 |
https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p/11815810.html |
|
作业学习目标 |
(1) 理解泛型概念; (2) 掌握泛型类的定义与使用; (3) 了解泛型方法的声明与使用; (4) 掌握泛型接口的定义与实现; (5) 理解泛型程序设计,理解其用途。 |
正文内容:
第一部分:总结第八章理论知识
8.1泛型程序设计(JDK 5.0 中增加,是Java 语言中类型安全的改进)
1.泛型:也称参数化类型,即在定义类、接口和方法时,通过类型参数指示将要处理的对象类型。eg:ArrayList类
2.泛型程序设计(Generic programming):编写的代码可以被多个不同类型的对象所重用。
类型参数的优点:改善程序的可读性,增强类型的使用安全性
3.泛型类的定义:格式:class Generics<K,V> (K,V是类的可变类型参数)
eg:public class Pair<T>
注:Pair类引入了一个类型变量T,用<>括起来,置于类名后面;
可以有多个类型变量,用,隔开
类定义中的类型变量用于指定方法的返回类型以及域、局部变量的类型。
4.泛型方法
(1)泛型方法:可以只单独定义一个方法作为泛型方法,用于指定方法参数或者返回值为泛型类型,留待方法调用时确定。
(2)可以声明在泛型类中,也可以声明在普通类中。
eg:public class ArrayTool
{
public static<E> void insert(E[] e,int i){...}
public static<E> valueAt(E[] e,int i){...}
}
5.泛型接口
(1)定义:public interface IPool<T>
{
T get();
int add(T t);
}
(2)实现:public class GenericPool<T> implements IPool<T>{...}
public class GenericPool implements IPool<Account>{...}
6.泛型变量的限定
(1)定义上界:public class NumberGeneric<T extends Number>
注:说明NumberGeneric类能处理的泛型变量需要和Number有继承关系
extends所申明的上界可以是一个类,也可以是一个接口
<T extends Bounding Type>表示T应是绑定类型的子类型
一个类型变量或通配符可以有多个限定,限定类型用&分割
eg:<T extends Comparable &Serializable>
(2)定义下界:List<? super CashCard>cards=new ArrayList<T>
注:super可以固定泛型参数的类型为某类型的超类
若一个方法的参数为限定类型时,可以使用下限通配符
eg:public static <T> void sort(T[] A,Comparator<? super T> c){...}
7.泛型类的约束与局限性(*):
a.不能用基本类型实例化类型参数
b.运行时类型查询只适用于原始类型
c.不能抛出也不能捕获泛型类实例
d.参数化类型的数组不合法
e.不能实例化类型变量
f.泛型类的静态上下文中类型变量无效
g.注意擦除后的冲突
8.泛型类型的继承规则(*)
(1)数组是协变的(covariant),但不适用于泛型类型
原因:避免破坏要提供类型的安全泛型
(2)泛型类不具协变性。
(3)泛型类可扩展或实现其它的泛型类。
8-2通配符
1.通配符类型
(1)“?”表明参数的类型可以是任何一种类型
( 2)三种用法:
单独的 ?,用于表示任何类型
? extends type,表示带有上界。
? super type,表示带有下界。
(3)通配符的类型限定
a)Pair<? extends Employee>
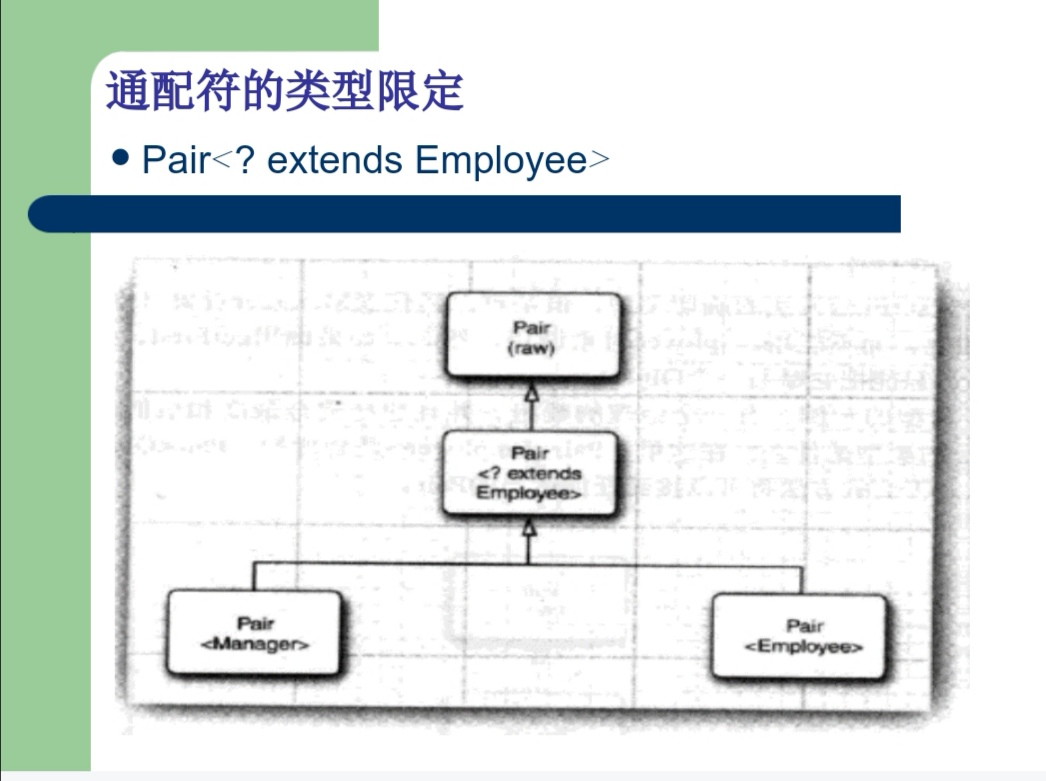
b) Pair<? super Manager>
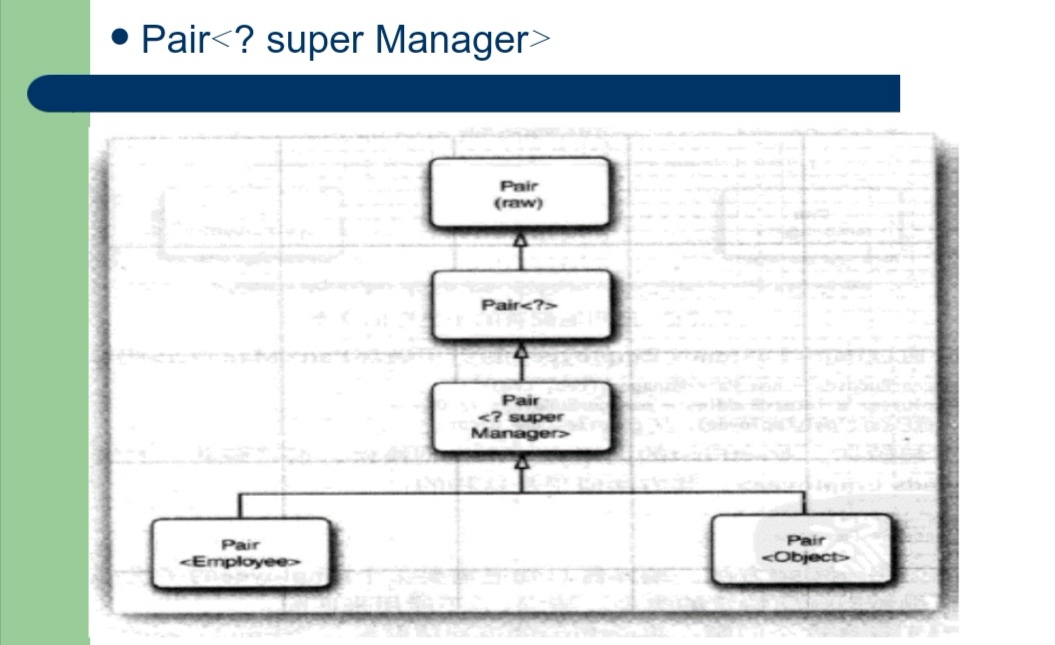
c) 无限定通配符:Pair<?>。
注:Pair<?>与Pair的不同:可以用任意Object 对象调用原始的Pair类的setObject方法。
8-3 泛型程序设计小结
1.定义泛型类时,在<>内定义形式类型参数,即<>内为类型
2.实例化泛型对象时,要在类名后指定类型参数的值(类型)
3.extents表示类型范围限制,不表示继承
4.泛型类不是协变的
第二部分:实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第8章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
编辑、调试、运行教材311、312页代码,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
在泛型类定义及使用代码处添加注释;
掌握泛型类的定义及使用。
代码:PairTest1.java
package pair1; /** * @version 1.01 2012-01-26 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class PairTest1 { public static void main(String[] args) { String[] words = { "Mary", "had", "a", "little", "lamb" };//字符串数组 Pair<String> mm = ArrayAlg.minmax(words);//用具体的类型替换类型变量 可以实例化泛型类型。创建Pair<String>类对象mm,通过类名ArrayAlg来调用minmax方法 System.out.println("min = " + mm.getFirst()); System.out.println("max = " + mm.getSecond()); } } class ArrayAlg//与类Pair是依赖关系 { /** * Gets the minimum and maximum of an array of strings. * @param a an array of strings * @return a pair with the min and max values, or null if a is null or empty */ public static Pair<String> minmax(String[] a) { if (a == null || a.length == 0) return null;//a==null空引用 String min = a[0]; String max = a[0]; for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) { if (min.compareTo(a[i]) > 0) min = a[i]; if (max.compareTo(a[i]) < 0) max = a[i]; } return new Pair<>(min, max); } }
Pair.java
package pair1; /** * @version 1.00 2004-05-10 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class Pair<T> //Pair类引入了一个类型变量T { private T first;//类定义中的类型变量指定方法的返回类型及域和局部变量的类型 private T second; public Pair() { first = null; second = null; } public Pair(T first, T second) { this.first = first; this.second = second; } public T getFirst() { return first; } public T getSecond() { return second; } public void setFirst(T newValue) { first = newValue; } public void setSecond(T newValue) { second = newValue; } }
结果:
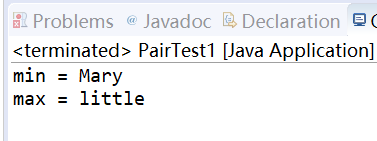
测试程序2:
编辑、调试运行教材315页 PairTest2,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
在泛型程序设计代码处添加相关注释;
了解泛型方法、泛型变量限定的定义及用途。
代码:PairTest2.java
package pair2; import java.time.*; /** * @version 1.02 2015-06-21 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class PairTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) { LocalDate[] birthdays = { LocalDate.of(1906, 12, 9), // G. Hopper LocalDate.of(1815, 12, 10), // A. Lovelace LocalDate.of(1903, 12, 3), // J. von Neumann LocalDate.of(1910, 6, 22), // K. Zuse }; Pair<LocalDate> mm = ArrayAlg.minmax(birthdays); System.out.println("min = " + mm.getFirst()); System.out.println("max = " + mm.getSecond()); } } class ArrayAlg { /** Gets the minimum and maximum of an array of objects of type T. @param a an array of objects of type T @return a pair with the min and max values, or null if a is null or empty */ public static <T extends Comparable> Pair<T> minmax(T[] a) //将T限制为实现了Comparable接口的类 { if (a == null || a.length == 0) return null; T min = a[0]; T max = a[0]; for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) { if (min.compareTo(a[i]) > 0) min = a[i]; if (max.compareTo(a[i]) < 0) max = a[i]; } return new Pair<>(min, max); } }
Pair.java
package pair2;
/**
* @version 1.00 2004-05-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Pair<T> //Pair类引入了一个类型变量T
{
private T first;
private T second;
public Pair() { first = null; second = null; }
public Pair(T first, T second) { this.first = first; this.second = second; }
public T getFirst() { return first; }
public T getSecond() { return second; }
public void setFirst(T newValue) { first = newValue; }
public void setSecond(T newValue) { second = newValue; }
}
结果:

测试程序3:
用调试运行教材335页 PairTest3,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
了解通配符类型的定义及用途。
代码:
Empolyee.java
package pair3; import java.time.*; public class Employee { private String name; private double salary; private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { this.name = name; this.salary = salary; hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public LocalDate getHireDay() { return hireDay; } public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) { double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; salary += raise; } }
Manager.java
package pair3; public class Manager extends Employee { private double bonus; /** @param name the employee's name @param salary the salary @param year the hire year @param month the hire month @param day the hire day */ public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { super(name, salary, year, month, day); bonus = 0; } public double getSalary() { double baseSalary = super.getSalary(); return baseSalary + bonus; } public void setBonus(double b) { bonus = b; } public double getBonus() { return bonus; } }
Pair.java
package pair3; /** * @version 1.00 2004-05-10 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class Pair<T> //Pair类引入了一个类型变量T { private T first; private T second; public Pair() { first = null; second = null; } public Pair(T first, T second) { this.first = first; this.second = second; } public T getFirst() { return first; } public T getSecond() { return second; } public void setFirst(T newValue) { first = newValue; } public void setSecond(T newValue) { second = newValue; } }
PariTest3.java
package pair3; /** * @version 1.01 2012-01-26 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class PairTest3 { public static void main(String[] args) { var ceo = new Manager("Gus Greedy", 800000, 2003, 12, 15); var cfo = new Manager("Sid Sneaky", 600000, 2003, 12, 15); var buddies = new Pair<Manager>(ceo, cfo); printBuddies(buddies); ceo.setBonus(1000000); cfo.setBonus(500000); Manager[] managers = { ceo, cfo }; var result = new Pair<Employee>(); minmaxBonus(managers, result); System.out.println("first: " + result.getFirst().getName() + ", second: " + result.getSecond().getName()); maxminBonus(managers, result); System.out.println("first: " + result.getFirst().getName() + ", second: " + result.getSecond().getName()); } public static void printBuddies(Pair<? extends Employee> p)//通配符类型,带有上界,extends关键字声明的上界既可以是一个类,也可以是一个接口 { Employee first = p.getFirst(); Employee second = p.getSecond(); System.out.println(first.getName() + " and " + second.getName() + " are buddies."); } public static void minmaxBonus(Manager[] a, Pair<? super Manager> result)//通配符类型,带有下界,必须是Manager的子类 { if (a.length == 0) return; Manager min = a[0]; Manager max = a[0]; for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) { if (min.getBonus() > a[i].getBonus()) min = a[i]; if (max.getBonus() < a[i].getBonus()) max = a[i]; } result.setFirst(min); result.setSecond(max); } public static void maxminBonus(Manager[] a, Pair<? super Manager> result)//通配符类型 { minmaxBonus(a, result); PairAlg.swapHelper(result); // OK--swapHelper captures wildcard type 用swapHelper捕获通配符类型 } // can't write public static <T super manager> . . . } class PairAlg { public static boolean hasNulls(Pair<?> p)//将hasNulls转换成泛型方法,来避免使用通配符类型 { return p.getFirst() == null || p.getSecond() == null; } public static void swap(Pair<?> p) { swapHelper(p); }//在交换时临时保存第一个元素,辅助方法swapHelper(泛型方法) public static <T> void swapHelper(Pair<T> p) { T t = p.getFirst(); p.setFirst(p.getSecond()); p.setSecond(t); } }
结果:

实验2:结对编程练习,将程序提交到PTA(2019面向对象程序设计基础知识测试题(2))
(1) 编写一个泛型接口GeneralStack,要求类中方法对任何引用类型数据都适用。GeneralStack接口中方法如下:
push(item); //如item为null,则不入栈直接返回null。
pop(); //出栈,如为栈为空,则返回null。
peek(); //获得栈顶元素,如为空,则返回null.
public boolean empty();//如为空返回true
public int size(); //返回栈中元素数量
(2)定义GeneralStack的子类ArrayListGeneralStack,要求:
ü 类内使用ArrayList对象存储堆栈数据,名为list;
ü 方法: public String toString()//代码为return list.toString();
ü 代码中不要出现类型不安全的强制转换。
(3)定义Car类,类的属性有:
private int id;
private String name;
方法:Eclipse自动生成setter/getter,toString方法。
(4)main方法要求
ü 输入选项,有quit, Integer, Double, Car 4个选项。如果输入quit,程序直接退出。否则,输入整数m与n。m代表入栈个数,n代表出栈个数。然后声明栈变量stack。
ü 输入Integer,打印Integer Test。建立可以存放Integer类型的ArrayListGeneralStack。入栈m次,出栈n次。打印栈的toString方法。最后将栈中剩余元素出栈并累加输出。
ü 输入Double ,打印Double Test。剩下的与输入Integer一样。
ü 输入Car,打印Car Test。其他操作与Integer、Double基本一样。只不过最后将栈中元素出栈,并将其name依次输出。
特别注意:如果栈为空,继续出栈,返回null
输入样例
Integer 5 2 1 2 3 4 5 Double 5 3 1.1 2.0 4.9 5.7 7.2 Car 3 2 1 Ford 2 Cherry 3 BYD quit
输出样例
Integer Test push:1 push:2 push:3 push:4 push:5 pop:5 pop:4 [1, 2, 3] sum=6 interface GeneralStack Double Test push:1.1 push:2.0 push:4.9 push:5.7 push:7.2 pop:7.2 pop:5.7 pop:4.9 [1.1, 2.0] sum=3.1 interface GeneralStack Car Test push:Car [id=1, name=Ford] push:Car [id=2, name=Cherry] push:Car [id=3, name=BYD] pop:Car [id=3, name=BYD] pop:Car [id=2, name=Cherry] [Car [id=1, name=Ford]] Ford interface GeneralStack
代码:
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Scanner; interface GeneralStack<T> { public T push(T item); //若item为null,则不入栈直接返回null。 public T pop(); //出栈,如为栈为空,则返回null。 public T peek(); //获得栈顶元素,如为空,则返回null. public boolean empty(); //如为空返回true public int size(); //返回栈中元素数量 } class ArrayListGeneralStack implements GeneralStack{ //泛型接口GeneralStack ArrayList list=new ArrayList(); @Override public String toString() { return list.toString(); } @Override public Object push(Object item) {//入栈 if (list.add(item)){ return item; }else { return false; } } @Override public Object pop() {//出栈 if (list.size()==0){ return null; } return list.remove(list.size()-1); } @Override public Object peek() { //取栈顶元素 return list.get(list.size()-1); } @Override public boolean empty() { if (list.size()==0){ return true; }else { return false; } } @Override public int size() { return list.size(); } } class Car{ //Car类 private int id; private String name; @Override public String toString() { return "Car [" + "id=" + id +", name=" + name +']'; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Car(int id, String name) { this.id = id; this.name = name; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { @SuppressWarnings("resource") Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); while (true){ String a=in.nextLine(); if (a.equals("Integer"))//为Integer { //System.out.println(""); int count=in.nextInt(); int pop_time=in.nextInt(); System.out.println("Integer Test"); ArrayListGeneralStack arrayListGeneralStack = new ArrayListGeneralStack(); for (int i=0;i<count;i++){ System.out.println("push:"+arrayListGeneralStack.push(in.nextInt())); } for (int i=0;i<pop_time;i++){ System.out.println("pop:"+arrayListGeneralStack.pop()); } System.out.println(arrayListGeneralStack.toString()); int size=arrayListGeneralStack.size(); int sum=0; for (int i=0;i<size;i++){ sum=sum+(int)(arrayListGeneralStack.pop()); } System.out.println("sum="+sum); System.out.println("interface GeneralStack"); }else if(a.equals("Double"))//为Double { System.out.println("Double Test"); int count=in.nextInt(); int pop_time=in.nextInt(); ArrayListGeneralStack arrayListGeneralStack = new ArrayListGeneralStack(); for (int i=0;i<count;i++) { System.out.println("push:"+arrayListGeneralStack.push(in.nextDouble())); } for (int i=0;i<pop_time;i++) { System.out.println("pop:"+arrayListGeneralStack.pop()); } System.out.println(arrayListGeneralStack.toString()); int size=arrayListGeneralStack.size(); double sum=0; for (int i=0;i < size;i++){ sum = sum + (double)(arrayListGeneralStack.pop()); } System.out.println("sum="+sum); System.out.println("interface GeneralStack"); }else if (a.equals("Car")) { System.out.println("Car Test"); int count=in.nextInt(); int pop_time=in.nextInt(); ArrayListGeneralStack arrayListGeneralStack = new ArrayListGeneralStack(); for (int i=0;i<count;i++) { int id=in.nextInt(); String name=in.next(); Car car = new Car(id,name); System.out.println("push:"+arrayListGeneralStack.push(car)); } for (int i=0;i<pop_time;i++) { System.out.println("pop:"+arrayListGeneralStack.pop()); } System.out.println(arrayListGeneralStack.toString()); if (arrayListGeneralStack.size()>0) { int size=arrayListGeneralStack.size(); for (int i=0;i<size;i++) { Car car=(Car) arrayListGeneralStack.pop(); System.out.println(car.getName()); } } System.out.println("interface GeneralStack"); }else if (s.equals("quit")) { break; } } } }
结果:

实验总结:
通过本次实验,我学到了:1.泛型类的定义与使用 2.泛型方法的声明与使用 3.泛型接口的定义与实现
4.理解泛型程序设计 5.通配符
本次实验验证理解性实验难度不大,在理解完整代码的基础上,加深了我对泛型类的理解,尝试着熟悉泛型类的定义,泛型方法的声明与使用,泛型接口的 使用,逐步体会到泛型程序设计的好处。但在较为综合的Pair3的理解较为困难,不断翻书,查找知识,基本上有了大致的理解。最为困难的要数结对编程练习,看到题目不知该如何下手,没有思路。在与同学讨论商量后大致有了一点思路,但在实现的过程中问题多多,困难重重,再多次修改,询问后基本差不多实现。自己的编程问题很多。在闲暇之余,要尝试解决简单问题,多敲,多调试。