1、list_head的简单说明
在Linux内核中,提供了一个用来创建的双向循环链表的结构list_head。
其在内核中的定义如下:
struct list_head { struct list_head *next, *prev; };
使用list_head的内存结构如下所示:
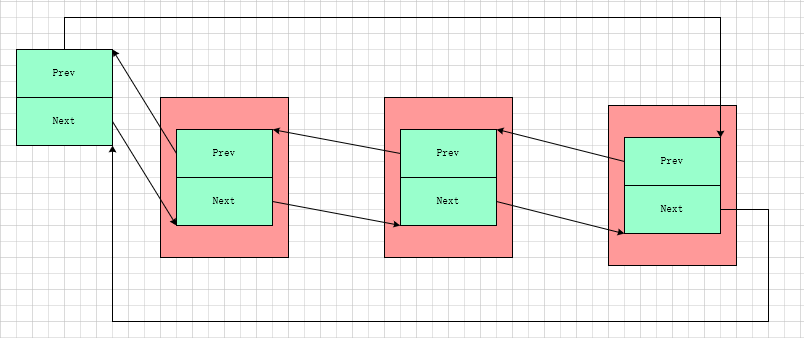
在数据结构的课本中,链表的经典定义方式通常是这样的
struct list_node { struct list_node *next; struct list_node *pre; ElemType data; };
我们知道在一般的双链表中,链表节点一般是含有数据域。而list_head这个结构模型和一般的链表结构模型最大的不同在于,list_head是没有数据域。在linux内核链表中不是在链表结构中包含数据,而是在数据中包含链表节点。
2、list_head提供的一些接口
2.1 初始化头结点
#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) } #define LIST_HEAD(name) struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list) { list->next = list; list->prev = list; }
2.2 遍历双向链表
#define list_for_each(pos, head) for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next)
2.3 插入操作
对链表的插入操作有两种:在表头插入和在表尾插入。Linux为此提供了两个接口。实际上我们可以看出来,这两个接口的差别并不大,一个从表头插入一个从表尾插入。
static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head) { __list_add(new, head, head->next); } static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head) { __list_add(new, head->prev, head); } static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *prev, struct list_head *next) { next->prev = new; new->next = next; new->prev = prev; prev->next = new; }
2.3 删除操作
static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry);
被删除的dentry的pre,next指针分别指向被设定为LIST_POSITION2和LIST_POSITION1两个特殊值,这样设置是为了保证不在链表中的节点项不可访问--对LIST_POSITION1和LIST_POSITION2的访问都将引起页故障。与之相对应,
list_del_init()函数将节点从链表中解下来之后,调用LIST_INIT_HEAD()将节点置为空链状态。
static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry) { __list_del(entry->prev, entry->next); entry->next = LIST_POISON1; entry->prev = LIST_POISON2; } static inline void __list_del(struct list_head * prev, struct list_head * next) { next->prev = prev; prev->next = next; } static inline void __list_del_entry(struct list_head *entry) { __list_del(entry->prev, entry->next); }
2.4 迁移操作
将节点list从其所在的链表迁移到head所在的链表。
static inline void list_move(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head);
static inline void list_move_tail(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head);
/** * list_move - delete from one list and add as another's head * @list: the entry to move * @head: the head that will precede our entry */ static inline void list_move(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head) { __list_del_entry(list); list_add(list, head); } /** * list_move_tail - delete from one list and add as another's tail * @list: the entry to move * @head: the head that will follow our entry */ static inline void list_move_tail(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head) { __list_del_entry(list); list_add_tail(list, head); }
2.5 合并
static inline void list_splic(struct list_head *list,struct list_head *head)
static inline void list_splice_init(struct list_head *list,struct list_head *head)
static inline void list_splic_tail(struct list_head *list,struct list_head *head)
static inline void list_splice_tail_init(struct list_head *list,struct list_head *head)
static inline void __list_splice(const struct list_head *list, struct list_head *prev, struct list_head *next) { struct list_head *first = list->next; struct list_head *last = list->prev; first->prev = prev; prev->next = first; last->next = next; next->prev = last; } /** * list_splice - join two lists, this is designed for stacks * @list: the new list to add. * @head: the place to add it in the first list. */ static inline void list_splice(const struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head) { if (!list_empty(list)) __list_splice(list, head, head->next); } /** * list_splice_tail - join two lists, each list being a queue * @list: the new list to add. * @head: the place to add it in the first list. */ static inline void list_splice_tail(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head) { if (!list_empty(list)) __list_splice(list, head->prev, head); } static inline void list_splice_init(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head) { if (!list_empty(list)) { __list_splice(list, head, head->next); INIT_LIST_HEAD(list); } } /** * list_splice_tail_init - join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list * @list: the new list to add. * @head: the place to add it in the first list. * * Each of the lists is a queue. * The list at @list is reinitialised */ static inline void list_splice_tail_init(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head) { if (!list_empty(list)) { __list_splice(list, head->prev, head); INIT_LIST_HEAD(list); } }
3 例子
#define MAX_NAME_LEN 32 #define MAX_ID_LEN 10 typedef struct student{ struct list_head list; char name[MAX_NAME_LEN]; char id[MAX_ID_LEN]; }student_t; static int list_test_init(void) { struct list_head head; struct list_head *p; student_t stu_1; student_t stu_2; student_t *entry; INIT_LIST_HEAD(&head); strcpy(stu_1.name,"lisi"); strcpy(stu_1.id,"001"); strcpy(stu_2.name,"linyp"); strcpy(stu_2.id,"002"); list_add(&stu_1.list,&head); list_add(&stu_2.list,&head); list_for_each(p,&head) { entry = list_entry(p,student_t,list); printk("name:%s ",entry->name); printk("id:%s ",entry->id); } list_del(&stu_1.list); printk("del student 1 "); list_for_each(p,&head) { entry = list_entry(p,student_t,list); printk("name:%s ",entry->name); printk("id:%s ",entry->id); } return 0; }