> 本文由 [简悦 SimpRead](http://ksria.com/simpread/) 转码, 原文地址 [zhuanlan.zhihu.com](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/64857243)
原文链接:
OpenCV OCR and text recognition with Tesseract - PyImageSearch
本教程将介绍如何使用 OpenCV OCR。我们将使用 OpenCV、Python 和 Tesseract 实现文本检测和文本识别。
上一篇文章讲了如何使用 OpenCV 的 EAST 深度学习模型执行文本检测。使用该模型能够检测和定位图像中文本的边界框坐标。
下一步就是使用 OpenCV 和 Tesseract 处理每一个包含文本的图像区域,识别这些文本并进行 OCR 处理。
使用 Tesseract 进行 OpenCV OCR 和文本识别
为了执行 OpenCV OCR 文本识别,首先需要安装 Tesseract v4,它包括一个用于文本识别的高准确率的深度学习模型。
然后,我将展示如何写一个 Python 程序,其中包括:
- 使用 OpenCV EAST 文本检测器执行文本检测,该模型是一个高准确率的深度学习文本检测器,被用于检测自然场景图像中的文本。
- 一旦我们使用 OpenCV 检测出图像中的文本区域后,提取出每个文本 ROI 并将其传入 Tesseract,从而构建完整的 OpenCV OCR 流程!
最后,我将展示一些使用 OpenCV 应用文本识别的示例结果,并讨论该方法的局限性和缺点。
How to install Tesseract 4


Tesseract 是一个很流行的开源 OCR 引擎,其在受限制的场景下能很好地运行,但是如果图像存在大量噪声或者图像在应用 Tesseract 之前没有经过合适的预处理,则性能较差。
深度学习影响了计算机视觉的几乎所有方面,字符识别和手写字体识别也不例外。基于深度学习的模型获得了前所未有的文字识别精度,远远超出了传统的特征提取和机器学习方法。
Tesseract 引入了深度学习模型来进一步提升 OCR 准确率,Tesseract (v4) 最新版本支持基于深度学习的 OCR,准确率显著提高。底层的 OCR 引擎使用的是一种 循环神经网络(RNN)——LSTM 网络。
在这篇博文的后面,您将学习如何将 OpenCV 的 EAST 文本检测算法与 Tesseract v4 结合起来,以自动执行 OpenCV OCR。
Install OpenCV
要运行本教程的脚本,您需要先安装 3.4.2 或更高版本的 OpenCV。安装教程可参考 这里,该教程可确保您下载合适的 OpenCV 和 OpenCV-contrib 版本。
Install Tesseract 4 on Ubuntu
根据您使用的是 Ubuntu 18.04 还是 Ubuntu 17.04 或更早版本,用于在 Ubuntu 上安装 Tesseract 4 的具体命令会有所不同。
使用 lsb_release 命令检查 Ubuntu 版本:
$ lsb\_release -a
No LSB modules are available.
Distributor ID: Ubuntu
Description: Ubuntu 18.04.1 LTS
Release: 18.04
Codename: bionic
对于 Ubuntu 18.04 的用户,Tesseract 4 是主 apt-get 库的一部分,通过下列命令就可以安装 Tesseract:
$ sudo apt install tesseract-ocr
如果您使用的是 Ubuntu 14、16 或 17 版本,那么由于依赖需求,您需要一些额外的命令。
好消息是 Alexander Pozdnyakov 创建了用于 Tesseract 的 Ubuntu PPA(Personal Package Archive),这使得在旧版本的 Ubuntu 上安装 Tesseract 4 变得非常容易。
只需要向系统添加 alex-p/tesseract-ocr PPA 库,更新您的包定义,然后安装 Tesseract:
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:alex-p/tesseract-ocr
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt install tesseract-ocr
如果没有错误,那么您应该已经成功安装了 Tesseract 4。
Install Tesseract 4 on macOS
如果您的系统中安装有 Homebrew(macOS「非官方」包管理器),那么在 macOS 上安装 Tesseract 4 只需要运行以下命令,确保指定 --HEAD,即可在 Mac 电脑上安装 Tesseract v4:
$ brew install tesseract --HEAD
如果您安装的 Tesseract 版本不是 v4,那么您需要先执行如下命令:
$ brew unlink tesseract
然后再执行带 --HEAD 的安装命令。
Verify your Tesseract version
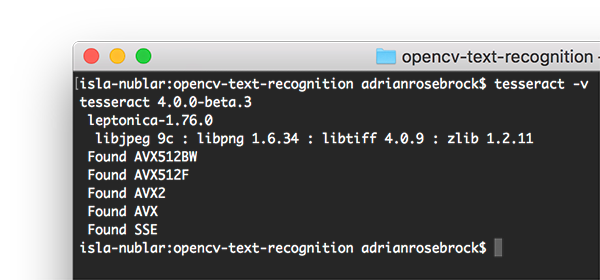
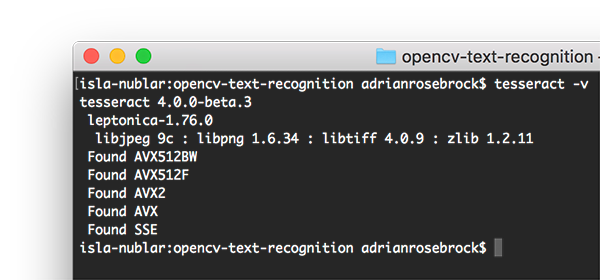
安装了 Tesseract 以后,您应该执行以下命令验证 Tesseract 的版本:
$ tesseract -v
tesseract 4.0.0-beta.3
leptonica-1.76.0
libjpeg 9c : libpng 1.6.34 : libtiff 4.0.9 : zlib 1.2.11
Found AVX512BW
Found AVX512F
Found AVX2
Found AVX
Found SSE
只要在输出中看到 tesseract 4,那么您就安装了 Tesseract 的最新版本。
Install your Tesseract + Python bindings
安装好 Tesseract 库之后,我们需要安装 Tesseract + Python 的捆绑,这样我们的 Python 脚本就可以通过 Tesseract,对 OpenCV 处理过的图像执行 OCR。
我们将使用 pip 来安装 Pillow(PIL 的 Python 版本),然后安装 pytesseract 和 imutils:
$ pip install pillow
$ pip install pytesseract
$ pip install imutils
现在打开 Python shell,确认导入 OpenCV 和 pytesseract 时没有出错: Now open up a Python shell and confirm that you can import both OpenCV and pytesseract :
$ python
Python 3.6.5 (default, Apr 1 2018, 05:46:30)
[GCC 7.3.0] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import cv2
>>> import pytesseract
>>> import imutils
>>>
Understanding OpenCV OCR and Tesseract text recognition
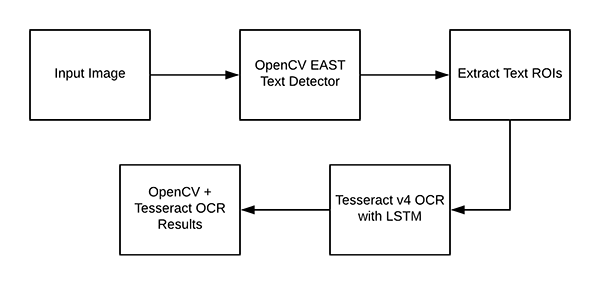
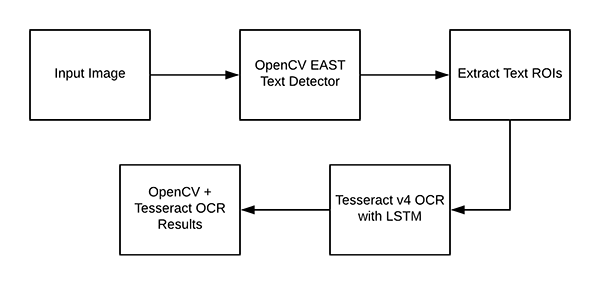
现在我们已经在系统上成功安装了 OpenCV 和 Tesseract ,我们需要简要回顾一下我们的流程和相关命令。
首先,我们使用 OpenCV 的 EAST text detector 来检测图像中的文本的存在。EAST 文本检测器将提供文本 ROI 的边界框坐标_(x, y)_。
我们将提取每个文本 ROI,并入到 Tesseract v4 的 LSTM 深度学习文本识别算法。LSTM 的输出将给出实际的 OCR 结果。最后,在输出图像上绘制 OpenCV OCR 结果。
其中使用到的 Tesseract 命令必须在 pytesseract 库下调用。在调用 tessarct 库时,我们需要提供几个 flag。最重要的三个 flag 是 -l、--oem 和 --ism。这三个参数的详细介绍可以查看该文章的最后部分。
Project structure
使用 tree 命令在终端中查看项目的目录结构:
$ tree --dirsfirst
.
├── images
│ ├── example\_01.jpg
│ ├── example\_02.jpg
│ ├── example\_03.jpg
│ ├── example\_04.jpg
│ └── example\_05.jpg
├── frozen\_east\_text\_detection.pb
└── text\_recognition.py
1 directory, 7 files
我们的项目包含一个目录和两个重要的文件:
images/: 一个包含六个含有场景文本的测试图像的目录。我们将使用这些图像进行 OpenCV OCR 操作。frozen_east_text_detection.pb: EAST 文本检测器。该 CNN 经过预训练,可用于文本检测。它是由 OpenCV 提供的。text_recognition.py: 我们的 OCR 程序。我们将逐行讲解该程序。它使用 EAST 文本检测器找到图像中的文本区域,然后利用 Tesseract v4 进行文本识别。
Implementing our OpenCV OCR algorithm
打开text_recognition.py文件并插入以下代码:
from imutils.object\_detection import non\_max\_suppression
import numpy as np
import pytesseract
import argparse
import cv2
最主要的是 pytesseract 和 OpenCV。imutils 包将用于非极大值抑制,因为 OpenCV 自带的 NMSBoxes 函数无法兼容 Python API。
接下来实现 decode_predictions 函数:
def decode\_predictions(scores, geometry):
# grab the number of rows and columns from the scores volume, then
# initialize our set of bounding box rectangles and corresponding
# confidence scores
(numRows, numCols) = scores.shape[2:4]
rects = []
confidences = []
# loop over the number of rows
for y in range(0, numRows):
# extract the scores (probabilities), followed by the
# geometrical data used to derive potential bounding box
# coordinates that surround text
scoresData = scores[0, 0, y]
xData0 = geometry[0, 0, y]
xData1 = geometry[0, 1, y]
xData2 = geometry[0, 2, y]
xData3 = geometry[0, 3, y]
anglesData = geometry[0, 4, y]
# loop over the number of columns
for x in range(0, numCols):
# if our score does not have sufficient probability,
# ignore it
if scoresData[x] < args["min\_confidence"]:
continue
# compute the offset factor as our resulting feature
# maps will be 4x smaller than the input image
(offsetX, offsetY) = (x * 4.0, y * 4.0)
# extract the rotation angle for the prediction and
# then compute the sin and cosine
angle = anglesData[x]
cos = np.cos(angle)
sin = np.sin(angle)
# use the geometry volume to derive the width and height
# of the bounding box
h = xData0[x] + xData2[x]
w = xData1[x] + xData3[x]
# compute both the starting and ending (x, y)-coordinates
# for the text prediction bounding box
endX = int(offsetX + (cos * xData1[x]) + (sin * xData2[x]))
endY = int(offsetY - (sin * xData1[x]) + (cos * xData2[x]))
startX = int(endX - w)
startY = int(endY - h)
# add the bounding box coordinates and probability score
# to our respective lists
rects.append((startX, startY, endX, endY))
confidences.append(scoresData[x])
# return a tuple of the bounding boxes and associated confidences
return (rects, confidences)
decode_predictions 在 这篇文章 中有详细介绍。该函数:
- 使用基于深度学习的文本检测器来检测(不是识别)图像中的文本区域。
- 该文本检测器生成两个数组,一个是给定区域包含文本的概率,另一个数组将这些概率映射到输入图像中的边界框坐标位置。
EAST 文本检测器生成两个变量:
scores:文本区域的概率。geometry:文本区域的边界框位置。
两个变量都是 decode_predictions 函数的参数。该函数处理输入数据,得出一个元组,其中包含文本边界框位置和该边界框包含文本的概率:
rects:该值基于geometry,其格式更加紧凑,方便我们稍后应用于 NMS。confidences:该列表中的置信度值对应rects中的每个矩形。
这两个值都由 decode_predictions 函数得出。
注意:理想情况下,旋转的边界框也在 rects 内,但是提取旋转边界框不利于解释本教程的一些概念。因此,我计算了水平的边界框矩形(把 angle 考虑在内)。如果您想提取文本的旋转边界框并输入到 Tesseract,您可以使用 angle = anglesData[x] 这里获取的角度。
下面我们来解析命令行参数:
# construct the argument parser and parse the arguments
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add\_argument("-i", "--image", type=str,
help="path to input image")
ap.add\_argument("-east", "--east", type=str,
help="path to input EAST text detector")
ap.add\_argument("-c", "--min-confidence", type=float, default=0.5,
help="minimum probability required to inspect a region")
ap.add\_argument("-w", "--width", type=int, default=320,
help="nearest multiple of 32 for resized width")
ap.add\_argument("-e", "--height", type=int, default=320,
help="nearest multiple of 32 for resized height")
ap.add\_argument("-p", "--padding", type=float, default=0.0,
help="amount of padding to add to each border of ROI")
args = vars(ap.parse\_args())
我们的 python 脚本需要两个命令行参数:
--image:输入图像的路径。 --east:预训练 EAST 文本检测器的路径。
下列命令行参数是可选的:
--min-confidence:检测到的文本区域的最小概率。 --width:图像输入 EAST 文本检测器之前需要重新调整的宽度,EAST 模型要求宽度是 32 的倍数。 --height:与宽度类似。EAST 模型要求调整后的高度是 32 的倍数。 --padding:填充到每个 ROI 边框的(可选)像素数量。如果您发现 OCR 结果不正确,那么您可以尝试 0.05、0.10 等值。
下面,我们将加载和预处理图像,并初始化关键变量:
# load the input image and grab the image dimensions
image = cv2.imread(args["image"])
orig = image.copy()
(origH, origW) = image.shape[:2]
# set the new width and height and then determine the ratio in change
# for both the width and height
(newW, newH) = (args["width"], args["height"])
rW = origW / float(newW)
rH = origH / float(newH)
# resize the image and grab the new image dimensions
image = cv2.resize(image, (newW, newH))
(H, W) = image.shape[:2]
先将图像加载到内存中,并拷贝一份(稍后我们可以在上面绘制输出结果)。
再获取原始宽度和高度(第 84 行),然后从命令行参数中提取新的宽度和高度。使用原始宽高和新的宽高计算比率,用于稍后在脚本中缩放边界框坐标。
然后调整图像大小,此处忽略长宽比。
接下来,我们将使用 EAST 文本检测器:
# define the two output layer names for the EAST detector model that
# we are interested in -- the first is the output probabilities and the
# second can be used to derive the bounding box coordinates of text
layerNames = [
"feature\_fusion/Conv\_7/Sigmoid",
"feature\_fusion/concat\_3"]
# load the pre-trained EAST text detector
print("[INFO] loading EAST text detector...")
net = cv2.dnn.readNet(args["east"])
先将两个输出层名称转换成列表格式。这两个输出层的介绍可以查看 这里。
然后将预训练 EAST 神经网络加载到内存中。至少需要 OpenCV 3.4.2 版本,它由 cv2.dnn.readNet 实现。
# construct a blob from the image and then perform a forward pass of
# the model to obtain the two output layer sets
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(image, 1.0, (W, H),
(123.68, 116.78, 103.94), swapRB=True, crop=False)
net.setInput(blob)
(scores, geometry) = net.forward(layerNames)
# decode the predictions, then apply non-maxima suppression to
# suppress weak, overlapping bounding boxes
(rects, confidences) = decode\_predictions(scores, geometry)
boxes = non\_max\_suppression(np.array(rects), probs=confidences)
为确定文本的位置,我们需要:
- 使用
cv2.dnn.blobFromImage构建四维输入数据blob。详情参见 这里。 - 将
blob传入 EAST 神经网络中,获取scores和geometry。 - 使用之前定义的
decode_predictions函数对预测结果进行解码。 - 通过 imutils 进行 非极大值抑制。NMS 实际上保留了最有可能的文本区域,剔除了其他重叠区域。
现在我们知道了文本区域的位置,接下来需要文本识别。我们开始在遍历所有边界框,并处理结果,为实际的文本识别做准备:
# initialize the list of results
results = []
# loop over the bounding boxes
for (startX, startY, endX, endY) in boxes:
# scale the bounding box coordinates based on the respective
# ratios
startX = int(startX * rW)
startY = int(startY * rH)
endX = int(endX * rW)
endY = int(endY * rH)
# in order to obtain a better OCR of the text we can potentially
# apply a bit of padding surrounding the bounding box -- here we
# are computing the deltas in both the x and y directions
dX = int((endX - startX) * args["padding"])
dY = int((endY - startY) * args["padding"])
# apply padding to each side of the bounding box, respectively
startX = max(0, startX - dX)
startY = max(0, startY - dY)
endX = min(origW, endX + (dX * 2))
endY = min(origH, endY + (dY * 2))
# extract the actual padded ROI
roi = orig[startY:endY, startX:endX]
我们定义一个 results 列表,用来包含我们的 OCR 边界框和文本。然后在 boxes 上进行遍历,我们:
- 基于之前计算的比率缩放边界框。
- 填充边界框。
- 最后,提取被填充的
ROI。
本文的文本识别部分可以通过使用 Tesseract v4 来完成:
# in order to apply Tesseract v4 to OCR text we must supply
# (1) a language, (2) an OEM flag of 4, indicating that the we
# wish to use the LSTM neural net model for OCR, and finally
# (3) an OEM value, in this case, 7 which implies that we are
# treating the ROI as a single line of text
config = ("-l eng --oem 1 --psm 7")
text = pytesseract.image\_to\_string(roi, config=config)
# add the bounding box coordinates and OCR'd text to the list
# of results
results.append(((startX, startY, endX, endY), text))
注意代码块中的注释,我们设置 Tesseract 的 config 参数(英语、LSTM 神经网络和单行文本)。
注:如果您获取了错误的 OCR 结果,那么您可能需要更改 --psm 的值。
pytesseract 库进行剩下的操作,调用 pytesseract.image_to_string,传递参数 roi 和 config。
只用这两行代码,您就使用 Tesseract v4 识别图像中的一个文本 ROI。记住,很多过程在底层进行。
我们的结果(边界框值和实际的 text 字符串)保存在 results 列表中。
然后我们继续该循环流程,对其他 ROI 进行处理。
接下来打印出最终结果,查看它是否真的有用:
# sort the results bounding box coordinates from top to bottom
results = sorted(results, key=lambda r:r[0][1])
for ((startX, startY, endX, endY), text) in results:
# display the text OCR'd by Tesseract
print("OCR TEXT")
print("========")
print("{}\n".format(text))
# strip out non-ASCII text so we can draw the text on the image
# using OpenCV, then draw the text and a bounding box surrounding
# the text region of the input image
text = "".join([c if ord(c) < 128 else "" for c in text]).strip()
output = orig.copy()
cv2.rectangle(output, (startX, startY), (endX, endY),
(0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(output, text, (startX, startY - 20),
cv2.FONT\_HERSHEY\_SIMPLEX, 1.2, (0, 0, 255), 3)
# show the output image
cv2.imshow("Text Detection", output)
cv2.waitKey(0)
先基于边界框的 y 坐标按自上而下的顺序对结果进行排序。
对 results 进行循环,我们:
- 将 OCR 得到的文本打印到终端。
- 从文本中去掉非 ASCII 字符,因为 OpenCV 的 cv2.putText 函数不支持非 ASCII 字符。
- 绘制 ROI 的边界框和识别的文本。
显示输出,并等待即将按下的任意键。
OpenCV text recognition results
现在我们已经实现了 OpenCV OCR 流程。执行以下命令:
$ python text\_recognition.py --east frozen\_east\_text\_detection.pb \
--image images/example\_01.jpg
[INFO] loading EAST text detector...
OCR TEXT
========
OH OK
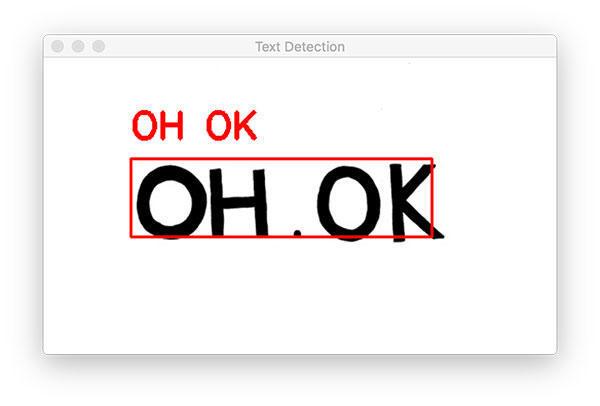
我们从一个简单的示例图片开始。
注意我们的 OpenCV OCR 系统正确地检测出了图像中的文本,然后识别出文本。
下一个示例图片更能代表我们在真实世界中看到的图像文本:
$ python text\_recognition.py --east frozen\_east\_text\_detection.pb \
--image images/example\_02.jpg
[INFO] loading EAST text detector...
OCR TEXT
========
® MIDDLEBOROUGH


OpenCV OCR 系统正确地定位文本位置和识别文本。但是,在终端输出中,有一个多余的符号,这里 Tesseract 可能被误导,因为 OpenCV EAST 文本检测器得到的边界框与标志牌后面的植物发生重叠。
下面我们来看另一个 OpenCV OCR 和文本识别的例子:
$ python text\_recognition.py --east frozen\_east\_text\_detection.pb \
--image images/example\_03.jpg
[INFO] loading EAST text detector...
OCR TEXT
========
ESTATE
OCR TEXT
========
AGENTS
OCR TEXT
========
SAXONS


该示例中有三个单独的文本区域。OpenCV 的文本检测器能够定位每一个文本区域,然后使用 OCR 准确识别出每个区域的文本内容。
下一个例子展示了在某些情况下添加 padding 的重要性:
$ python text\_recognition.py --east frozen\_east\_text\_detection.pb \
--image images/example\_04.jpg
[INFO] loading EAST text detector...
OCR TEXT
========
CAPTITO
OCR TEXT
========
SHOP
OCR TEXT
========
|.


在对这个烘焙店店面进行 OCR 的第一次尝试中,我们发现 “SHOP” 是被正确地识别,但是:
- “CAPUTO” 中的 “U” 被错误地识别为 “TI”。
- “CAPUTO’S” 中缺少 “'S”。
- “BAKE” 被错误识别为 “|.”。
现在通过添加一点填充,从而扩展 ROI 的边界框坐标,并准确识别文本:
$ python text\_recognition.py --east frozen\_east\_text\_detection.pb \
--image images/example\_04.jpg --padding 0.05
[INFO] loading EAST text detector...
OCR TEXT
========
CAPUTO'S
OCR TEXT
========
SHOP
OCR TEXT
========
BAKE


只需在边框的每个角落添加 5% 的填充,我们不仅能够正确识别 “BAKE”,还能够识别“CAPUTO” 中的 “U” 和“S”。
当然,OpenCV 也有的完全失败的案例:
$ python text\_recognition.py --east frozen\_east\_text\_detection.pb \
--image images/example\_05.jpg --padding 0.25
[INFO] loading EAST text detector...
OCR TEXT
========
Designer
OCR TEXT
========
a


我把填充增加到 25%,以适应这个标志牌中单词的角度 / 视角。这使得 “Designer” 可以正确地被 EAST 和 Tesseract v4 进行文本识别。但是较小的单词失败的原因,可能是字母的颜色与背景很相似。
在这种情况下,我们无能为力,但我建议参考下面的 Limitations and Drawbacks 部分,了解在遇到不正确的 OCR 结果时如何改进 OpenCV 文字识别流程。
Limitations and Drawbacks
记住,完美的 OCR 系统是不存在的,尤其是在现实世界条件下。期望 100% 的 OCR 准确率是不切实际的。
我们的 OpenCV OCR 系统可以很好地处理一些图像,但在处理其他图像时会失败。该文本识别流程失败的两个主要原因:
- 文本倾斜 / 旋转。
- The font of the text itself is not similar to what the Tesseract model was trained on. 文本字体与 Tesseract 模型训练的字体相差太远。
即使 Tesseract v4 与 v3 相比更加强大、准确率更高,但该深度学习模型仍然受限于它的训练数据。如果文本字体与训练数据字体相差太大,那么 Tesseract 不可能对该文本进行很好地处理。
其次,Tesseract 假设输入图像或 ROI 已经经过合适地预处理。但是当我们在自然场景图像上执行文本识别时,该假设不总是成立。
对于预处理干净过的图像,Tesseract 可以得到很好的图像。总的来说,我们的 OpenCV OCR 最适合于:(1)以图像的 90 度角 (即自上而下、鸟瞰) 捕获的文本,(2)相对容易从背景中分割的文本。
如果实际情况并非如此,您可以应用透视变换来校正视图,请记住,今天的 Python + EAST 文本检测器不支持旋转边界框。
如果您需要更高的精确度,我建议您尝试 “三大” 计算机视觉 API 服务之一:
每种方法都使用运行在云服务器上的更先进的 OCR 方法。
Summary
本教程介绍了如何使用 OpenCV OCR 系统执行文本检测和文本识别。
为了实现该任务,我们:
- 利用 OpenCV 的 EAST 文本检测器定位图像中的文本区域。
- 提取每个文本 ROI,然后使用 OpenCV 和 Tesseract v4 进行文本识别。
该 OpenCV OCR 流程在一些情况下效果很好,在另一些情况下并不那么准确。要想获得最好的 OpenCV 文本识别结果,我建议您确保:
- 输入的 ROI 应尽量经过清洗和预处理。在理想情况中,您的文本应该能够与图像的其他部分完美分割,但是在现实情况下,这并不总是可能的。
- 文本是从相机 90 度角的情况下拍摄的,类似于自上而下、鸟瞰的角度。如果不是,可以使用透视变换来获得更好的结果。
源码链接: