""" Pipeline Example. """ # $example on$ from pyspark.ml import Pipeline from pyspark.ml.classification import LogisticRegression from pyspark.ml.feature import HashingTF, Tokenizer # $example off$ from pyspark.sql import SparkSession if __name__ == "__main__": spark = SparkSession .builder .appName("PipelineExample") .getOrCreate() # $example on$ # Prepare training documents from a list of (id, text, label) tuples. training = spark.createDataFrame([ (0, "a b c d e spark", 1.0), (1, "b d", 0.0), (2, "spark f g h", 1.0), (3, "hadoop mapreduce", 0.0) ], ["id", "text", "label"]) # Configure an ML pipeline, which consists of three stages: tokenizer, hashingTF, and lr. tokenizer = Tokenizer(inputCol="text", outputCol="words") hashingTF = HashingTF(inputCol=tokenizer.getOutputCol(), outputCol="features") lr = LogisticRegression(maxIter=10, regParam=0.001) pipeline = Pipeline(stages=[tokenizer, hashingTF, lr]) # Fit the pipeline to training documents. model = pipeline.fit(training) # Prepare test documents, which are unlabeled (id, text) tuples. test = spark.createDataFrame([ (4, "spark i j k"), (5, "l m n"), (6, "spark hadoop spark"), (7, "apache hadoop") ], ["id", "text"]) # Make predictions on test documents and print columns of interest. prediction = model.transform(test) selected = prediction.select("id", "text", "probability", "prediction") for row in selected.collect(): rid, text, prob, prediction = row print("(%d, %s) --> prob=%s, prediction=%f" % (rid, text, str(prob), prediction)) # $example off$ spark.stop()
""" Decision Tree Classification Example. """ from __future__ import print_function # $example on$ from pyspark.ml import Pipeline from pyspark.ml.classification import DecisionTreeClassifier from pyspark.ml.feature import StringIndexer, VectorIndexer from pyspark.ml.evaluation import MulticlassClassificationEvaluator # $example off$ from pyspark.sql import SparkSession if __name__ == "__main__": spark = SparkSession .builder .appName("DecisionTreeClassificationExample") .getOrCreate() # $example on$ # Load the data stored in LIBSVM format as a DataFrame. data = spark.read.format("libsvm").load("data/mllib/sample_libsvm_data.txt") # Index labels, adding metadata to the label column. # Fit on whole dataset to include all labels in index. labelIndexer = StringIndexer(inputCol="label", outputCol="indexedLabel").fit(data) # Automatically identify categorical features, and index them. # We specify maxCategories so features with > 4 distinct values are treated as continuous. featureIndexer = VectorIndexer(inputCol="features", outputCol="indexedFeatures", maxCategories=4).fit(data) # Split the data into training and test sets (30% held out for testing) (trainingData, testData) = data.randomSplit([0.7, 0.3]) # Train a DecisionTree model. dt = DecisionTreeClassifier(labelCol="indexedLabel", featuresCol="indexedFeatures") # Chain indexers and tree in a Pipeline pipeline = Pipeline(stages=[labelIndexer, featureIndexer, dt]) # Train model. This also runs the indexers. model = pipeline.fit(trainingData) # Make predictions. predictions = model.transform(testData) # Select example rows to display. predictions.select("prediction", "indexedLabel", "features").show(5) # Select (prediction, true label) and compute test error evaluator = MulticlassClassificationEvaluator( labelCol="indexedLabel", predictionCol="prediction", metricName="accuracy") accuracy = evaluator.evaluate(predictions) print("Test Error = %g " % (1.0 - accuracy)) treeModel = model.stages[2] # summary only print(treeModel) # $example off$ spark.stop()
管道里的主要概念
MLlib提供标准的接口来使联合多个算法到单个的管道或者工作流,管道的概念源于scikit-learn项目。
1.数据框:机器学习接口使用来自Spark SQL的数据框形式数据作为数据集,它可以处理多种数据类型。比如,一个数据框可以有不同的列存储文本、特征向量、标签值和预测值。
2.转换器:转换器是将一个数据框变为另一个数据框的算法。比如,一个机器学习模型就是一个转换器,它将带有特征数据框转为预测值数据框。
3.估计器:估计器是拟合一个数据框来产生转换器的算法。比如,一个机器学习算法就是一个估计器,它训练一个数据框产生一个模型。
4.管道:一个管道串起多个转换器和估计器,明确一个机器学习工作流。
5.参数:管道中的所有转换器和估计器使用共同的接口来指定参数。
工作原理
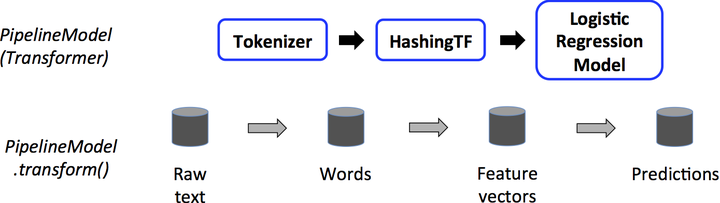
管道由一系列有顺序的阶段指定,每个状态时转换器或估计器。每个状态的运行是有顺序的,输入的数据框通过每个阶段进行改变。在转换器阶段,transform()方法被调用于数据框上。对于估计器阶段,fit()方法被调用来产生一个转换器,然后该转换器的transform()方法被调用在数据框上。
下面的图说明简单的文档处理工作流的运行。