转自:http://cek.io/blog/2015/12/03/event-loop/
What is JavaScript
What is JavaScript anyway? Some words:
- It’s a single-threaded, non-blocking, asynchronous, concurrent language”
- It has a call stack, an event loop, a callback queue, some other apis and stuff
If you’re like me (or Philip Roberts, it seems), these words themselves don’t mean a ton. So let’s parse that out.
JavaScript Runtimes
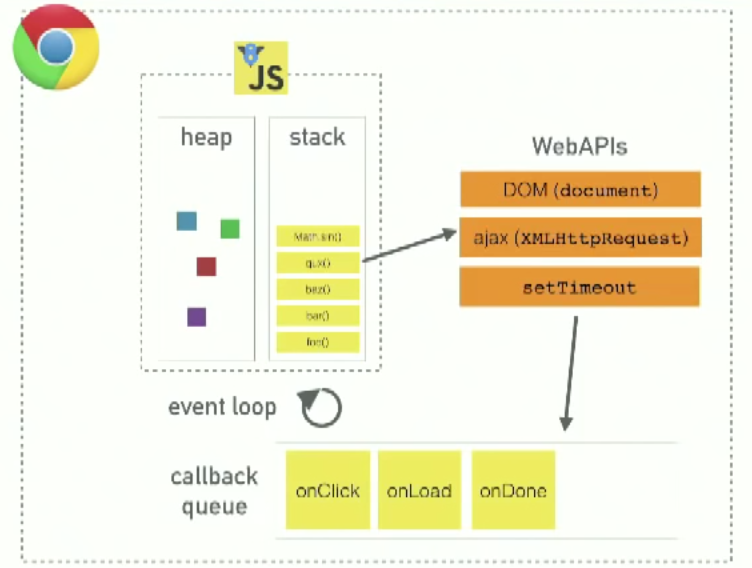
JavaScript runtimes (like V8) have a heap (memory allocation) and stack (execution contexts). But they don’t have setTimeout, the DOM, etc. Those are web APIs in the browser.
JavaScript as we know it
JavaScript in the browser has:
- a runtime like V8 (heap/stack)
- Web APIs that the browser provides, like the DOM, ajax, and
setTimeout - a callback queue for events with callbacks like
onClick,onLoad,onDone - an event loop
What’s the call stack?
JavaScript is single-threaded, meaning it has a single call stack, meaning it can do one thing at a time. The call stack is basically a data structure which records where in the program we are. If we step into a function, we push something onto the stack. If we return from a function, we pop off the top of the stack.
When our program throws an error, we see the call stack in the console. We see the state of the stack (which functions have been called) when that error happened.
Blocking
An important question that this relates to: what happens when things are slow? In other words, blocking. Blocking doesn’t have a strict definition; really it’s just things that are slow. console.log isn’t slow, but while loops from 1 to 1,000,000,000, image processing, or network requests are slow. Those things that are slow and on the stack are blocking.
Since JS is single-threaded, we make a network request and have to wait until it’s done. This is a problem in the browser—while we wait on a request, the browser is blocked (can’t click things, submit forms, etc.). The solution is asynchronous callbacks.
Concurrency, where we realize there’s a lie above
It’s a lie that JavaScript can only do one thing at a time. It’s true: JavaScript the runtime can only do one thing at a time. It can’t make an ajax request while doing other code. It can’t do a setTimeout while doing other code. But we can do things concurrently, because the browser is more than the runtime (remember the grainy image above).
The stack can put things into web APIs, which (when done) push callbacks onto task queue, and then…the event loop. Finally we get to the event loop. It’s the simplest little piece in this equation, and it has one very simple job. Look at the stack and look at the task queue; if the stack is empty, it takes the first thing off of the queue and pushes it onto the stack (back in JS land, back inside V8).
Louping it all together
Philip built an awesome tool to visualize all of this, called Loupe. It’s a tool that can visualize the JavaScript runtime at runtime.
Let’s use it to look at a simple example: logging a few things to the console, with one console.log happening asynchronously in a setTimeout.
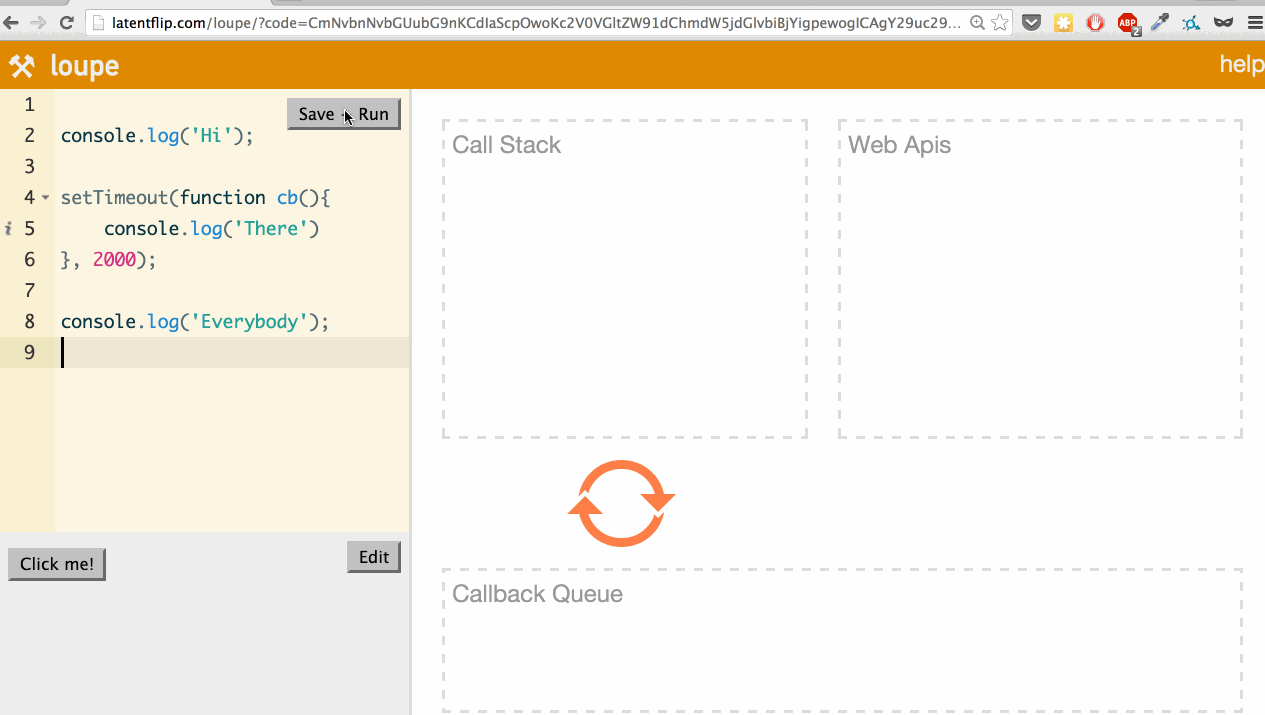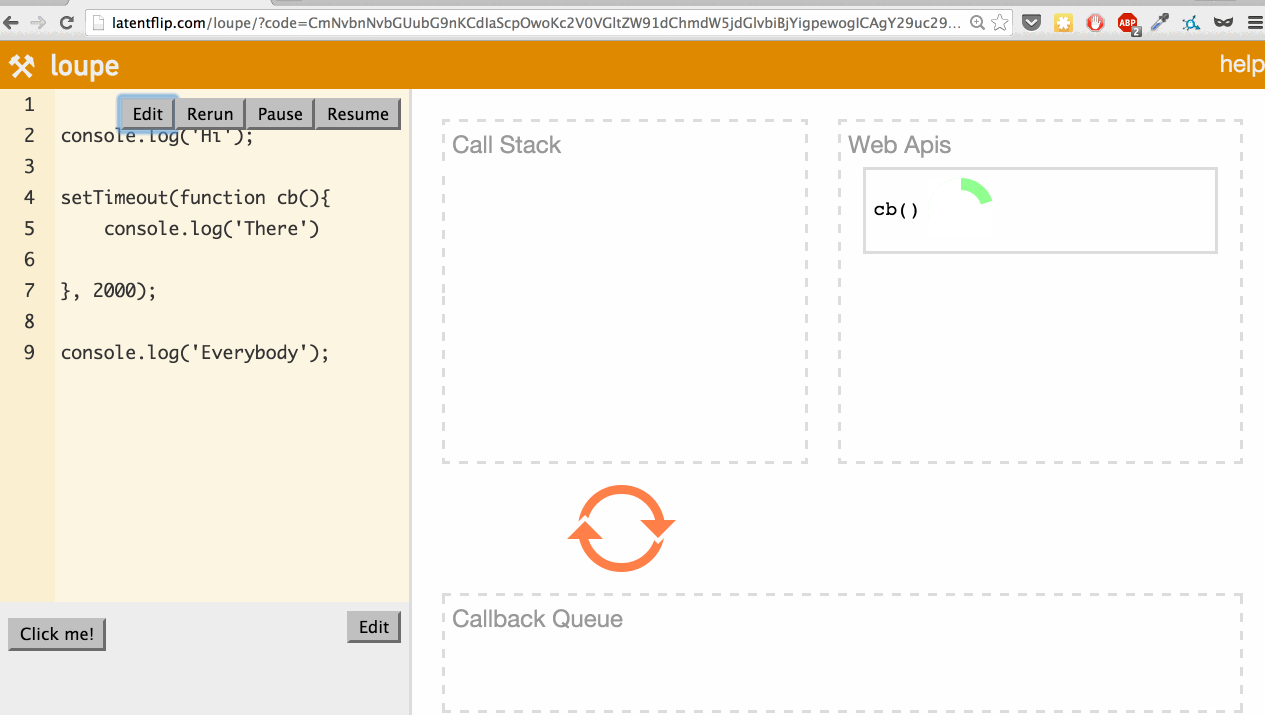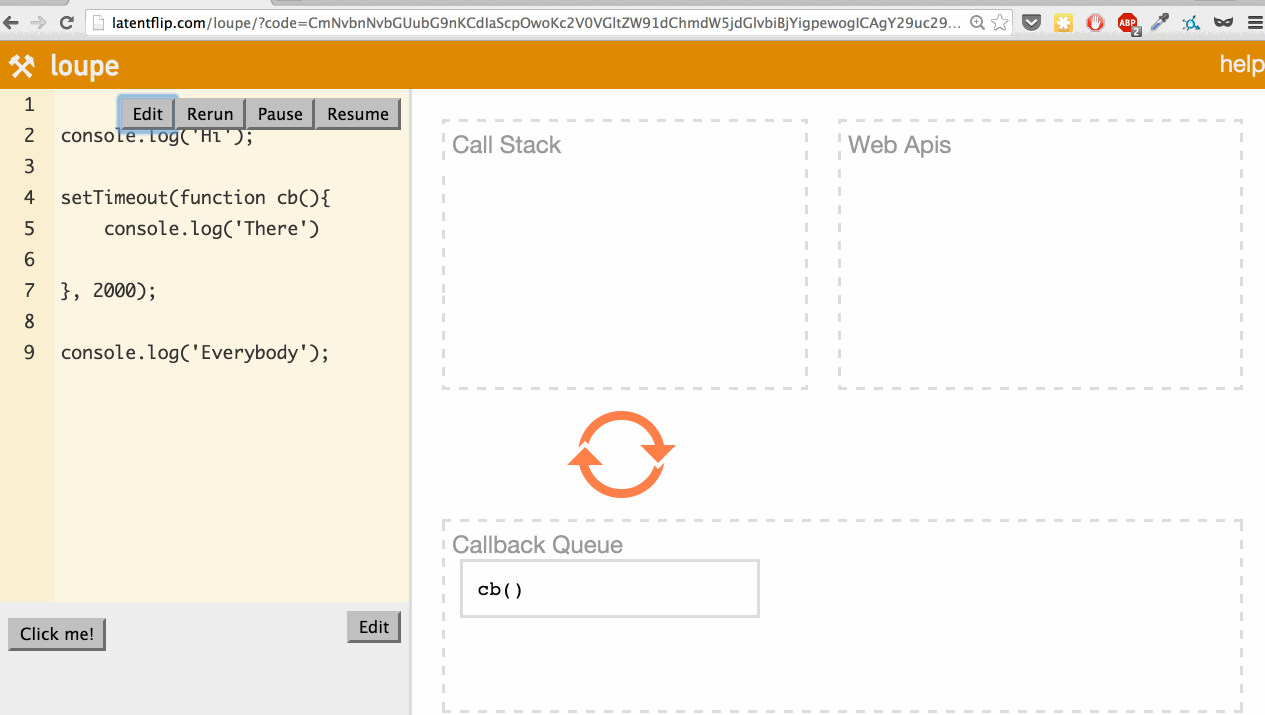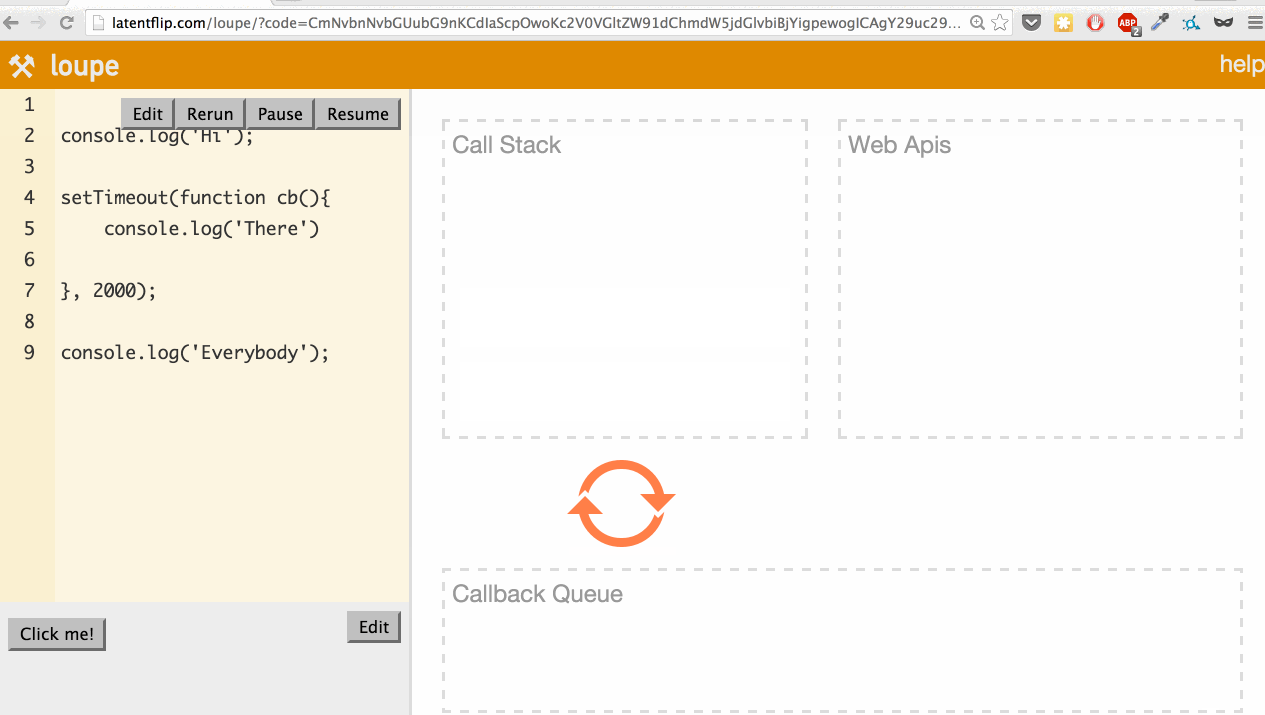
What’s actually happening here? Let’s go through it:
- We step into the
console.log('Hi');function, so it’s pushed onto the call stack. console.log('Hi');returns, so it’s popped off the top of the stack.- We step into the
setTimeoutfunction, so it’s pushed onto the call stack. setTimeoutis part of the web API, so the web API handles that and times out the 2 seconds.- We continue our script, stepping into the
console.log('Everybody')function, pushing it onto the stack. console.log('Everybody')returns, so it’s popped off the stack.- The 2-second timeout completes, so the callback moves to the callback queue.
- The event loop checks if the call stack is empty. If it were not empty, it would wait. Because it is empty, the callback is pushed onto the call stack.
console.log('Everybody')returns, so it’s popped off the call stack.
An interesting aside: setTimeout(function(...), 0). setTimeout with 0 isn’t necessarily intuitive, except when considered in the context of call stack and event loop. It basically defers something until the stack is clear.