一、授权流程
二、三种授权方式
2.1、编程式:通过写if/else 授权代码块完成:
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); if(subject.hasRole(“admin”)) { //有权限 } else { //无权限 }
2.2、注解式:通过在执行的Java方法上放置相应的注解完成:
@RequiresRoles("admin")
public void hello() {
//有权限
}
2.3、JSP/GSP 标签:在JSP/GSP 页面通过相应的标签完成:
<shiro:hasRole name="admin"> <!— 有权限—> </shiro:hasRole>
三、建立权限配置
shiro-permission.ini里边的内容相当于在数据库
#用户 [users] #用户zhang的密码是123,此用户具有role1和role2两个角色 zhang=123,role1,role2 wang=123,role2 #权限 [roles] #角色role1对资源user拥有create、update权限 role1=user:create,user:update #角色role2对资源user拥有create、delete权限 role2=user:create,user:delete #角色role3对资源user拥有create权限 role3=user:create
权限标识符号规则【中间使用半角:分隔】:资源:操作:实例
user:create:01 表示对用户资源的01实例进行create操作。
user:create 表示对用户资源进行create操作,相当于user:create:*,对所有用户资源实例进行create操作。
user:*:01 表示对用户资源实例01进行所有操作。
四、代码开发
4.1、测试ini程序

// 角色授权、资源授权测试 @Test public void testAuthorization() { // 创建SecurityManager工厂 Factory<SecurityManager> factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro-permission.ini"); // 创建SecurityManager SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance(); // 将SecurityManager设置到系统运行环境,和spring后将SecurityManager配置spring容器中,一般单例管理 SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager); // 创建subject Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); // 创建token令牌 UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("zhangsan", "123"); // 执行认证 try { subject.login(token); } catch (AuthenticationException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("认证状态:" + subject.isAuthenticated()); // 认证通过后执行授权 // 基于角色的授权 // hasRole传入角色标识 boolean ishasRole = subject.hasRole("role1"); System.out.println("单个角色判断" + ishasRole); // hasAllRoles是否拥有多个角色 boolean hasAllRoles = subject.hasAllRoles(Arrays.asList("role1", "role2", "role3")); System.out.println("多个角色判断" + hasAllRoles); // 使用check方法进行授权,如果授权不通过会抛出异常 // subject.checkRole("role13"); // 基于资源的授权 // isPermitted传入权限标识符 boolean isPermitted = subject.isPermitted("user:create:1"); System.out.println("单个权限判断" + isPermitted); boolean isPermittedAll = subject.isPermittedAll("user:create:1", "user:delete"); System.out.println("多个权限判断" + isPermittedAll); // 使用check方法进行授权,如果授权不通过会抛出异常 subject.checkPermission("items:create:1"); }
4.2、自定义realm
上边的程序通过shiro-permission.ini对权限信息进行静态配置,实际开发中从数据库中获取权限数据。就需要自定义realm,由realm从数据库查询权限数据。
realm根据用户身份查询权限数据,将权限数据返回给authorizer(授权器)。
4.2.1、realm编写,结合上节完善写法
在原来自定义的realm中,修改doGetAuthorizationInfo方法。

package com.lhx.shiro.realm; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken; import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authz.SimpleAuthorizationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm; import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection; /** * * <p> * Title: CustomRealm * </p> * <p> * Description:自定义realm * </p> * @version 1.0 */ public class CustomRealm extends AuthorizingRealm { // 设置realm的名称 @Override public void setName(String name) { super.setName("customRealm"); } // 用于认证 @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo( AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { // token是用户输入的 // 第一步从token中取出身份信息 String userCode = (String) token.getPrincipal(); // 第二步:根据用户输入的userCode从数据库查询 // .... // 如果查询不到返回null //数据库中用户账号是zhangsansan /*if(!userCode.equals("zhangsansan")){// return null; }*/ // 模拟从数据库查询到密码 String password = "111111"; // 如果查询到返回认证信息AuthenticationInfo SimpleAuthenticationInfo simpleAuthenticationInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo( userCode, password, this.getName()); return simpleAuthenticationInfo; } // 用于授权 @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo( PrincipalCollection principals) { //从 principals获取主身份信息 //将getPrimaryPrincipal方法返回值转为真实身份类型(在上边的doGetAuthenticationInfo认证通过填充到SimpleAuthenticationInfo中身份类型), String userCode = (String) principals.getPrimaryPrincipal(); //根据身份信息获取权限信息 //连接数据库... //模拟从数据库获取到数据 List<String> permissions = new ArrayList<String>(); permissions.add("user:create");//用户的创建 permissions.add("items:add");//商品添加权限 //.... //查到权限数据,返回授权信息(要包括 上边的permissions) SimpleAuthorizationInfo simpleAuthorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo(); //将上边查询到授权信息填充到simpleAuthorizationInfo对象中 simpleAuthorizationInfo.addStringPermissions(permissions); return simpleAuthorizationInfo; } }
4.2.2、在shiro-realm.ini中配置自定义的realm,将realm设置到securityManager中
[main] #自定义 realm customRealm=com.lhx.shiro.realm.CustomRealm #将realm设置到securityManager相当于spring中注入 securityManager.realms=$customRealm
4.2.3、测试程序

// 自定义realm进行资源授权测试 @Test public void testAuthorizationCustomRealm() { // 创建SecurityManager工厂 Factory<SecurityManager> factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro-realm.ini"); // 创建SecurityManager SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance(); // 将SecurityManager设置到系统运行环境,和spring后将SecurityManager配置spring容器中,一般单例管理 SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager); // 创建subject Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); // 创建token令牌 UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("zhangsan", "111111"); // 执行认证 try { subject.login(token); } catch (AuthenticationException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("认证状态:" + subject.isAuthenticated()); // 认证通过后执行授权 // 基于资源的授权,调用isPermitted方法会调用CustomRealm从数据库查询正确权限数据 // isPermitted传入权限标识符,判断user:create:1是否在CustomRealm查询到权限数据之内 boolean isPermitted = subject.isPermitted("user:create:1"); System.out.println("单个权限判断" + isPermitted); boolean isPermittedAll = subject.isPermittedAll("user:create:1", "user:create"); System.out.println("多个权限判断" + isPermittedAll); // 使用check方法进行授权,如果授权不通过会抛出异常 subject.checkPermission("items:add:1"); }
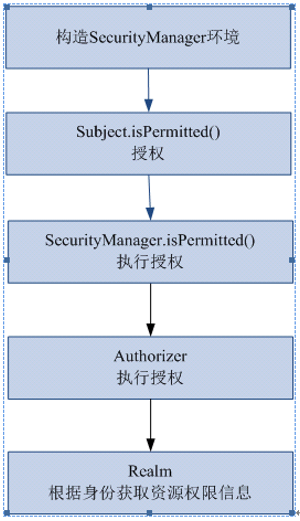
4.3、授权流程
1、对subject进行授权,调用方法isPermitted("permission串")
2、SecurityManager执行授权,通过ModularRealmAuthorizer执行授权
3、ModularRealmAuthorizer执行realm(自定义的CustomRealm)从数据库查询权限数据
调用realm的授权方法:doGetAuthorizationInfo
4、realm从数据库查询权限数据,返回ModularRealmAuthorizer
5、ModularRealmAuthorizer调用PermissionResolver进行权限串比对
6、如果比对后,isPermitted中"permission串"在realm查询到权限数据中,说明用户访问permission串有权限,否则 没有权限,抛出异常。
小结:以上004-006即是shiro基础权限认证,后续将编写结合spring,cache等文章
