String类的签名(JDK 8):
public final class String implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence { }
String是不可变类,即String对象也是不可变对象。
这意味着当修改一个String对象的内容时,JVM不会改变原来的对象,而是生成一个新的String对象。
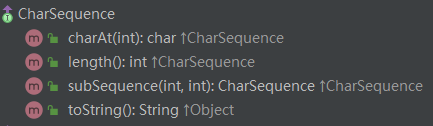
一、CharSequence 接口
CharSequence API 解释,CharSequence的实例是一个包含“一个或者多个字符值(char values)”的可读序列。这个接口的功能就是对不同种类的字符序列提供统一的只读访问。
CharSequence的实现类有String,StringBuffer,StringBuilder等。
CharSequence接口要求实现的方法如下:

二、String类的字段
2.1 private final char value[];
存储组成字符串值的字符数组value,也是不可变的。
2.2 private int hash;
缓存String实例的hash值
2.3 private static final long serialVersionUID = -6849794470754667710L;
这个没太懂,注释解释如下:
use serialVersionUID from JDK 1.0.2 for interoperability(互操作性)
2.4 private static final ObjectStreamField[] serialPersistentFields =new ObjectStreamField[0];
注释解释:Class String is special cased within the Serialization Stream Protocol
StackOverflow上有讨论:why String in java does not override readObject?
Strings, arrays and enums are special cases in serialization, and are not serialized through readObject/writeObject like other Objects are.
Java中,字符串、数组和枚举在序列化方面是特殊的类,他们没有像其他对象一样通过readObject/writeObject进行序列化。
2.5 public static final Comparator<String> CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER= new CaseInsensitiveComparator();
CaseInsensitiveComparator类是一个String类中自己实现的比较器类。
这个比较器对象通过compareToIgnoreCase对String对象进行排序的比较器。compareToIgnoreCase是String类中方法,功能是按字典顺序比较两个字符串,忽略大小写差异。返回正值,0,或者负值。
该比较器是可序列化的。
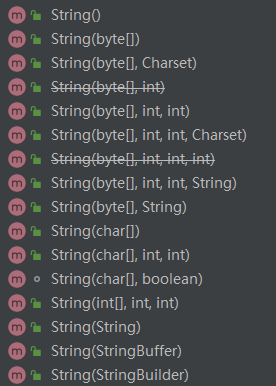
三、构造函数
划线的表示本版JDK中已经被抛弃的。
四、源自CharSequence接口的方法
这些方法功能很明确,实现也并不复杂。
五、源自Comparable的方法
public int compareTo(String anotherString)
按字典顺序比较两个字符串(上面有个字段也与比较有关,但与这个函数没有关系),这个是大小写敏感的,而且返回值也不是简单地以正负值表示比较结果。
直接上源码:
public int compareTo(String anotherString) {
int len1 = value.length;
int len2 = anotherString.value.length;
int lim = Math.min(len1, len2);
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int k = 0;
while (k < lim) {
char c1 = v1[k];
char c2 = v2[k];
if (c1 != c2) {
return c1 - c2;
}
k++;
}
return len1 - len2;
}
当String 的equals方法返回true时,该方法返回0.
至于字典序到底怎么算大小,可以总结一下:
小写字母>大写字母;同大小写,越靠字母表后面越大。
ps:看完这个源码,我产生了疑惑,同一个类的不同实例竟然可以相互访问各自的private成员!!??
是的,确实可以!!
六、其它重要方法
1、substring()——public String substring(int beginIndex);
public String substring(int beginIndex) {
if (beginIndex < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(beginIndex);
}
int subLen = value.length - beginIndex;
if (subLen < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(subLen);
}
return (beginIndex == 0) ? this : new String(value, beginIndex, subLen);
}
sublen是索要生成的子串的长度,这个函数生成的子字符串为从内部的value字符数组中索引为beginIndex处到末尾处字符组成的字符串。
如果beginIndex为0,则返回字符串本身;
如果beginIndex不为0,则返回new String(value, beginIndex, subLen)
下面上构造函数String(char value[], int offset, int count)源码:
public String(char value[], int offset, int count) {
if (offset < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset);
}
if (count <= 0) {
if (count < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(count);
}
if (offset <= value.length) {
this.value = "".value;
return;
}
}
// Note: offset or count might be near -1>>>1.
if (offset > value.length - count) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset + count);
}
this.value = Arrays.copyOfRange(value, offset, offset+count);
}
方法最后返回的是Arrays.copyOfRange(value, offset, offset+count),继续跟踪:
public static char[] copyOfRange(char[] original, int from, int to) {
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
char[] copy = new char[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
System.arraycopy()方法是一个native方法,它将指定源数组src中的数组从指定位置srcPos开始复制到目标数组dest的指定位置destPos,而length是所复制的长度。
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,
Object dest, int destPos, int length)
newLength是要复制的长度,copy是根据这个长度新建的char数组。这个copy将作为新建子串的value值。
2、substring()——public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) {
if (beginIndex < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(beginIndex);
}
if (endIndex > value.length) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(endIndex);
}
int subLen = endIndex - beginIndex;
if (subLen < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(subLen);
}
return ((beginIndex == 0) && (endIndex == value.length)) ? this
: new String(value, beginIndex, subLen);
}
基本一样,subLen是根据endIndex和beginIndex得到的子串长度,需要注意endindex索引处的字符不包含在子串中。