https://blog.csdn.net/a67474506/article/details/52608855
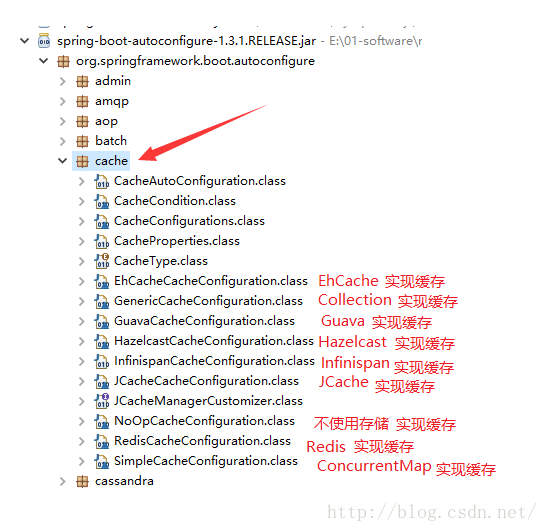
在不适用任何额外配置的情况下,默认使用SimpleCacheConfiguration
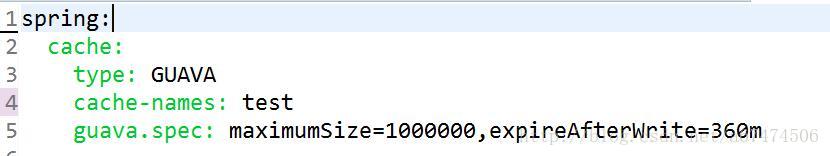
SpringBoot通过spring.cache为前缀来配置缓存
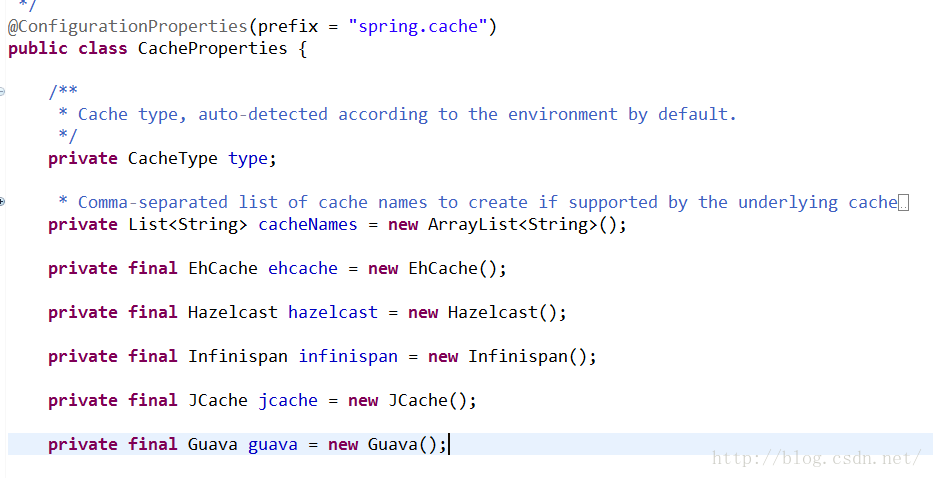
使用这些缓存实现的话,只需导入相关缓存的依赖,并在配置类中使用@EnableCaching开启缓存即可
Guava实现
这里简单介绍下使用Guava实现
引入的依赖
pom.xml
-
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
-
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
-
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
-
<groupId>com.ibigsea</groupId>
-
<artifactId>spirngboot-cache-demo</artifactId>
-
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
-
-
-
<properties>
-
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
-
<boot.version>1.3.5.RELEASE</boot.version>
-
</properties>
-
-
<dependencies>
-
<dependency>
-
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
-
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
-
<version>${boot.version}</version>
-
</dependency>
-
<dependency>
-
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
-
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
-
<version>${boot.version}</version>
-
<scope>test</scope>
-
</dependency>
-
<dependency>
-
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
-
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
-
<version>${boot.version}</version>
-
</dependency>
-
<dependency>
-
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
-
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
-
<version>19.0</version>
-
</dependency>
-
</dependencies>
-
</project>
dataCache.java
-
package com.ibigsea.springboot_cache_demo.cache;
-
-
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
-
import java.util.Date;
-
import java.util.HashMap;
-
import java.util.Map;
-
-
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
-
-
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheConfig;
-
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
-
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
-
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
-
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
-
-
-
public class DataCache {
-
-
private Map<Long, String> dataMap = new HashMap<>();
-
-
/**
-
* 初始化
-
*/
-
-
public void init() {
-
dataMap.put(1L, "张三");
-
dataMap.put(2L, "李四");
-
dataMap.put(3L, "王五");
-
}
-
-
/**
-
* 查询
-
* 如果数据没有缓存,那么从dataMap里面获取,如果缓存了,
-
* 那么从guavaDemo里面获取
-
* 并且将缓存的数据存入到 guavaDemo里面
-
* 其中key 为 #id+dataMap
-
*/
-
-
public String query(Long id) {
-
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
-
System.out.println(sdf.format(new Date()) + " : query id is " + id);
-
return dataMap.get(id);
-
}
-
-
/**
-
* 插入 或者更新
-
* 插入或更新数据到dataMap中
-
* 并且缓存到 guavaDemo中
-
* 如果存在了那么更新缓存中的值
-
* 其中key 为 #id+dataMap
-
*/
-
-
public String put(Long id, String value) {
-
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
-
System.out.println(sdf.format(new Date()) + " : add data ,id is "+ id);
-
dataMap.put(id, value);
-
// data persistence
-
return value;
-
}
-
-
/**
-
* 删除
-
* 删除dataMap里面的数据
-
* 并且删除缓存guavaDemo中的数据
-
* 其中key 为 #id+dataMap
-
*/
-
-
public void remove(Long id) {
-
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
-
System.out.println(sdf.format(new Date()) + " : remove id is "+ id + " data");
-
dataMap.remove(id);
-
// data remove
-
}
-
-
-
}
关于缓存注解中的value,就是配置文件中的cache-names
关于注解中的key这个值,如果不指定的话 ,那么会取方法参数当做Key
application.yml
-
spring:
-
cache:
-
#缓存名称
-
cache-names: guavaDemo
-
#缓存最大数量500条, 缓存失效时间 6个小时
-
guava.spec: maximumSize=500,expireAfterWrite=360m
App.java
-
package com.ibigsea.springboot_cache_demo;
-
-
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
-
import java.util.Date;
-
-
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
-
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
-
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
-
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
-
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
-
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
-
-
import com.ibigsea.springboot_cache_demo.cache.DataCache;
-
-
/**
-
* 是Spring Boot项目的核心注解,主要是开启自动配置
-
*/
-
-
-
// 开启缓存
-
-
public class App {
-
-
-
private DataCache dataCache;
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
-
}
-
-
-
public String put(Long id, String value) {
-
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
-
return sdf.format(new Date()) + " : value is " + dataCache.put(id, value) ;
-
}
-
-
-
public String query(Long id){
-
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
-
return sdf.format(new Date()) + " : value is " +dataCache.query(id) ;
-
}
-
-
-
public String remove(Long id) {
-
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
-
dataCache.remove(id) ;
-
return sdf.format(new Date()) + " : success " ;
-
}
-
-
}
运行结果
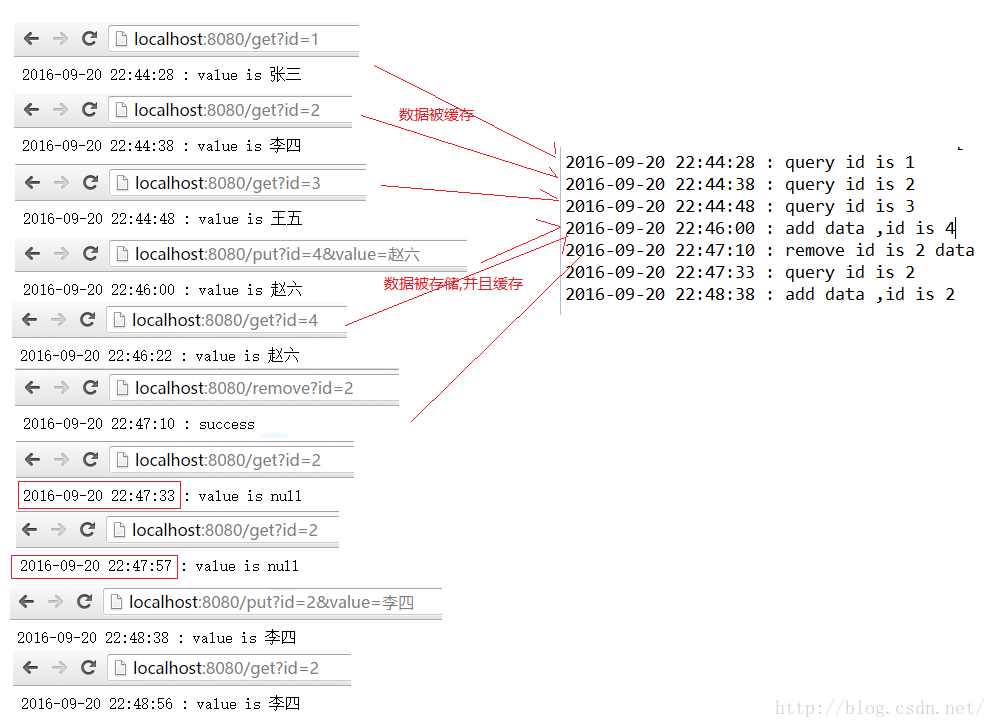
关于注解配置:
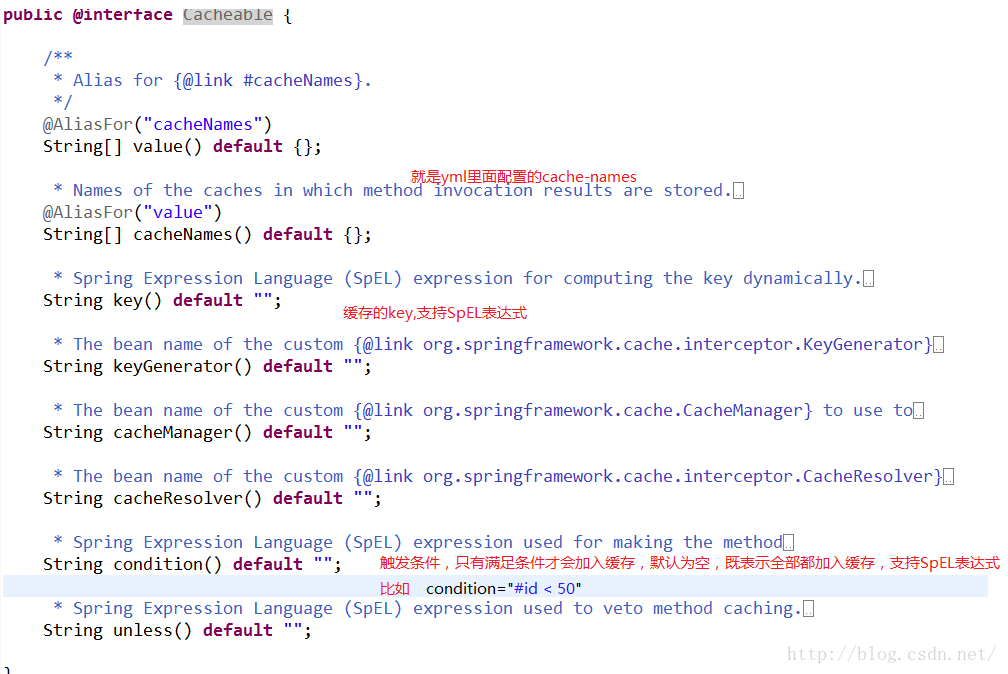
@Cacheable
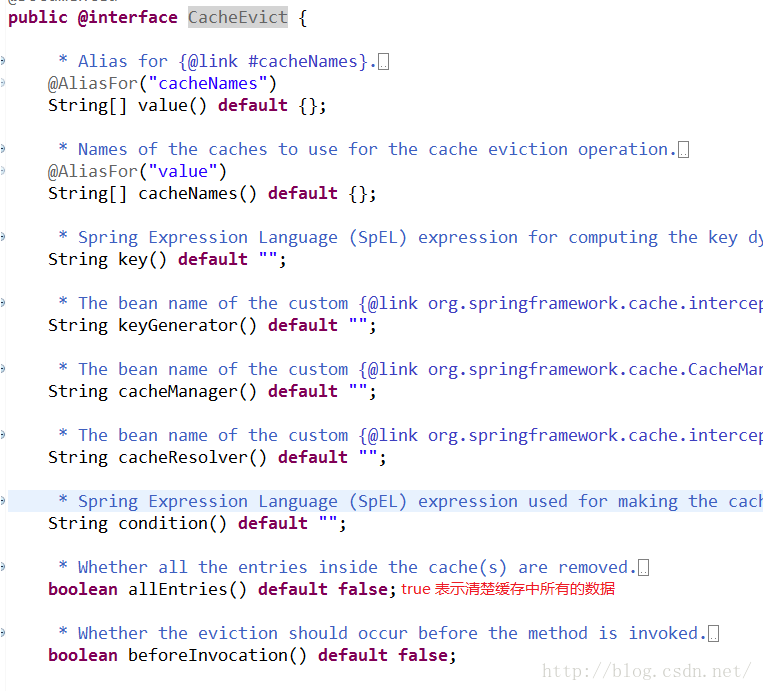
@CacheEvict
@CachePut
和上面的一样,只是这个注解是用来更新或者插入数据到缓存中的,
其中key自己定义,返回值会缓存
还有就是SpringBoot会根据你的类路径里面的依赖jar,来确定使用什么类型进行缓存,所以基本是我们是不用配置spring.cache.type这个属性的
Redis实现
Redis缓存:
如果是用redis作为缓存的话
我们只需要引入redis相关依赖,修改yml配置属性
-
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
-
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
-
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
-
<groupId>com.ibigsea</groupId>
-
<artifactId>spirngboot-cache-demo</artifactId>
-
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
-
-
-
<properties>
-
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
-
<boot.version>1.3.5.RELEASE</boot.version>
-
</properties>
-
-
<dependencies>
-
<dependency>
-
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
-
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
-
<version>${boot.version}</version>
-
</dependency>
-
<dependency>
-
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
-
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
-
<version>${boot.version}</version>
-
<scope>test</scope>
-
</dependency>
-
<dependency>
-
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
-
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
-
<version>${boot.version}</version>
-
</dependency>
-
<dependency>
-
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
-
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-redis</artifactId>
-
<version>${boot.version}</version>
-
</dependency>
-
<!-- <dependency> -->
-
<!-- <groupId>com.google.guava</groupId> -->
-
<!-- <artifactId>guava</artifactId> -->
-
<!-- <version>19.0</version> -->
-
<!-- </dependency> -->
-
</dependencies>
-
</project>
application.yml
-
spring:
-
cache:
-
#缓存名称
-
cache-names: guavaDemo
-
#缓存最大数量500条, 缓存失效时间 6个小时
-
#guava.spec: maximumSize=500,expireAfterWrite=360m
-
# REDIS (RedisProperties)
-
redis :
-
host : localhost # server host
-
port : 6379 # connection port
-
pool.max-idle : 8 # pool settings ...
-
pool.min-idle : 1
-
pool.max-active : 8
-
pool.max-wait : -1
就这样就OK了,代码什么的都是不用改变的,是不是很方便
测试结果
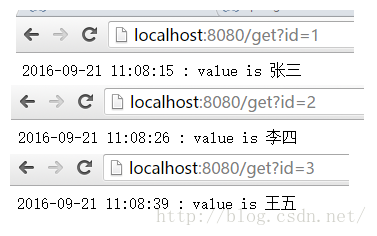
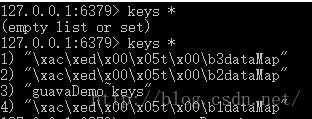
数据都会缓存到redis里面
其他的地方就不测试了 都是差不多的
使用其他实现导入对应的依赖,然后添加配置即可
注意:
如果使用guava缓存的时候 ,同时添加了redis的jar依赖,或者其他的依赖,可能会出现异常
这个时候加上 type: GUAVA 就可以