前言
任何系统即使做的再大,都会有可能出现各种各样的突发状况。尽管你可以说我在软件层面上已经做到所有情况的意外处理了,但是万一硬件出问题了或者说物理层面上出了问题,恐怕就不是多写几行代码能够立刻解决的吧,说了这么多,无非就是想强调HA,系统高可用性的重要性。在YARN中,NameNode的HA方式估计很多人都已经了解了,那本篇文章就来为大家梳理梳理RM资源管理器HA方面的知识,并不是指简单的RM的HA配置,确切的说是RM的应用状态存储于恢复。
RM应用状态存储使用
RM应用状态存储是什么意思呢,我们知道,RM全称ResourceManager,好比一个大管家,他不仅要与各个节点上的ApplicationMaster进行通信,还要与NodeManager进行心跳包的传输,自然在RM上会注册进来很多的应用,每个应用由1个ApplicationMaster负责掌管整个应用周期。既然RM角色这么重要,就有必要保存一下RM的信息状态,以免RM进程异常退出导致的应用状态信息丢失,RM重启无法重跑之前的应用的现象。
保存什么应用信息
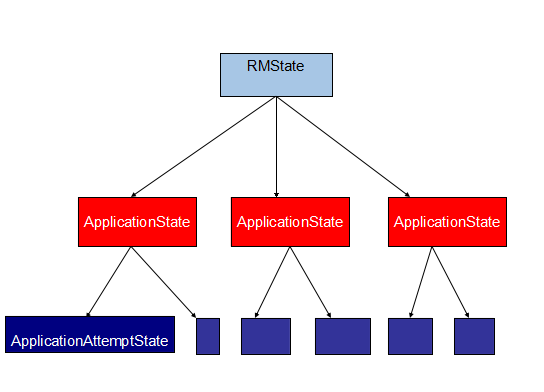
既然目标已经明确了,那么在YARN中,保存的应用信息到底是哪些数据信息呢,应用状态信息只是1个笼统的概念。下面用一张图来表示。
可以看到,这是一张分层多叉树的形状,这个图类似于MapReduce作用运行的分层执行状态图,做个简单介绍,最上面就是1个RMState的状态,这个状态中包含若干个ApplicationState的应用状态信息,每个应用状态信息中包含了很多歌应用尝试信息状态。
应用状态信息如何保存
RM应用状态信息保存的方式又哪些呢:
1.MemoryRMStateStore--信息状态保存在内存中的实现类。
2.FileSystemRMStateStore--信息状态保存在HDFS文件系统中,这个是做了持久化了。
3.NullRMStateStore--do nothing,什么都不做,就是不保存应用状态信息。
4.ZKRMStateStore--信息状态保存在Zookeeper中。
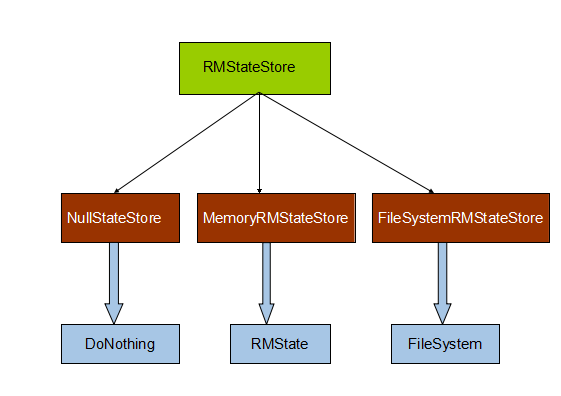
由于我分析的源码中还没有ZKRMStateStore这个类,所以只针对前3种做一个简单的介绍。上面列举的几个类都是具体实现类,那么就一定存在更加上层级的类来定义更基本的变量和方法,答案是RMStateStore类,所以继承关系就是下面这张图所表示
下面蓝色箭头所表示的意思实现类的依托对象。具体什么意思,看接下来的源码分析。首先RMStateStore类对象
/**
* Base class to implement storage of ResourceManager state.
* Takes care of asynchronous notifications and interfacing with YARN objects.
* Real store implementations need to derive from it and implement blocking
* store and load methods to actually store and load the state.
* 保存RM资源状态信息的基类,也是一个服务对象类
*/
public abstract class RMStateStore extends AbstractService {
....
/**
* State of an application attempt
* 一次应用尝试状态信息类
*/
public static class ApplicationAttemptState {
//应用尝试ID
final ApplicationAttemptId attemptId;
//主容器
final Container masterContainer;
//凭证信息
final Credentials appAttemptCredentials;
....
}
/**
* State of an application application
* 应用状态信息类
*/
public static class ApplicationState {
//应用提交上下文对象
final ApplicationSubmissionContext context;
//应用提交时间
final long submitTime;
//提交者
final String user;
//应用尝试信息对
Map<ApplicationAttemptId, ApplicationAttemptState> attempts =
new HashMap<ApplicationAttemptId, ApplicationAttemptState>();
....
}
public static class RMDTSecretManagerState {
// DTIdentifier -> renewDate
//RM身份标识符ID对时间的映射
Map<RMDelegationTokenIdentifier, Long> delegationTokenState =
new HashMap<RMDelegationTokenIdentifier, Long>();
Set<DelegationKey> masterKeyState =
new HashSet<DelegationKey>();
int dtSequenceNumber = 0;
....
}
/**
* State of the ResourceManager
* RM状态信息类
*/
public static class RMState {
//RM中的应用状态对图
Map<ApplicationId, ApplicationState> appState =
new HashMap<ApplicationId, ApplicationState>();
RMDTSecretManagerState rmSecretManagerState = new RMDTSecretManagerState();
....
}/**
* Non-Blocking API
* ResourceManager services use this to store the application's state
* This does not block the dispatcher threads
* RMAppStoredEvent will be sent on completion to notify the RMApp
* 保存应用状态方法,触发一次保存event事件,此方法为非阻塞方法
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public synchronized void storeApplication(RMApp app) {
ApplicationSubmissionContext context = app
.getApplicationSubmissionContext();
assert context instanceof ApplicationSubmissionContextPBImpl;
ApplicationState appState = new ApplicationState(
app.getSubmitTime(), context, app.getUser());
//触发一次应用信息保存事件,由中央调度器进行事件分发处理
dispatcher.getEventHandler().handle(new RMStateStoreAppEvent(appState));
}
/**
* Blocking API
* Derived classes must implement this method to store the state of an
* application.
* 保存应用状态信息的阻塞方法,由子类具体实现
*/
protected abstract void storeApplicationState(String appId,
ApplicationStateDataPBImpl appStateData)
throws Exception;/**
* Non-blocking API
* ResourceManager services call this to remove an application from the state
* store
* This does not block the dispatcher threads
* There is no notification of completion for this operation.
* There is no notification of completion for this operation.
* RM中移除应用状态信息,主要是移除里面的应用尝试信息列表
*/
public synchronized void removeApplication(RMApp app) {
ApplicationState appState = new ApplicationState(
app.getSubmitTime(), app.getApplicationSubmissionContext(),
app.getUser());
//取出此应用中的运行尝试信息状态
for(RMAppAttempt appAttempt : app.getAppAttempts().values()) {
Credentials credentials = getCredentialsFromAppAttempt(appAttempt);
ApplicationAttemptState attemptState =
new ApplicationAttemptState(appAttempt.getAppAttemptId(),
appAttempt.getMasterContainer(), credentials);
appState.attempts.put(attemptState.getAttemptId(), attemptState);
}
//进行移除操作
removeApplication(appState);
}/**
* Non-Blocking API
*/
public synchronized void removeApplication(ApplicationState appState) {
dispatcher.getEventHandler().handle(new RMStateStoreRemoveAppEvent(appState));
}
/**
* Blocking API
* Derived classes must implement this method to remove the state of an
* application and its attempts
*/
protected abstract void removeApplicationState(ApplicationState appState)
throws Exception;public static class RMDTSecretManagerState {
// DTIdentifier -> renewDate
//RM身份标识符ID对时间的映射
Map<RMDelegationTokenIdentifier, Long> delegationTokenState =
new HashMap<RMDelegationTokenIdentifier, Long>();
Set<DelegationKey> masterKeyState =
new HashSet<DelegationKey>();
int dtSequenceNumber = 0;
....
}MemoryRMStateStore
内存保存实现类,RM的应用状态信息在RMStateStore已经被抽象成了RMState类,所以在MemoryRMStateStore类中,肯定会有对应的变量
//内存RM状态信息保存类实现
public class MemoryRMStateStore extends RMStateStore {
RMState state = new RMState();
@VisibleForTesting
public RMState getState() {
return state;
}
...@Override
public void storeApplicationState(String appId,
ApplicationStateDataPBImpl appStateData)
throws Exception {
//生成新的应用状态对象实例
ApplicationState appState = new ApplicationState(
appStateData.getSubmitTime(),
appStateData.getApplicationSubmissionContext(), appStateData.getUser());
if (state.appState.containsKey(appState.getAppId())) {
Exception e = new IOException("App: " + appId + " is already stored.");
LOG.info("Error storing info for app: " + appId, e);
throw e;
}
//加入state对象中
state.appState.put(appState.getAppId(), appState);
}@Override
public synchronized void storeApplicationAttemptState(String attemptIdStr,
ApplicationAttemptStateDataPBImpl attemptStateData)
throws Exception {
ApplicationAttemptId attemptId = ConverterUtils
.toApplicationAttemptId(attemptIdStr);
...
ApplicationAttemptState attemptState =
new ApplicationAttemptState(attemptId,
attemptStateData.getMasterContainer(), credentials);
ApplicationState appState = state.getApplicationState().get(
attemptState.getAttemptId().getApplicationId());
if (appState == null) {
throw new YarnRuntimeException("Application doesn't exist");
}
if (appState.attempts.containsKey(attemptState.getAttemptId())) {
Exception e = new IOException("Attempt: " +
attemptState.getAttemptId() + " is already stored.");
LOG.info("Error storing info for attempt: " +
attemptState.getAttemptId(), e);
throw e;
}
//加入appState的运行尝试信息状态列表中
appState.attempts.put(attemptState.getAttemptId(), attemptState);
}//相当于返回一个内存中维护的RM状态拷贝对象
@Override
public synchronized RMState loadState() throws Exception {
// return a copy of the state to allow for modification of the real state
//新建一个RMState对象,拷贝内存中维护的RMstate对象
RMState returnState = new RMState();
//拷贝appState
returnState.appState.putAll(state.appState);
returnState.rmSecretManagerState.getMasterKeyState()
.addAll(state.rmSecretManagerState.getMasterKeyState());
returnState.rmSecretManagerState.getTokenState().putAll(
state.rmSecretManagerState.getTokenState());
returnState.rmSecretManagerState.dtSequenceNumber =
state.rmSecretManagerState.dtSequenceNumber;
return returnState;
}FileSystemRMStateStore
文件系统RM应用信息状态保存类,此类做的一个核心操作就是把应用状态信息持久化到HDFS中了。
/**
* A simple class for storing RM state in any storage that implements a basic
* FileSystem interface. Does not use directories so that simple key-value
* stores can be used. The retry policy for the real filesystem client must be
* configured separately to enable retry of filesystem operations when needed.
* RM状态信息文件系统保存类
*/
public class FileSystemRMStateStore extends RMStateStore {
public static final Log LOG = LogFactory.getLog(FileSystemRMStateStore.class);
private static final String ROOT_DIR_NAME = "FSRMStateRoot";
private static final String RM_DT_SECRET_MANAGER_ROOT = "RMDTSecretManagerRoot";
private static final String RM_APP_ROOT = "RMAppRoot";
private static final String DELEGATION_KEY_PREFIX = "DelegationKey_";
private static final String DELEGATION_TOKEN_PREFIX = "RMDelegationToken_";
private static final String DELEGATION_TOKEN_SEQUENCE_NUMBER_PREFIX =
"RMDTSequenceNumber_";
//文件系统对象
protected FileSystem fs;
//RM保存的文件路径
private Path rootDirPath;
private Path rmDTSecretManagerRoot;
private Path rmAppRoot;
private Path dtSequenceNumberPath = null;
@VisibleForTesting
Path fsWorkingPath;@Override
public synchronized void storeApplicationState(String appId,
ApplicationStateDataPBImpl appStateDataPB) throws Exception {
Path appDirPath = getAppDir(rmAppRoot, appId);
fs.mkdirs(appDirPath);
//获取待写入的目录路径
Path nodeCreatePath = getNodePath(appDirPath, appId);
LOG.info("Storing info for app: " + appId + " at: " + nodeCreatePath);
//获取待写入的状态数据
byte[] appStateData = appStateDataPB.getProto().toByteArray();
try {
// currently throw all exceptions. May need to respond differently for HA
// based on whether we have lost the right to write to FS
//进行状态信息的写入
writeFile(nodeCreatePath, appStateData);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.info("Error storing info for app: " + appId, e);
throw e;
}
}@Override
public synchronized RMState loadState() throws Exception {
//新建RM状态对象
RMState rmState = new RMState();
//调用方法,从文件中进行恢复
// recover DelegationTokenSecretManager
loadRMDTSecretManagerState(rmState);
// recover RM applications
loadRMAppState(rmState);
return rmState;
}private void loadRMAppState(RMState rmState) throws Exception {
try {
List<ApplicationAttemptState> attempts =
new ArrayList<ApplicationAttemptState>();
for (FileStatus appDir : fs.listStatus(rmAppRoot)) {
for (FileStatus childNodeStatus : fs.listStatus(appDir.getPath())) {
assert childNodeStatus.isFile();
String childNodeName = childNodeStatus.getPath().getName();
//读取文件数据信息
byte[] childData =
readFile(childNodeStatus.getPath(), childNodeStatus.getLen());
//如果是应用状态信息
if (childNodeName.startsWith(ApplicationId.appIdStrPrefix)) {
// application
LOG.info("Loading application from node: " + childNodeName);
ApplicationId appId = ConverterUtils.toApplicationId(childNodeName);
ApplicationStateDataPBImpl appStateData =
new ApplicationStateDataPBImpl(
ApplicationStateDataProto.parseFrom(childData));
ApplicationState appState =
new ApplicationState(appStateData.getSubmitTime(),
appStateData.getApplicationSubmissionContext(),
appStateData.getUser());
// assert child node name is same as actual applicationId
assert appId.equals(appState.context.getApplicationId());
rmState.appState.put(appId, appState);
} else if (childNodeName
.startsWith(ApplicationAttemptId.appAttemptIdStrPrefix)) {
// attempt
//如果是应用产生信息
LOG.info("Loading application attempt from node: " + childNodeName);
ApplicationAttemptId attemptId =
ConverterUtils.toApplicationAttemptId(childNodeName);
ApplicationAttemptStateDataPBImpl attemptStateData =
new ApplicationAttemptStateDataPBImpl(
ApplicationAttemptStateDataProto.parseFrom(childData));
Credentials credentials = null;
if (attemptStateData.getAppAttemptTokens() != null) {
credentials = new Credentials();
DataInputByteBuffer dibb = new DataInputByteBuffer();
dibb.reset(attemptStateData.getAppAttemptTokens());
credentials.readTokenStorageStream(dibb);
}
ApplicationAttemptState attemptState =
new ApplicationAttemptState(attemptId,
attemptStateData.getMasterContainer(), credentials);
// assert child node name is same as application attempt id
assert attemptId.equals(attemptState.getAttemptId());
attempts.add(attemptState);
} else {
LOG.info("Unknown child node with name: " + childNodeName);
}
}
}NullRMStateStore
空方法实现类,就是不保存状态信息操作,方法很简单,继承了方法,但不实现代码逻辑
//空RM信息状态保存类,不实现保存方法的任何操作
@Unstable
public class NullRMStateStore extends RMStateStore {
....
//不实现加载状态方法
@Override
public RMState loadState() throws Exception {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Cannot load state from null store");
}
//具体保存应用方法也不实现
@Override
protected void storeApplicationState(String appId,
ApplicationStateDataPBImpl appStateData) throws Exception {
// Do nothing
}
@Override
protected void storeApplicationAttemptState(String attemptId,
ApplicationAttemptStateDataPBImpl attemptStateData) throws Exception {
// Do nothing
}
@Override
protected void removeApplicationState(ApplicationState appState)
throws Exception {
// Do nothing
}
.....
}那么如何使用上面这些类呢,在yarn的配置属性中,通过参数yarn.resource-manager.store.class进行类对象配置,填入类名称即可。
全部代码的分析请点击链接https://github.com/linyiqun/hadoop-yarn,后续将会继续更新YARN其他方面的代码分析。
参考文献
《Hadoop技术内部–YARN架构设计与实现原理》.董西成