开发中间件
——编写用于Express应用程序的中间件
概念
中间件函数是可以访问请求对象 (req),响应对象(res)以及next应用程序请求 - 响应周期中的函数的函数。该next功能是Express路由器中的一个功能,当被调用时,它将执行当前中间件之后的中间件。
中间件功能可以执行以下任务:
- 执行任何代码。
- 更改请求和响应对象。
- 结束请求 - 响应周期。
- 调用堆栈中的下一个中间件。
如果当前的中间件函数没有结束请求 - 响应周期,则必须调用next()以将控制传递给下一个中间件函数。否则,请求将被挂起。
下图显示了中间件函数调用的元素:
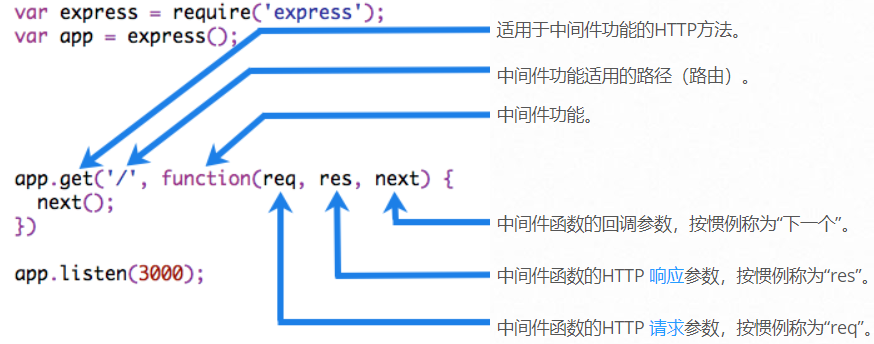
例
以下是一个简单的“Hello World”Express应用程序示例。本文的其余部分将定义并向应用程序添加两个中间件函数:一个调用myLogger打印一个简单的日志消息,另一个调用requestTime,显示HTTP请求的时间戳。
var express = require('express') var app = express() app.get('/', function (req, res) { res.send('Hello World!') }) app.listen(3000)
中间件功能myLogger
这是一个名为“myLogger”的中间件函数的简单示例。当对应用程序的请求通过时,此函数只打印“LOGGED”。中间件函数被分配给名为的变量myLogger。
var myLogger = function (req, res, next) { console.log('LOGGED') next() }
注意上面的调用
next()。调用此函数会调用应用程序中的下一个中间件函数。该next()函数不是Node.js或Express API的一部分,而是传递给中间件函数的第三个参数。该next()函数可以命名为任何东西,但按照惯例,它总是被命名为“next”。为避免混淆,请始终使用此约定。
要加载中间件功能,请调用app.use(),指定中间件功能。例如,以下代码myLogger在到根路径(/)的路由之前加载中间件函数。
var express = require('express') var app = express() var myLogger = function (req, res, next) { console.log('LOGGED') next() } app.use(myLogger) app.get('/', function (req, res) { res.send('Hello World!') }) app.listen(3000)
每次应用程序收到请求时,它都会向终端输出消息“LOGGED”。
中间件加载的顺序很重要:首先加载的中间件函数也会先执行。
如果myLogger在到根路径的路由之后加载,则请求永远不会到达它并且应用程序不会打印“LOGGED”,因为根路径的路由处理程序终止请求 - 响应循环。
中间件函数myLogger只是打印一条消息,然后通过调用该next()函数将请求传递给堆栈中的下一个中间件函数。
中间件功能requestTime
接下来,我们将创建一个名为“requestTime”的中间件函数,并将其添加为requestTime 对请求对象调用的属性。
var requestTime = function (req, res, next) { req.requestTime = Date.now() next() }
该应用程序现在使用requestTime中间件功能。此外,根路径路由的回调函数使用中间件函数添加的属性req(请求对象)。
var express = require('express') var app = express() var requestTime = function (req, res, next) { req.requestTime = Date.now() next() } app.use(requestTime) app.get('/', function (req, res) { var responseText = 'Hello World!<br>' responseText += '<small>Requested at: ' + req.requestTime + '</small>' res.send(responseText) }) app.listen(3000)
当您向应用程序的根目录发出请求时,应用程序现在会在浏览器中显示您的请求的时间戳。
因为您可以访问请求对象,响应对象,堆栈中的下一个中间件函数以及整个Node.js API,所以中间件函数的可能性是无穷无尽的。
可配置的中间件
如果您需要配置中间件,请导出一个接受选项对象或其他参数的函数,然后根据输入参数返回中间件实现。
文件: my-middleware.js
module.exports = function(options) { return function(req, res, next) { // Implement the middleware function based on the options object next() } }
现在可以使用中间件,如下所示。
var mw = require('./my-middleware.js') app.use(mw({ option1: '1', option2: '2' }))
使用中间件
Express是一种路由和中间件Web框架,它具有自己的最小功能:Express应用程序本质上是一系列中间件函数调用。
中间件函数是可以访问请求对象 (req),响应对象(res)以及应用程序的请求 - 响应周期中的下一个中间件函数的函数。下一个中间件函数通常由名为的变量表示next。
中间件功能可以执行以下任务:
- 执行任何代码。
- 更改请求和响应对象。
- 结束请求 - 响应周期。
- 调用堆栈中的下一个中间件函数。
如果当前的中间件函数没有结束请求 - 响应周期,则必须调用next()以将控制传递给下一个中间件函数。否则,请求将被挂起。
Express应用程序可以使用以下类型的中间件:
您可以使用可选的装载路径加载应用程序级和路由器级中间件。您还可以将一系列中间件功能加载在一起,从而在安装点创建中间件系统的子堆栈。
应用程序级中间件
通过使用和函数将应用程序级中间件绑定到app对象的实例,其中是中间件函数以小写形式处理的请求的HTTP方法(例如GET,PUT或POST)。app.use()app.METHOD()METHOD
此示例显示了没有装载路径的中间件功能。每次应用程序收到请求时都会执行该功能。
var app = express() app.use(function (req, res, next) { console.log('Time:', Date.now()) next() })
此示例显示了/user/:id路径上安装的中间件功能。对/user/:id路径上的任何类型的HTTP请求执行该函数。
app.use('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {
console.log('Request Type:', req.method)
next()
})
此示例显示了路由及其处理函数(中间件系统)。该函数处理对/user/:id路径的GET请求。
app.get('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {
res.send('USER')
})
下面是一个使用挂载路径在挂载点加载一系列中间件函数的示例。它说明了一个中间件子堆栈,它将任何类型的HTTP请求的请求信息打印到/user/:id路径。
app.use('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {
console.log('Request URL:', req.originalUrl)
next()
}, function (req, res, next) {
console.log('Request Type:', req.method)
next()
})
路径处理程序使您可以为路径定义多个路径。下面的示例为/user/:id路径的GET请求定义了两个路由。第二个路由不会引起任何问题,但它永远不会被调用,因为第一个路由结束了请求 - 响应周期。
此示例显示了一个中间件子堆栈,用于处理对/user/:id路径的GET请求。
app.get('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {
console.log('ID:', req.params.id)
next()
}, function (req, res, next) {
res.send('User Info')
})
// handler for the /user/:id path, which prints the user ID
app.get('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {
res.end(req.params.id)
})
要从路由器中间件堆栈中跳过其余的中间件功能,请调用next('route')将控制权传递给下一个路由。 注意:next('route')仅适用于使用app.METHOD()或router.METHOD()函数加载的中间件函数。
此示例显示了一个中间件子堆栈,用于处理对/user/:id路径的GET请求。
app.get('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {
// if the user ID is 0, skip to the next route
if (req.params.id === '0') next('route')
// otherwise pass the control to the next middleware function in this stack
else next()
}, function (req, res, next) {
// send a regular response
res.send('regular')
})
// handler for the /user/:id path, which sends a special response
app.get('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {
res.send('special')
})
路由器级中间件
路由器级中间件的工作方式与应用程序级中间件的工作方式相同,不同之处在于它绑定到的实例express.Router()。
var router = express.Router()
使用router.use()和router.METHOD()函数加载路由器级中间件。
以下示例代码通过使用路由器级中间件复制上面显示的应用程序级中间件的中间件系统:
var app = express() var router = express.Router() // a middleware function with no mount path. This code is executed for every request to the router router.use(function (req, res, next) { console.log('Time:', Date.now()) next() }) // a middleware sub-stack shows request info for any type of HTTP request to the /user/:id path router.use('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) { console.log('Request URL:', req.originalUrl) next() }, function (req, res, next) { console.log('Request Type:', req.method) next() }) // a middleware sub-stack that handles GET requests to the /user/:id path router.get('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) { // if the user ID is 0, skip to the next router if (req.params.id === '0') next('route') // otherwise pass control to the next middleware function in this stack else next() }, function (req, res, next) { // render a regular page res.render('regular') }) // handler for the /user/:id path, which renders a special page router.get('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) { console.log(req.params.id) res.render('special') }) // mount the router on the app app.use('/', router)
要跳过路由器中间件的其余功能,请调用next('router') 将控制权交还给路由器实例。
此示例显示了一个中间件子堆栈,用于处理对/user/:id路径的GET请求。
var app = express() var router = express.Router() // predicate the router with a check and bail out when needed router.use(function (req, res, next) { if (!req.headers['x-auth']) return next('router') next() }) router.get('/', function (req, res) { res.send('hello, user!') }) // use the router and 401 anything falling through app.use('/admin', router, function (req, res) { res.sendStatus(401) })
错误处理中间件
错误处理中间件总是需要四个参数。您必须提供四个参数以将其标识为错误处理中间件函数。即使您不需要使用该next对象,也必须指定它以保持签名。否则,该next对象将被解释为常规中间件,并且将无法处理错误。
以与其他中间件函数相同的方式定义错误处理中间件函数,除了四个参数而不是三个,特别是签名(err, req, res, next)):
app.use(function (err, req, res, next) { console.error(err.stack) res.status(500).send('Something broke!') })
内置中间件
从版本4.x开始,Express不再依赖于Connect。之前包含在Express中的中间件功能现在位于单独的模块中; 查看中间件功能列表。
Express具有以下内置中间件功能:
- express.static提供静态资源,如HTML文件,图像等。
- express.json使用JSON有效负载解析传入的请求。注意:适用于Express 4.16.0+
- express.urlencoded用URL编码的有效负载解析传入的请求。 注意:适用于Express 4.16.0+
第三方中间件
使用第三方中间件为Express应用程序添加功能。
安装Node.js模块以获得所需的功能,然后在应用程序级别或路由器级别将其加载到您的应用程序中。
以下示例说明了安装和加载cookie解析中间件功能cookie-parser。
$ npm install cookie-parser var express = require('express') var app = express() var cookieParser = require('cookie-parser') // load the cookie-parsing middleware app.use(cookieParser())