1.查找表 是 由同一类型的数据元素 或者 记录 构成的集合
关键字 是数据元素中某个数据项的值。 就是某一个字段
主关键字,就相当于字段的id 此关键字 非 id的字段
次关键字,就相当非关键的字段
--------------------------------------------------
静态查找表:只作查找操作的查找表 表数据不会动
动态查找表:查找过程中,同时插入 查找表中 不存在的数据元素, 或者从查找表中删除 已存在的元素
例子:比如一个字典要收录一个词。 插入时,先看数据库中有没有改词,没有的话,再确认位置。
删除某条数据,找到删除。 这就用到动态查找表了
---------------------------------------------------
2.顺序查找表(线性查找)
@Test public void lineSearch(){ int arr[] = {3,4,7,9,6,2,-1}; int result = 0,key = 2; for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ if(arr[i]==key){ result = i; } } System.out.println(result); } //优化 @Test public void betterlineSearch(){ int arr[] = {3,4,7,9,6,2,-1}; int key=-1; arr[0] = key; int i=arr.length-1; for(;i>=0;i--){ if(arr[i]==key){ break; } } System.out.println(i); }
3.有序表查找
3.1 折半查找
/** * 有序查找 折半 */ @Test public void halfSearch(){ int arr[] = {3,4,7,9,6,2,-1,45,89,55}; Arrays.sort(arr); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); int half = half(9,arr,0,arr.length); System.out.println(half); } public int half(int key,int [] arr,int low,int high){ if(low>high){ return -1; } int mid = low + (high-low)/2; //return arr; if(arr[mid]>key){ return half(key,arr,low,mid); }else if(arr[mid]<key){ return half(key, arr, mid+1, high); }else{ return mid; } }
@Test public void half(){ int arr[] = {3,4,7,9,6,2,-1,45,89,55}; Arrays.sort(arr); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); int half = half1(9,arr,arr.length); System.out.println(half); } public int half1(int key,int [] arr,int n){ int high = n; int low = 1; int mid; while(high>=low){ mid = (low+high)/2; //mid =low + (high-low)*(key-arr[low])/(arr[high]-arr[low]); 书上说这是修改mid 就是插值;插值适合分布比较均匀,表比较长的 if(key<arr[mid]){ high = mid-1; }else if(key>arr[mid]){ low = mid+1; }else{ return mid; } } return -1;//没有找到 }
3.2 斐波那契查找
https://www.nowcoder.com/discuss/3345
PS:他的性能是优于其他的。 这三种有序表的查找本质就是分割点的不同。
--------------------------------------------------------------------
4.索引查找
PS:在现实生活中,数据增长非常快。一般采用添加 索引 来处理
1.索引按结构来分,分为 线索、树形索引、多级索引。;
2.线性索引:就是把所有的索引项组织为线性结构。又称为线性表。 重点讲 稠密索引、分块索引、倒排索引
2.1稠密索引:就是一条记录对应一条索引项。 那么查找的时候就可以用到二分查找.....;但是一条记录对应一个id,有点太多了,内存可能吃不消。
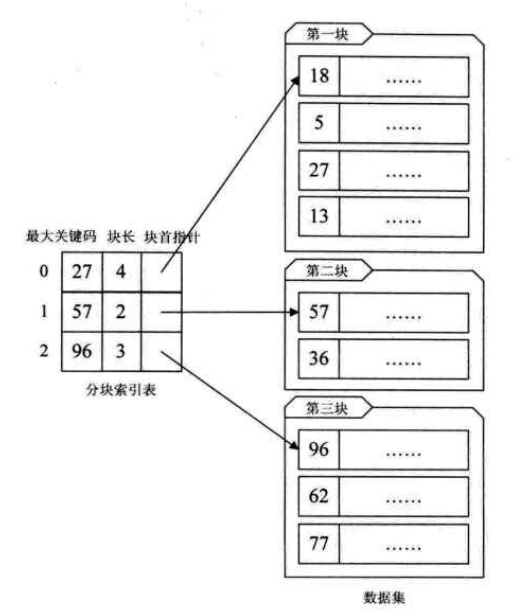
2.2 分块索引:
要求: 块内无序,块间有序
查找过程:先找块,再找索引
3.3倒排索引
*******************************************动态表查询*******************************************
二叉排序树(左小右大) (BST) binary sort tree
PS:之前那种都是静态的,如果数据量很大的时候,查找会变得很慢。高效的实现查找算法。在
查找时插入和删除的查找表称为动态查找表

package search; /** * 难度是在删除这个节点,删除节点还有保存好二叉排序树(binary sort tree)树的结构 * */ import java.util.Stack; public class BinarySortTree { private Node root = null; //根节点 /**中序非递归遍历二叉树 * 获得有序序列 * */ public void nrInOrderTraverse(){ Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); Node node = root; while(node != null || !stack.isEmpty()){ while(node != null){ stack.push(node); node = node.getLeft(); } node = stack.pop(); System.out.print(node.getValue()+" "); node = node.getRight(); } } /** * 删除二叉排序树中的结点 * 分为三种情况:(删除结点为*p ,其父结点为*f) * (1)要删除的*p结点是叶子结点,只需要修改它的双亲结点的指针为空 * (2)若*p只有左子树或者只有右子树,直接让左子树/右子树代替*p * (3)若*p既有左子树,又有右子树 * 用p左子树中最大的那个值(即最右端S)代替P,删除s,重接其左子树 * */ public void deleteBST(int key){ deleteBST(root, key); } private boolean deleteBST(Node node, int key) { if(node == null) return false; else{ if(key == node.getValue()){ return delete(node); } else if(key < node.getValue()){ return deleteBST(node.getLeft(), key); } else{ return deleteBST(node.getRight(), key); } } } /** * 这里是关键 * @param node * @return */ private boolean delete(Node node) { Node temp = null; /**右子树空,只需要重接它的左子树 * 如果是叶子结点,在这里也把叶子结点删除了 * */ if(node.getRight() == null){ temp = node; node = node.getLeft(); } /**左子树空, 重接它的右子树*/ else if(node.getLeft() == null){ temp = node; node = node.getRight(); } /**左右子树均不为空*/ else{ temp = node; Node s = node; /**转向左子树,然后向右走到“尽头”*/ s = s.getLeft(); while(s.getRight() != null){ temp = s; s = s.getRight(); } node.setValue(s.getValue()); //找节点来保留,下面是重新设置数的结构 if(temp != node){ temp.setRight(s.getLeft()); } else{ temp.setLeft(s.getLeft()); } } return true; } public static void main(String[] args) { BinarySortTree bst = new BinarySortTree(); /**构建的二叉树没有相同元素*/ int[] num = {4,7,2,1,10,6,9,3,8,11,2, 0, -2}; for(int i = 0; i < num.length; i++){ bst.insertBST(num[i]); } bst.nrInOrderTraverse(); System.out.println(bst.searchBST(10)); System.out.println(bst.searchBST1(-2)); //我自己写的也是对的 bst.deleteBST(2); bst.nrInOrderTraverse(); } /**查找二叉排序树中是否有key值*/ public boolean searchBST(int key){ Node current = root; while(current != null){ if(key == current.getValue()) return true; else if(key < current.getValue()) current = current.getLeft(); else current = current.getRight(); } return false; } public boolean searchBST1(int key){ return searchBST1(key,root); } /**查找二叉排序树中是否有key值 * 递归使用 * */ public boolean searchBST1(int key,Node cur){ //cur = root; if(cur ==null){ return false; }else if(cur.getValue()==key){ return true; }else if(key>cur.getValue()){ return searchBST1(key, cur.getRight()); }else if(key<cur.getValue()){ return searchBST1(key, cur.getLeft()); } return false; } /** * 向BST插入节点,左小右大 * @param i */ private void insertBST(int key) { Node p = root; Node prev =null; /**一直查找下去,直到到达满足条件的结点位置*/ while(p!=null){ prev = p; if(key>p.getValue()){ p = p.getRight(); }else if(key<p.getValue()){ p=p.getLeft(); }else{ return ; } } /**prve是要安放结点的父节点,根据结点值得大小,放在相应的位置*/ if(root == null){ root = new Node(key); } else if(key < prev.getValue()) { prev.setLeft(new Node(key)); } else{ prev.setRight(new Node(key)); } } } /** * 二叉链表的数据结构 * @author bee * */ class Node{ private int value; private Node left; private Node right; public Node(int key) { this.value = key; } public int getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } public Node getLeft() { return left; } public void setLeft(Node left) { this.left = left; } public Node getRight() { return right; } public void setRight(Node right) { this.right = right; } }
***********AVL(平衡二叉树)*****
PS:他是二叉排序树的一种特例。 特别的地方就是 每一个节点的左子树和右子树的高度差至多为1. (-1,0,1)平衡因子
高度差大于等于1的节点为根的子树,称为最小不平衡子树。
二叉平衡树,创建原理,插入一个节点,看他是否保持平衡。思想就是要不不平衡消灭在最早的时刻。
http://blog.csdn.net/liyong199012/article/details/29219261
*************************多路查找树(B)*****


PS:之前学习的树,都是一个节点只能存储一个元素。多路查找树,就是一个节点孩子的个数可以多余2个。且每一个节点处可以存储多个元素。
孩子数的多少是非常关键的,我们讲解4种形式。 2-3树,2-3-4树。B+和B-树。
PS: 2-3树是B树的一种特例
--红黑树 R-B树 R-B Tree,全称是Red-Black Tree,又称为“红黑树”,它一种特殊的二叉查找树。红黑树的每个节点上都有存储位表示节点的颜色,可以是红(Red)或黑(Black)。
http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3245399.html#a1
********************************************散列表

PS:之前找一个值需要对比很多,才能找到存储的位置。散列技术就是根据key直接找到存储位置。
PS:HashTable其实是一个内存

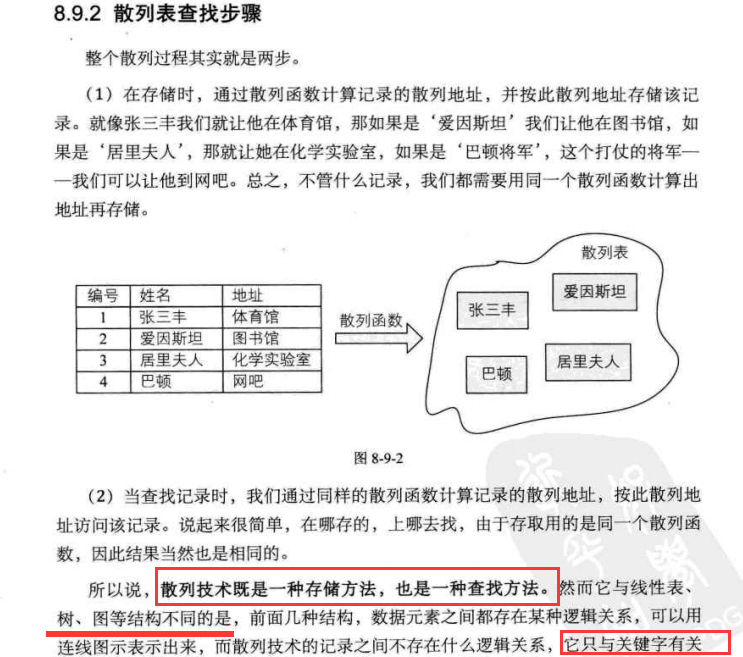
冲突: Java是通过hashcode和equals来解决的


