PS:Spring中有各种的Templeate,比如jdncTemplate,主要是为了避免各种模板的代码,抽象出来的
PS:

PS: @Configration、@Bean是用来替代xml那种解析方式
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------

PS: ApplicatonContext加载所有的bean,加载原则的get/set
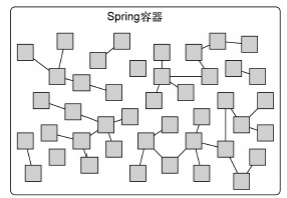
PS:Spring管理下 bean的声明周期
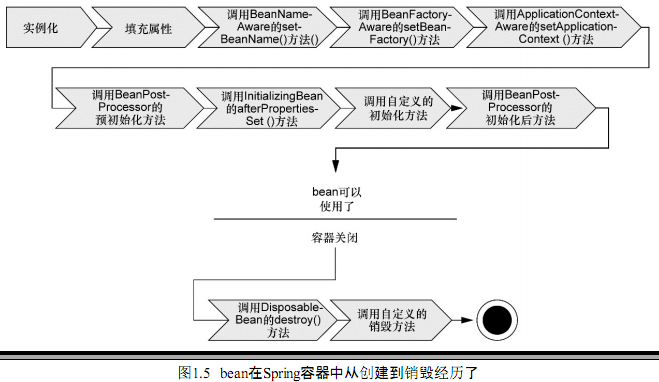
PS:Spring4 的模块
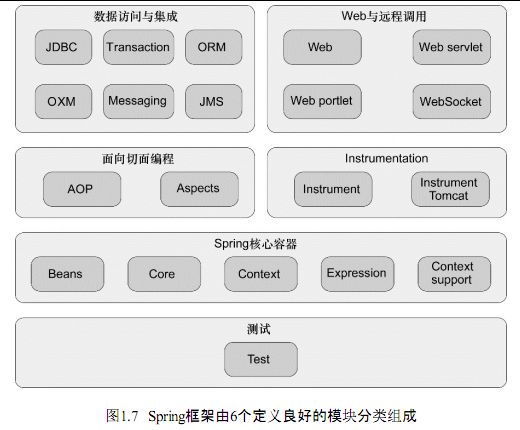


PS: 建议使用自动装配的机制
PS: @Component 会默认以类名第一个字母小写作为id名字, 表明该类会作为组件类
PS: @ComponentScan会默认扫描该类子包所有Component的bean



PS: @Componet只适合单独bean的状态,无依赖,如果说是bean和bean之间有依赖的话,还是要用Autowired(也就是Bean中Bean)
@Autowried 和 @inject可以互换




PS: 传统装配的类型
PS: 有些第三方的类无法装配bean,就只能使用java代码装配了。也就是之前的并不可能解决所有的问题。
PS: 并不是所有的场景都可以自动的装配的,这时候就得使用 xml配置或者 Java(JavaConfig是替代Java更好的解决方案)配置了


1.创建配置类 @Configration(如果ComponentScan去掉就不报错,还必须使用@Bean把对象注入进去)
2.声明bean @Bean

3.借助JavaConfig实现注入
package soundsystem; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class CDPlayerConfig { @Bean public CompactDisc compactDisc() { return new SgtPeppers(); } @Bean public CDPlayer cdPlayer(CompactDisc compactDisc) { return new CDPlayer(compactDisc); } }
通过xml装配bean









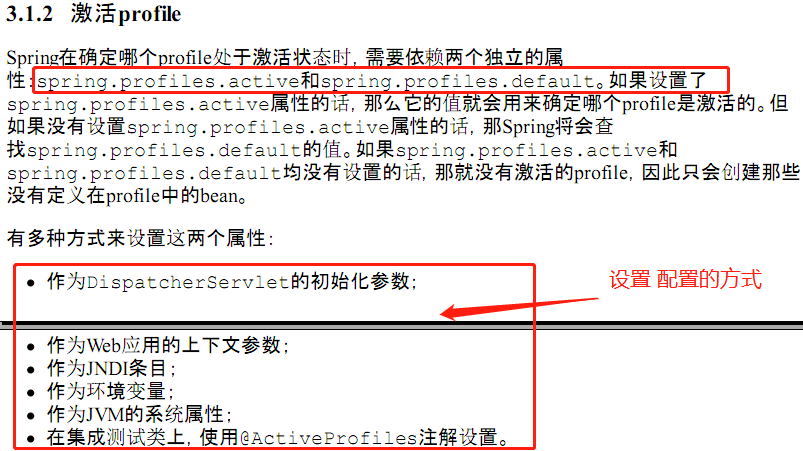
PS: 根据环境的变化,修改配置文件
package com.myapp; import javax.sql.DataSource; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile; import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.embedded.EmbeddedDatabaseBuilder; import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.embedded.EmbeddedDatabaseType; import org.springframework.jndi.JndiObjectFactoryBean; @Configuration public class DataSourceConfig { @Bean(destroyMethod = "shutdown") @Profile("dev") public DataSource embeddedDataSource() { return new EmbeddedDatabaseBuilder() .setType(EmbeddedDatabaseType.H2) .addScript("classpath:schema.sql") .addScript("classpath:test-data.sql") .build(); } @Bean @Profile("prod") public DataSource jndiDataSource() { JndiObjectFactoryBean jndiObjectFactoryBean = new JndiObjectFactoryBean(); jndiObjectFactoryBean.setJndiName("jdbc/myDS"); jndiObjectFactoryBean.setResourceRef(true); jndiObjectFactoryBean.setProxyInterface(javax.sql.DataSource.class); return (DataSource) jndiObjectFactoryBean.getObject(); } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc" xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <beans profile="dev"> <jdbc:embedded-database id="dataSource" type="H2"> <jdbc:script location="classpath:schema.sql" /> <jdbc:script location="classpath:test-data.sql" /> </jdbc:embedded-database> </beans> <beans profile="prod"> <jee:jndi-lookup id="dataSource" lazy-init="true" jndi-name="jdbc/myDatabase" resource-ref="true" proxy-interface="javax.sql.DataSource" /> </beans> </beans>
--------------------------在Autowired的时候会存在歧义

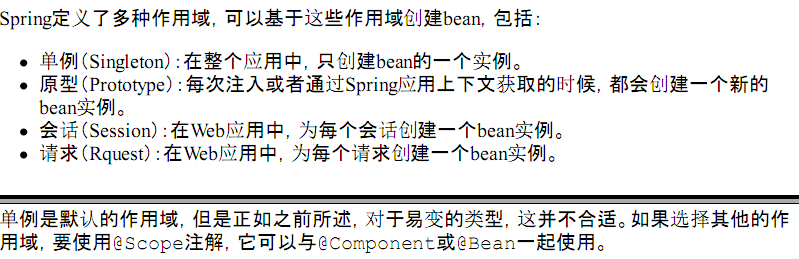
PS: prototype就是多例
@Scope
----------运行时注入,读取配置文件
@ProtertySource
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
 例子是抄电表
例子是抄电表

Spring AOP详解

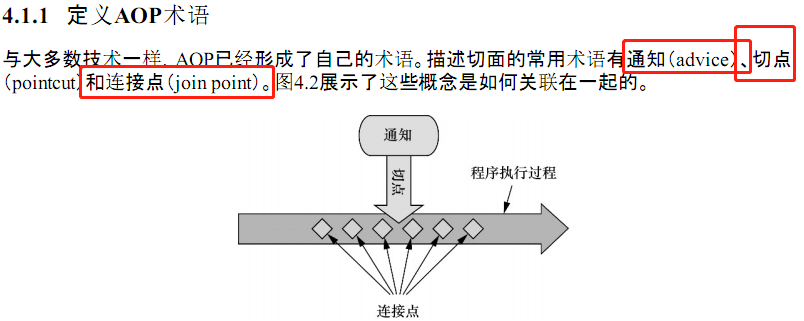

PS: 重点!!!!!!!!!!!! 这五种方式说明何时调用通知










PS: 这两个是一样的


PS: home 视图解析, home将会被解析为/WEB-INF/views/home.jsp

PS:春河说的校验表单参数



package spittr; import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull; import javax.validation.constraints.Size; import org.apache.commons.lang3.builder.EqualsBuilder; import org.apache.commons.lang3.builder.HashCodeBuilder; import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Email; public class Spitter { private Long id; @NotNull @Size(min=5, max=16) private String username; @NotNull @Size(min=5, max=25) private String password; @NotNull @Size(min=2, max=30) private String firstName; @NotNull @Size(min=2, max=30) private String lastName; @NotNull @Email private String email; public Spitter() {} public Spitter(String username, String password, String firstName, String lastName, String email) { this(null, username, password, firstName, lastName, email); } public Spitter(Long id, String username, String password, String firstName, String lastName, String email) { this.id = id; this.username = username; this.password = password; this.firstName = firstName; this.lastName = lastName; this.email = email; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getFirstName() { return firstName; } public void setFirstName(String firstName) { this.firstName = firstName; } public String getLastName() { return lastName; } public void setLastName(String lastName) { this.lastName = lastName; } public String getEmail() { return email; } public void setEmail(String email) { this.email = email; } @Override public boolean equals(Object that) { return EqualsBuilder.reflectionEquals(this, that, "firstName", "lastName", "username", "password", "email"); } @Override public int hashCode() { return HashCodeBuilder.reflectionHashCode(this, "firstName", "lastName", "username", "password", "email"); } }


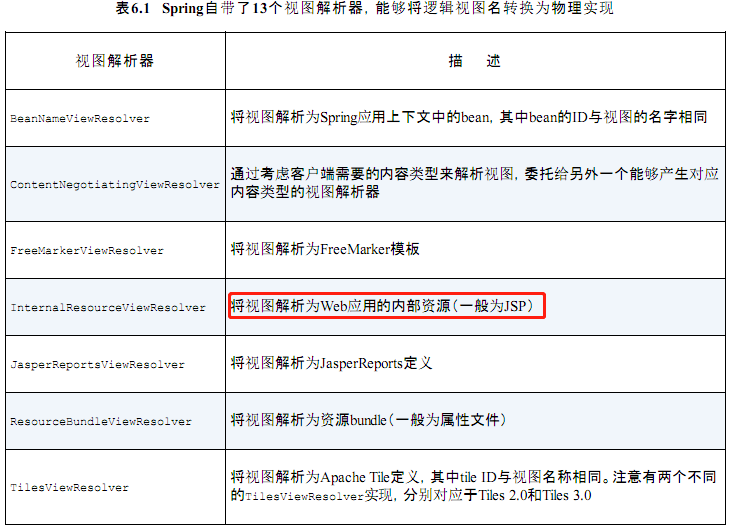
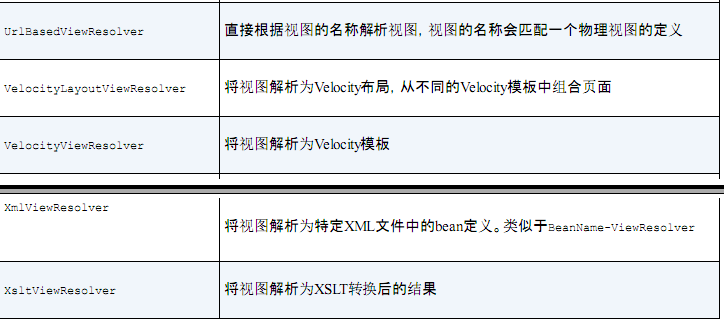


 PS: 看公司代码
PS: 看公司代码


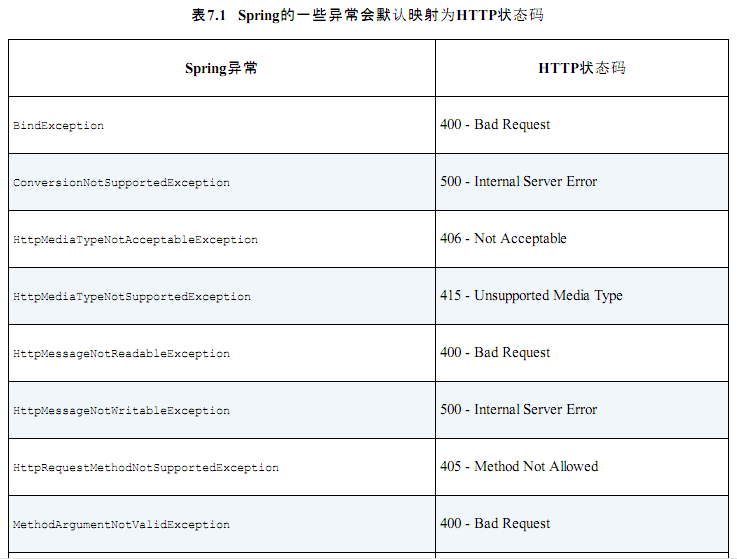
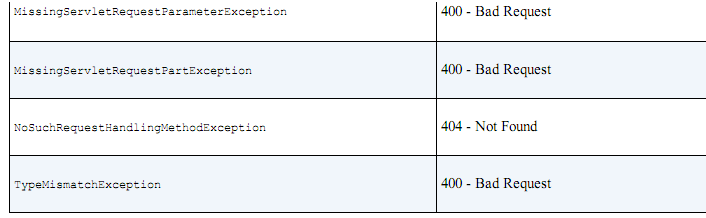

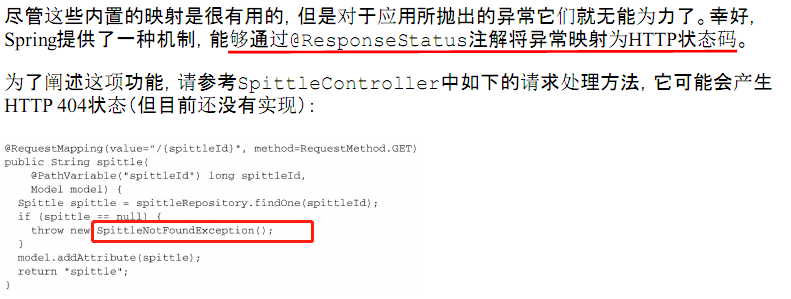


PS:自定义异常处理
通常是使用
@ControllerAdvice


PS: 这个就是 执行的顺序, 有点类似Activity


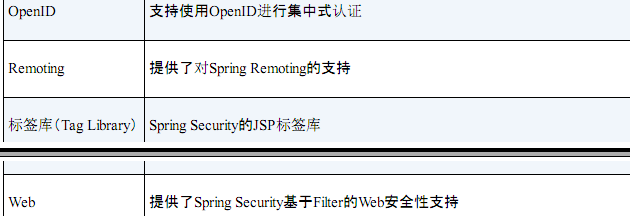
PS: 使用spring 的拦截器,只用一个就行 了。
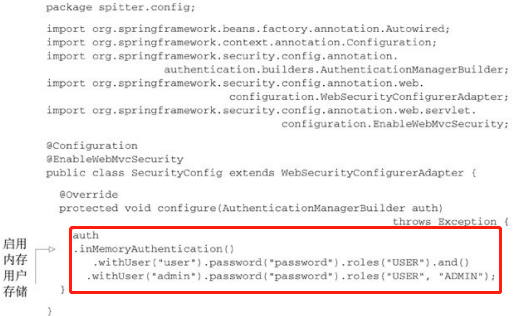
PS: 可以在测试 和 调试阶段添加 验证账户


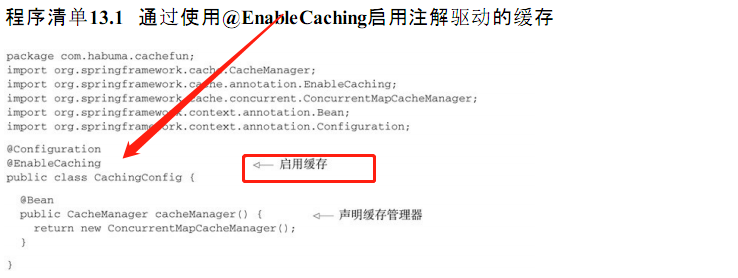
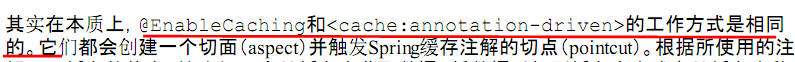

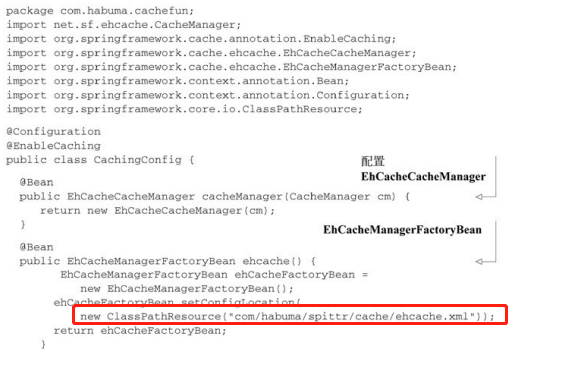
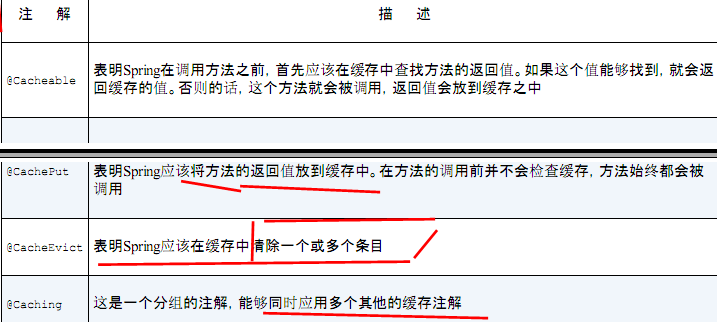

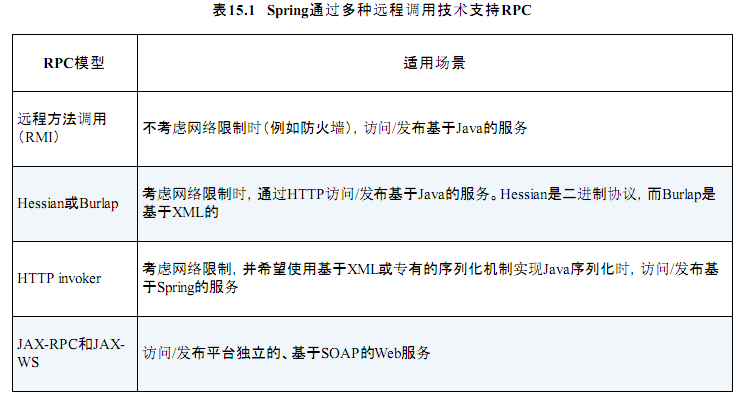




----------------------------------------Spring源码学习
PS:学习的代码是spring 3.2
PS:阅读源码最好的办法就是跟着 事例 操作一遍


PS: XMLBeanFactory继承自 1, 而 1 是整个bean加载的核心部分;



-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------




PS: SpringMVC是基于Servlet功能实现的