三天不写手生,半年不写成渣。。
以翔一般的手速写翔一般的代码,趴。还是要经常写写。
//今年三题都对都不一定能进下一轮,= = 简直手速赛,比起去年两题+第三题小数据就能混进round2
Problem A. The Last Word
给一个长度为1000的字符串S和一个空串T,从左到右一个个取出S里的字符,放进T中,放进T时可以放在最左边或最右边。
e.g. for S = CAB,
- put the
AbeforeCto formAC, then put theBbeforeACto formBAC - put the
AbeforeCto formAC, then put theBafterACto formACB - put the
AafterCto formCA, then put theBbeforeCAto formBCA - put the
AafterCto formCA, then put theBafterCAto formCAB
问所有可能的T里,字典序最大的是哪一个。
solution:简单的贪心策略,对于每一个要放的字符c,如果它大于等于T串中最左边的字符,则将其放在T的左边,否则放在右边。
code:

#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int N = 2005; char str[N]; int main(){ freopen("A-large.in", "r", stdin); freopen("large.out", "w", stdout); int TC, tc; scanf("%d", &TC); for(tc = 1; tc <= TC; tc++){ scanf("%s", str); int n = strlen(str); deque<char>dq; char leftest = 0; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ if(str[i] >= leftest){ dq.push_front(str[i]); leftest = str[i]; }else { dq.push_back(str[i]); } } printf("Case #%d: ", tc); while(!dq.empty()){ printf("%c", dq.front()); dq.pop_front(); } printf(" "); } return 0; }
Problem B. Rank and File
这道题很有意思,有一个N*N的矩阵,(N<=50),保证每行严格递增,每列严格递增。
将每行列出来,每列列出来,可以得到2N个数字序列。
现在把这些序列打乱(也就是说,不知道每一个序列是行序列还是列序列,也不知道他们是第几行or第几列),从中删除一个序列。
给出剩下的(2*N-1)个序列,问删除的那个序列长什么样子。
solution:一开始想的是如何花样复原矩阵,想了好久想不出来。
换个思路,对于2*N个数字序列,每个矩阵中的数字一定出现偶数次(行一次,列一次),因此,对于2*N-1个序列,他们中只出现奇数次的数就是删掉的序列里的数。

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int N = 2600; int cnt[N]; int main(){ freopen("A-large.in", "r", stdin); freopen("large.out", "w", stdout); int TC, tc; scanf("%d", &TC); for(tc = 1; tc<= TC; tc++){ int n; int x; scanf("%d", &n); vector<int>ans; int m = 2 * n - 1; memset(cnt, 0, sizeof(cnt)); for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){ for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++){ scanf("%d", &x); cnt[x] ++; } } for(int i = 1; i <= 2500; i++){ if(cnt[i] & 1){ ans.push_back(i); } } printf("Case #%d:", tc); for(int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++){ printf(" %d", ans[i]); } printf(" "); } return 0; }
Problem C. BFFs
有N个人(3 ≤ N ≤ 1000.),每个人都有一个喜欢的人。(不一定互相喜欢)
现在需要从中挑出一些人,让他们坐成一个圈,使得每个人喜欢的人能够坐在他的左边或者右边。
问最多能挑出多少人。
solution:如果看成一个图的话,这是一个每个点出度都为1的图。
很显然的,对于图中的一个环,能够符合上述条件。挑出的最大(长?)的环是符合条件的一个候选答案,设为maxloop。
但还有一种构造,注意到有一种特别的环,A喜欢B,B喜欢A。对于这种长度为2的环,可以安排AB坐在一起,接下来A旁边坐喜欢A的C,再坐喜欢C的D,依次类推。。同理B。
设上述这种长度为2的环带两条链(当然也可能没有链或一条链)为X。
有出度为1这个限制,最大环中不能加人。所有的X可以拼接(大概如图这样拼)
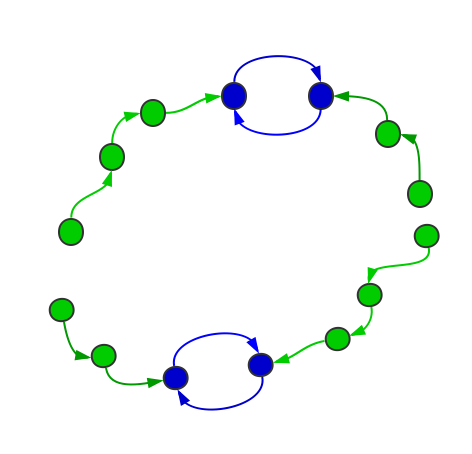
因此答案为max{len(maxloop),sum(len(Xi))}
因此首先(代码中第一次bfs)找出这个图中的最大的环,BFS DFS都可以,注意的点是,一般是枚举一个点然后去找他左右能通向的点,一路标记,如果标到了已经有深度的点就看深度(距离?dis),但是可能出现找到一个其他的点所标记的点,所以找环的时候一定要保证找到的环上的点是同一个祖先找出来的,方法有很多,我写得挫请不要借鉴。
然后(代码中第二次bfs)对于所有的点,也要记录反向边。对所有长度为2的环,对环两端的点分别沿反向边找到最远的点,链长就是len(Xi)
对两个求最大值即可。

#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int N = 1005; int head[N]; struct point{ int x, y, next; point(){}; point(int _x, int _y, int _next){ x = _x, y = _y, next = _next; } }p[N]; struct favpair{ int x, y; favpair(){}; favpair(int _x, int _y){ x = _x, y = _y; }; }; int ans; int fav[N]; int no; int vis[N], dis[N]; vector<int>backedge[N]; void init(){ memset(head, -1, sizeof(head)); memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)); memset(dis, 0, sizeof(dis)); fill(backedge, backedge + N, vector<int>() ); no = 0; ans = 0; } void add(int x, int y){ p[no] = point(x, y, head[x]); head[x]=no++; } void bfs(int x){ int s = x; queue<int>q; q.push(x); vis[x] = true; bool inthisloop[N]; memset(inthisloop, 0, sizeof(inthisloop)); while(!q.empty()){ x = q.front(); q.pop(); for(int i = head[x]; i != -1; i = p[i].next){ int y = p[i].y; if(dis[y]) continue; inthisloop[y] = true; if(!vis[y]){ vis[y] = true; q.push(y); } } } dis[s] = 1; q.push(s); while(!q.empty()){ x = q.front(); q.pop(); for(int i = head[x]; i != -1; i = p[i].next){ int y = p[i].y; if(!inthisloop[y]) continue; //printf("?y:%d %d ", y, dis[y]); if(dis[y] == 0){ dis[y] = dis[x] + 1; q.push(y); }else{ //printf("%d %d %d %d %d ",x, y, dis[x], dis[y], dis[x] - dis[y] + 1); ans = max(ans, dis[x] - dis[y] + 1); } } } //printf("!%d ", ans); } int bfs(int x, int y){ queue<int>q; q.push(x); dis[x] = 1; int len = 1; while(!q.empty()){ x = q.front(); q.pop(); for(int i = 0; i < backedge[x].size(); i++){ int st = backedge[x][i]; if(st == y) continue; dis[st] = dis[x] + 1; len = max(dis[st], len); q.push(st); } } return len; } int main(){ freopen("A-large.in", "r", stdin); freopen("large.out", "w", stdout); int tc, TC; scanf("%d", &TC); for(tc = 1; tc <= TC; tc++){ int n; scanf("%d", &n); init(); for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ scanf("%d", &fav[i]); add(i, fav[i]); backedge[fav[i]].push_back(i); } for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ if(!vis[i]){ bfs(i); } } vector<struct favpair>favp; favp.clear(); for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ if(fav[fav[i]] == i){ if(fav[i] > i) favp.push_back(favpair(i, fav[i])); } } memset(dis, 0, sizeof(dis)); int temp = 0; for(int i = 0; i < favp.size(); i++){ int x = favp[i].x; int y = favp[i].y; temp += bfs(x, y); // printf("%d %d ", x, temp); temp += bfs(y, x); } printf("Case #%d: %d ",tc, max(ans, temp)); } return 0; }
