一、LinkedHashMap结构
-
这是一个有序的,底层是继承于 HashMap 实现的,由一个双向链表所构成,具有和 HashMap 一样的快速查找特性。
-
LinkedHashMap的排序方式有两种:- 根据写入顺序排序。
- 根据访问顺序排序,每次
get都会将访问的值移动到链表末尾,这样重复操作就能得到一个按照访问顺序排序的链表。
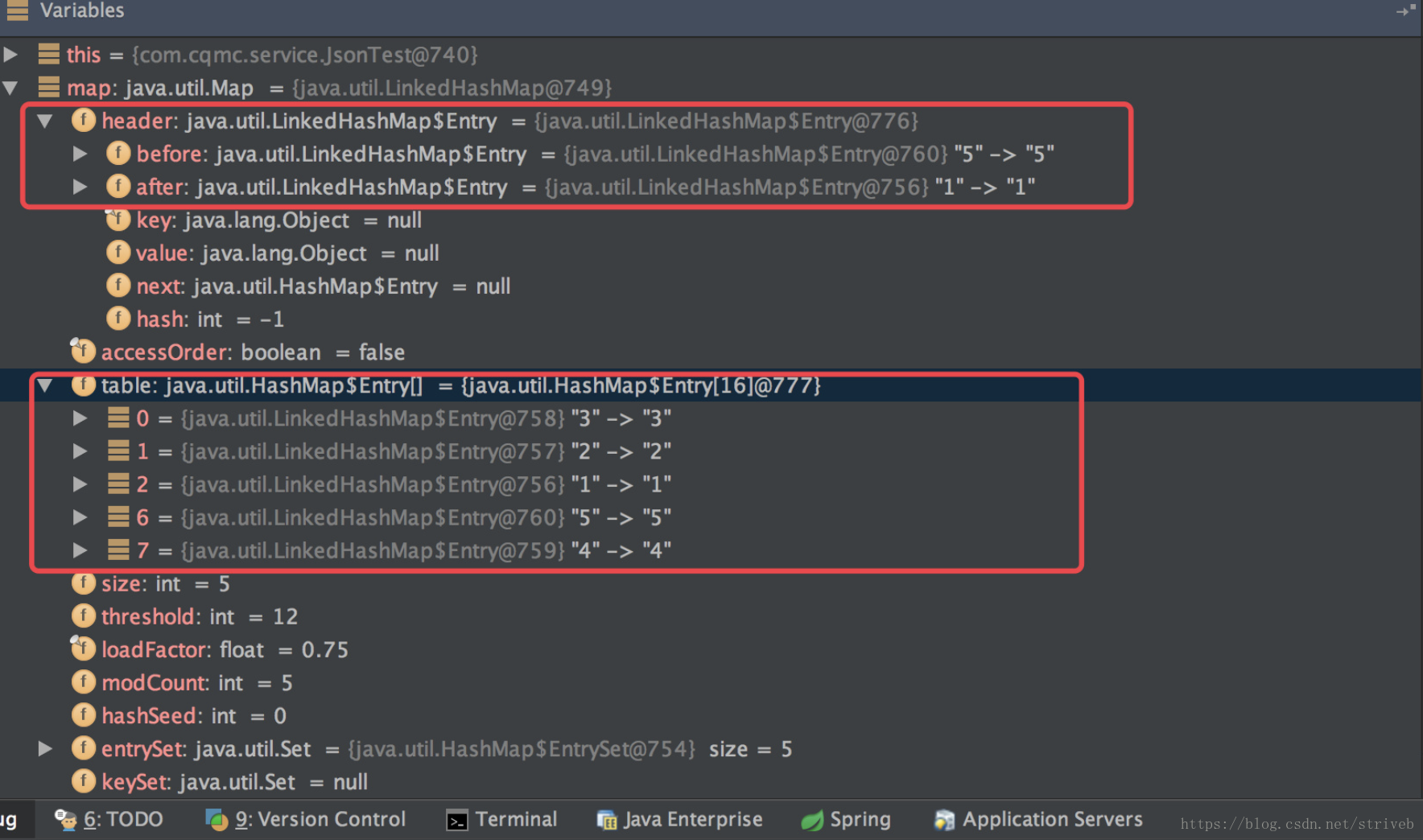
- 数据结构,通过以下代码调试可以看到
map的组成:@Test public void test(){ Map<String, Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap<String, Integer>(); map.put("1",1) ; map.put("2",2) ; map.put("3",3) ; map.put("4",4) ; map.put("5",5) ; System.out.println(map.toString()); }
/**
* The head of the doubly linked list.
*/
private transient Entry<K,V> header;
/**
* The iteration ordering method for this linked hash map: <tt>true</tt>
* for access-order, <tt>false</tt> for insertion-order.
*
* @serial
*/
private final boolean accessOrder;
private static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Entry<K,V> {
// These fields comprise the doubly linked list used for iteration.
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, HashMap.Entry<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
} 其中 Entry 继承于 HashMap 的 Entry,并新增了上下节点的指针,也就形成了双向链表。还有一个 header 的成员变量,是这个双向链表的头结点。
第一个类似于 HashMap 的结构,利用 Entry 中的 next 指针进行关联。下边则是 LinkedHashMap 如何达到有序的关键。就是利用了头节点和其余的各个节点之间通过 Entry 中的 after 和 before 指针进行关联。其中还有一个 accessOrder 成员变量,默认是 false,默认按照插入顺序排序,为 true 时按照访问顺序排序,也可以调用:
这个构造方法可以显示的传入 accessOrder。
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor,
boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}二、LinkedHashMap相关方法
-
构造方法就是调用
HashMap的构造方法:public LinkedHashMap() { super(); accessOrder = false; } // HashMap实现: public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity); if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor); this.loadFactor = loadFactor; threshold = initialCapacity; //HashMap 只是定义了改方法,具体实现交给了 LinkedHashMap init(); }可以看到里面有一个空的
init(),具体是由LinkedHashMap来实现的:@Override void init() { header = new Entry<>(-1, null, null, null); header.before = header.after = header; }其实也就是对
header进行了初始化,从这个方法可以看出,实现了双向。 -
put() 方法:主体的实现都是借助于
HashMap来完成的,只是对其中的recordAccess(), addEntry(), createEntry()进行了重写。如下是HashMap的put方法:public V put(K key, V value) { if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) { inflateTable(threshold); } if (key == null) return putForNullKey(value); int hash = hash(key); int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; //空实现,交给 LinkedHashMap 自己实现 e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } } modCount++; // LinkedHashMap 对其重写 addEntry(hash, key, value, i); return null; } // LinkedHashMap 对其重写 void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) { resize(2 * table.length); hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0; bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length); } createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex); } // LinkedHashMap 对其重写 void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex]; table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e); size++; }//就是判断是否是根据访问顺序排序,如果是则需要将当前这个 Entry 移动到链表的末尾 void recordAccess(HashMap<K,V> m) { LinkedHashMap<K,V> lm = (LinkedHashMap<K,V>)m; if (lm.accessOrder) { lm.modCount++; remove(); addBefore(lm.header); } } //调用了 HashMap 的实现,并判断是否需要删除最少使用的 Entry(默认不删除) void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { super.addEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex); // Remove eldest entry if instructed Entry<K,V> eldest = header.after; if (removeEldestEntry(eldest)) { removeEntryForKey(eldest.key); } } void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { HashMap.Entry<K,V> old = table[bucketIndex]; Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, old); //就多了这一步,将新增的 Entry 加入到 header 双向链表中 table[bucketIndex] = e; e.addBefore(header); size++; } //写入到双向链表中 private void addBefore(Entry<K,V> existingEntry) { after = existingEntry; before = existingEntry.before; before.after = this; after.before = this; }以上是LinkedHashMap的实现。 -
get 方法,LinkedHashMap 的
get()方法也重写了:public V get(Object key) { Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)getEntry(key); if (e == null) return null; //多了一个判断是否是按照访问顺序排序,是则将当前的 Entry 移动到链表头部。 e.recordAccess(this); return e.value; } void recordAccess(HashMap<K,V> m) { LinkedHashMap<K,V> lm = (LinkedHashMap<K,V>)m; if (lm.accessOrder) { lm.modCount++; //删除 remove(); //添加到头部 addBefore(lm.header); } }clear()方法:
//只需要把指针都指向自己即可,原本那些 Entry 没有引用之后就会被 JVM 自动回收。 public void clear() { super.clear(); header.before = header.after = header; }总的来说
LinkedHashMap其实就是对HashMap进行了拓展,使用了双向链表来保证了顺序性。因为是继承与HashMap的,所以一些HashMap存在的问题LinkedHashMap也会存在,比如不支持并发等。
内部维护了一个双向链表,用来维护插入顺序或者 LRU 顺序。
/**
* The head (eldest) of the doubly linked list.
*/
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> head;
/**
* The tail (youngest) of the doubly linked list.
*/
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> tail;accessOrder 决定了顺序,默认为 false,此时维护的是插入顺序。
final boolean accessOrder;
LinkedHashMap 最重要的是以下用于维护顺序的函数,它们会在 put、get 等方法中调用。
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> p) { }
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { }afterNodeAccess()
当一个节点被访问时,如果 accessOrder 为 true,则会将该节点移到链表尾部。也就是说指定为 LRU 顺序之后,在每次访问一个节点时,会将这个节点移到链表尾部,保证链表尾部是最近访问的节点,那么链表首部就是最近最久未使用的节点。
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) { // move node to last
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last;
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
p.after = null;
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a != null)
a.before = b;
else
last = b;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
tail = p;
++modCount;
}
}afterNodeInsertion()
在 put 等操作之后执行,当 removeEldestEntry() 方法返回 true 时会移除最晚的节点,也就是链表首部节点 first。
evict 只有在构建 Map 的时候才为 false,在这里为 true。
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { // possibly remove eldest
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> first;
if (evict && (first = head) != null && removeEldestEntry(first)) {
K key = first.key;
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true);
}
}removeEldestEntry() 默认为 false,如果需要让它为 true,需要继承 LinkedHashMap 并且覆盖这个方法的实现,这在实现 LRU 的缓存中特别有用,通过移除最近最久未使用的节点,从而保证缓存空间足够,并且缓存的数据都是热点数据。protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K,V> eldest) {
return false;
}分享一个不错的连接:https://www.imooc.com/article/22931