https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/5674/B
题意
现在有一棵树,你要从1开始跳一遍所有的点并且每条边只能走两次,再回到1,每条边都有一个边权,你走过这条边会先消耗(w_i)点HP,每个点都有一个果子,吃掉这个果子会上升(a_i)点HP,你在任何时候的HP不能小于0.并且你如果休息一秒钟会恢复1点HP。问你最少要休息多少时间才能走完这棵树。
题解
设(f[u])为遍历完子树增加多少体力,(g[u])表示体力为0遍历完子树最低减少到多少
那么最后答案显然为(min(0, -g[1]))
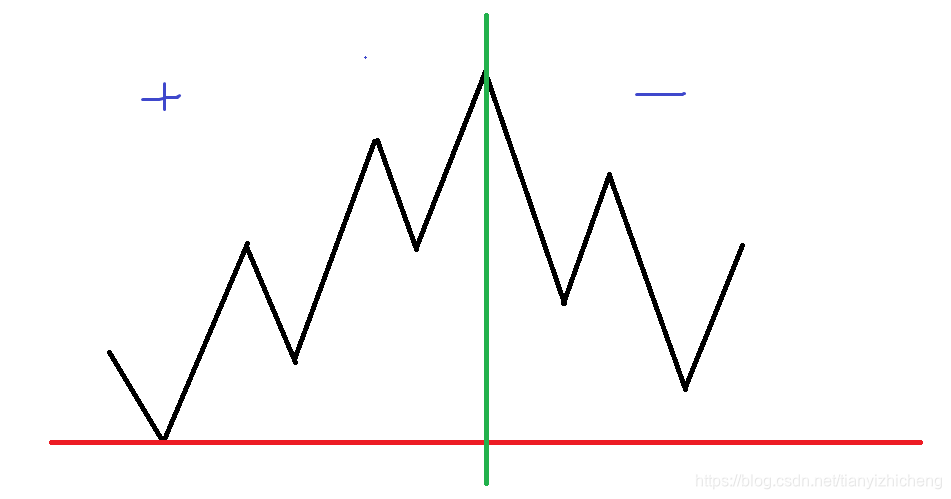
考虑这张图,绿线左边的是增加体力为正的情况,显然要g大的的排在前面,这样保证最低点最高,对于绿线右边,可以想到,我们需要的是最低点低的,且增加体力相对多的排在前面,所以按f-g排序,按树形dp转移即可
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
struct READ {
inline char read() {
#ifdef _WIN32
return getchar();
#endif
static const int IN_LEN = 1 << 18 | 1;
static char buf[IN_LEN], *s, *t;
return (s == t) && (t = (s = buf) + fread(buf, 1, IN_LEN, stdin)), s == t ? -1 : *s++;
}
template <typename _Tp> inline READ & operator >> (_Tp&x) {
static char c11, boo;
for(c11 = read(),boo = 0; !isdigit(c11); c11 = read()) {
if(c11 == -1) return *this;
boo |= c11 == '-';
}
for(x = 0; isdigit(c11); c11 = read()) x = x * 10 + (c11 ^ '0');
boo && (x = -x);
return *this;
}
} in;
const int N = 1e5 + 50;
int a[N];
struct node {
int v, w;
node(int v = 0, int w = 0): v(v), w(w) {}
};
vector<node> G[N];
ll f[N], g[N];//f遍历完子树增加多少体力,g体力为0遍历完子树最低减少到多少
struct S1 {
ll x, y;
bool operator < (const S1 &b) const {
return y > b.y;
}
};
struct S2 {
ll x, y;
bool operator < (const S2 &b) const {
return x - y > b.x - b.y;
}
};
void dfs(int u, int fa) {
for (node e : G[u]) {
if (e.v == fa) continue;
dfs(e.v, u);
}
vector<S1> s1; vector<S2> s2;
for (node e : G[u]) {
if (e.v == fa) continue;
f[e.v] -= 2ll * e.w;
g[e.v] -= e.w;
g[e.v] = min(g[e.v], (ll)-e.w);
g[e.v] = min(g[e.v], f[e.v]);
if (f[e.v] >= 0) s1.push_back({f[e.v], g[e.v]});
else s2.push_back({f[e.v], g[e.v]});
}
sort(s1.begin(), s1.end()); sort(s2.begin(), s2.end());
for (auto e : s1) {
g[u] = min(g[u], e.y + f[u]);
f[u] += e.x;
}
for (auto e : s2) {
g[u] = min(g[u], e.y + f[u]);
f[u] += e.x;
}
f[u] += a[u]; g[u] += a[u];
}
void solve() {
int n; in >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) in >> a[i], G[i].clear(), f[i] = g[i] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int u, v, w; in >> u >> v >> w;
G[u].push_back(node(v, w));
G[v].push_back(node(u, w));
}
dfs(1, 0);
printf("%lld
", max(0ll, -g[1]));
}
int main() {
int t; in >> t;
while (t--) solve();
return 0;
}