实验四 类的继承
•实验目的
•理解抽象类与接口的使用;
•了解包的作用,掌握包的设计方法。
•实验要求
•掌握使用抽象类的方法。
•掌握使用系统接口的技术和创建自定义接口的方法。
•了解 Java 系统包的结构。
•掌握创建自定义包的方法。
•实验内容
(一)抽象类的使用
1.设计一个类层次,定义一个抽象类--形状,其中包括有求形状的面积的抽象方法。 继承该抽象类定义三角型、矩形、圆。 分别创建一个三角形、矩形、圆存对象,将各类图形的面积输出。
注:三角形面积s=sqrt(p(p-a)(p-b)*(p-c)) 其中,a,b,c为三条边,p=(a+b+c)/2
2.编程技巧
(1) 抽象类定义的方法在具体类要实现;
(2) 使用抽象类的引用变量可引用子类的对象;
(3) 通过父类引用子类对象,通过该引用访问对象方法时实际用的是子类的方法。可将所有对象存入到父类定义的数组中。
package chouxianglei;
abstract class shape {
public abstract double print();
}
class sanjiao extends shape {
private double a;
private double b;
private double c;
public sanjiao(double a,double b,double c){
this.a=a;
this.b=b;
this.c=c;
}
public double print() {
double p=(a+b+c)/2;
return Math.sqrt(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c));
}
}
class juxing extends shape {
private double width;
private double height;
public juxing(double width, double height){
this.height=height;
this.width=width;
}
public double print() {
return width*height;
}
}
class yuan extends shape {
double radious;
public yuan(double radious){
this.radious=radious;
}
public double print() {
return Math.PI*radious*radious;
}
}
public class chouxianglei {
public static void main(String[] args){
shape s1=new sanjiao(3,4,5);
shape s2=new juxing(5,8);
shape s3=new yuan(6);
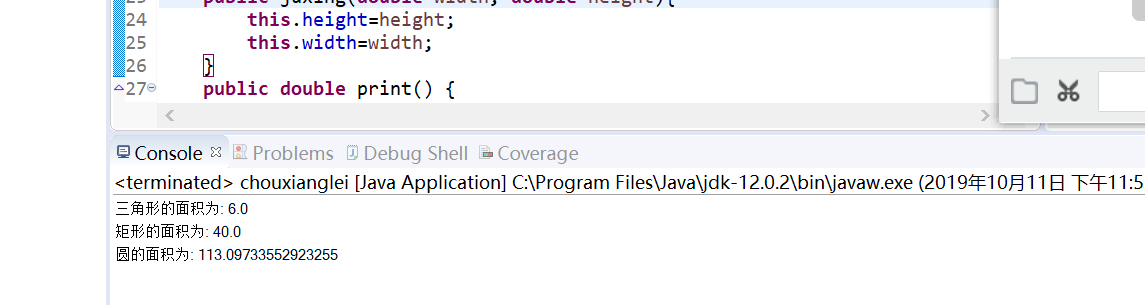
System.out.println("三角形的面积为: "+s1.print());
System.out.println("矩形的面积为: "+s2.print());
System.out.println("圆的面积为: "+s3.print());
}
}
(二)使用接口技术
1定义接口Shape,其中包括一个方法size(),设计“直线”、“圆”、类实现Shape接口。分别创建一个“直线”、“圆”对象,将各类图形的大小输出。
2.编程技巧
(1) 接口中定义的方法在实现接口的具体类中要重写实现;
(2) 利用接口类型的变量可引用实现该接口的类创建的对象
package jiekou;
public interface Shape {
public abstract void size();
}
class zhixian implements Shape{
private double zhixian;
public zhixian(double zhixian){
this.zhixian=zhixian;
}
public void size() {
System.out.println("直线的长度: "+zhixian);
}
}
class yuan implements Shape{
private double radious;
public yuan(double radious){
this.radious=radious;
}
public void size(){
System.out.println("圆的面积: "+Math.PI*radious*radious);
}
}
package jiekou;
public class jiekou {
public static void main(String[] args){
Shape s1=new zhixian(5);
Shape s2=new yuan(7);
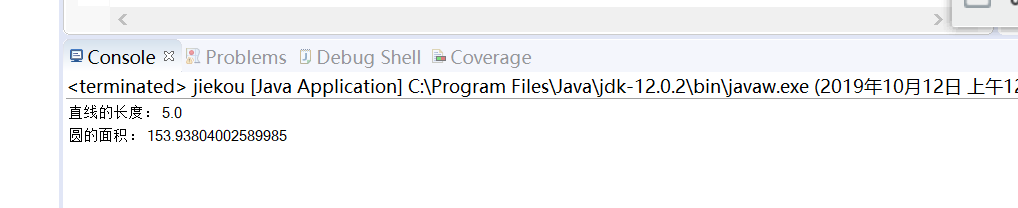
s1.size();
s2.size();
}
}
第七周学习总结
1.Object类:公共父类。所有的对象都可以向Object类进行向上转型。
2.通过实验报告五自己动手编写代码,学习了抽象类与接口的运用。
3.抽象类不能直接用来产生对象,必须通过对象的多态性进行实例化操作。
4.抽象类与接口的区别:抽象类有单继承的局限,但是接口就没有等等。