Objectives
After completing this lesson,you should be table to do the following:
- Determine the SQL statements that can be directly included in a PL/SQL executeable block.
- Manipulate data with DML statements in PL/SQL
- Use transaction control statements in PL/SQL
- Make use of the INTO clause to hold the values returned by a SQL statement
- Differentiate between implicit cursors and explicit cursors
- Use SQL cursor attributes
Agenda
- Retrieving data with PL/SQL
- Manipulating data with PL/SQL
- Introducing SQL cursors
SQL Statements in PL/SQL
- Retrieve a row from the database by using the SELECT command.
- Make chanages to rows in the database by using DML commands.
- Control a transaction with COMMIT,ROLLBACK,or SAVEPOINT command;
一个PL/SQL的blokc中,如果执行完毕了,里面的事务不会自动处理(COMMIT,ROLLBACK),必须显示处理.
SELECT Statements in PL/SQL
Retrieve data from the database with a SELECT statement.
Syntax:(带有明显PL/SQL烙印的SELECT)
SELECT select_list INTO { variable_name[,variable_name]... | record_name } FROM table [WHERE condition]
- The INTO clause is required.
- Queries must return only one row.
 Demo 01
Demo 01
DECLARE v_fname employees.first_name%TYPE; --v_fname VARCHAR2(25); BEGIN SELECT first_name INTO v_fname FROM employees WHERE employee_id = 200; DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('First Name is ' || v_fname); END; /
Retrieving Data in PL/SQL:Example
Retrieving hire_date and salary for the specified employee.
 Demo 02
Demo 02
DECLARE v_emp_hire_date employees.hire_date%TYPE; v_emp_salary employees.salary%TYPE; BEGIN SELECT hire_date,salary INTO v_emp_hire_date,v_emp_salary FROM employees WHERE employee_id = 100; DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(TO_CHAR(v_emp_hire_date,'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS') || '->' || TO_CHAR(v_emp_salary,'$999,999.00')); END; /
Return the sum of salaries for all the employees in the specified department.
Example:
 Demo 03
Demo 03
DECLARE v_sum_sal employees.salary%TYPE; v_dept_no employees.department_id%TYPE := 60; BEGIN SELECT SUM(salary) --group function INTO v_sum_sal FROM employees WHERE department_id = v_dept_no; DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('The sum of salary is ' || TO_CHAR(v_sum_sal,'$999,999.00')); END; /
Naming Ambiguities(含糊不清)
 Demo 01
Demo 01
DECLARE hire_date employees.hire_date%TYPE; sysdate hire_date%TYPE; employee_id employees.employee_id%TYPE := 176; BEGIN SELECT hire_date,sysdate INTO hire_date,sysdate FROM employees WHERE employee_id = employee_id; END; / SQL> @s3_2 DECLARE * ERROR at line 1: ORA-01422: exact fetch returns more than requested number of rows ORA-06512: at line 6
问题出在:WHERE employee_id = employee_id;PL/SQL优先会将employee_id当做列名来处理.employee = employee_id;就相当于1 = 1;所以会查询出很多列来.就出现了上述的错误.
Naming Conventions
- Use a naming convention to avoid ambiguity in the WHERE clause.
- Avoid using database column names as identifiers.
- Syntax can arise because PL/SQL checks the database first for a column in the table.
- The names of local variables and formal parameters take precedences over the names of database tables.
- The names of database table columns take precedence over the names of local variables.(可以联想Naming Ambiguities中的Demo)
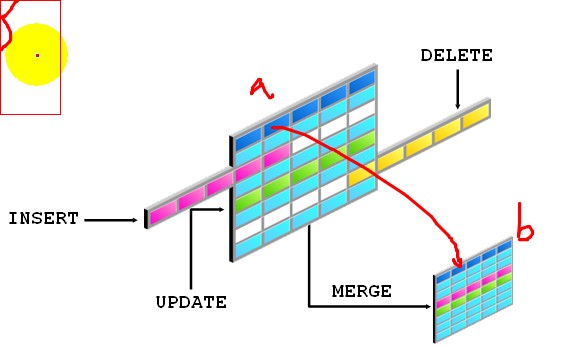
Using PL/SQL to Manipulate Data
Make change to database tables by using DML commands:
- INSERT
- UPDATE
- DELETE
- MERGE
 Demo 01
Demo 01
BEGIN INSERT INTO emp(employee_id,first_name,last_name,email,hire_date,job_id,salary) VALUES(employees_seq.NEXTVAL,'Ruth','Cores','ROCRES',CURRENT_DATE,'AD_ASST',4000); COMMIT; END; / SELECT * FROM emp ORDER BY employee_id;
Updating Data:Example
Increase the salary of all employees who are stock clerks.
 Demo 02
Demo 02
SELECT employee_id,last_name,salary,job_id FROM emp WHERE job_id = 'ST_CLERK'; DECLARE sal_increase employees.salary%TYPE := 800; BEGIN UPDATE emp SET salary = salary + sal_increase WHERE job_id = 'ST_CLERK'; COMMIT; END; / SELECT employee_id,last_name,salary,job_id FROM emp WHERE job_id = 'ST_CLERK';
