In this document
Considerations
在你的应用使用Android设备上的相机之前,考虑下面的几点:
Camera Requirement :相机功能是否很重要,以至于你不想让你的应用装到没有相机的设备上。如果是,在mainfest上声明。
Quick Picture or Customized Camera:你是想简单的拍个照,还是自定义一个相机。
Storage :你的应用生成的图片和录像,是可以共享给其他应用,还是私有?当应用被卸载的时候,图片和录像是否仍然保存下来?
The Basics
android拍照和录像有两种方式:一是通过使用 android.hardware.camera2 的API,二是使用Intent启动自带的相机程序。用到的类如下:
Camera 过时了
MediaStore.ACTION_IMAGE_CAPTURE or MediaStore.ACTION_VIDEO_CAPTURE,一个用来拍照一个用来录像。
Manifest Declarations
在进行开发之前,需要声明相应的权限。
Camera Permission 使用相机必须声明下面的权限,如果是使用Intent来启动相机,则不用声明
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />
Camera Features 可以在GooglePlay用来过滤设备,下面的代码表示,只有有相机的设备,才可以安装该应用
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera" android:required="false" />
Storage Permission 保存图片和录像到SD Card需要下面的权限
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
Audio Recording Permission 录像权限
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO" />
Location Permission 如果你想给图片加上GPS位置标签,需要下面的权限
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION" />
Using Existing Camera Apps
通过Intent来启动相机,有如下的几步:
1.Compose a Camera Intent 根据你的需求(拍照/录像)来创建不同的Intent
MediaStore.ACTION_IMAGE_CAPTURE 拍照时传这个Action
MediaStore.ACTION_VIDEO_CAPTURE 录像时传这个Action
2.Start the Camera Intent 用startActivityForResult() 方法来启动相机程序。
3.Receive the Intent Result 复写onActivityResult()方法,并在这个方法里面接收通过Intent传递过来的数据。当用户拍照/录像完毕或者取消,都会回调这个方法。
Image capture intent
使用Intent拍照,还可以在Intent里面传递一些其他的信息:
MediaStore.EXTRA_OUTPUT 传递一个uri进去,这个uri包含了图片储存的位置和文件名。如果没有指定,图片会以默认的名字储存在默认的位置。
下面给一个demo:
private static final int CAPTURE_IMAGE_ACTIVITY_REQUEST_CODE = 100;
private Uri fileUri;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
// create Intent to take a picture and return control to the calling application
Intent intent = new Intent(MediaStore.ACTION_IMAGE_CAPTURE);
fileUri = getOutputMediaFileUri(MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE); // create a file to save the image,这个方法具体实现见下面
intent.putExtra(MediaStore.EXTRA_OUTPUT, fileUri); // set the image file name
// start the image capture Intent
startActivityForResult(intent, CAPTURE_IMAGE_ACTIVITY_REQUEST_CODE);
}
Video capture intent
使用Intent录像,也可以传递一些额外信息:
MediaStore.EXTRA_VIDEO_QUALITY 0~1, 0表示最低质量和最小大小,1表示最高质量和最大大小
MediaStore.EXTRA_DURATION_LIMIT 限制录像的时间,单位为秒(s)
MediaStore.EXTRA_SIZE_LIMIT 限制文件大小,单位是字节(byte)
仍然给demo:
private static final int CAPTURE_VIDEO_ACTIVITY_REQUEST_CODE = 200;
private Uri fileUri;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
//create new Intent
Intent intent = new Intent(MediaStore.ACTION_VIDEO_CAPTURE);
fileUri = getOutputMediaFileUri(MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO); // create a file to save the video,实现见下面
intent.putExtra(MediaStore.EXTRA_OUTPUT, fileUri); // set the image file name
intent.putExtra(MediaStore.EXTRA_VIDEO_QUALITY, 1); // set the video image quality to high
// start the Video Capture Intent
startActivityForResult(intent, CAPTURE_VIDEO_ACTIVITY_REQUEST_CODE);
}
Receiving camera intent result
下面的demo展示了如果拦截Camera Intent的回调,并处理数据。
private static final int CAPTURE_IMAGE_ACTIVITY_REQUEST_CODE = 100;
private static final int CAPTURE_VIDEO_ACTIVITY_REQUEST_CODE = 200;
@Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {
if (requestCode == CAPTURE_IMAGE_ACTIVITY_REQUEST_CODE) {
if (resultCode == RESULT_OK) {
// Image captured and saved to fileUri specified in the Intent
Toast.makeText(this, "Image saved to:
" +
data.getData(), Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
} else if (resultCode == RESULT_CANCELED) {
// User cancelled the image capture
} else {
// Image capture failed, advise user
}
}
if (requestCode == CAPTURE_VIDEO_ACTIVITY_REQUEST_CODE) {
if (resultCode == RESULT_OK) {
// Video captured and saved to fileUri specified in the Intent
Toast.makeText(this, "Video saved to:
" +
data.getData(), Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
} else if (resultCode == RESULT_CANCELED) {
// User cancelled the video capture
} else {
// Video capture failed, advise user
}
}
}
Building a Camera App
如何自定义一个相机?下面的介绍都是以老的过时的Camera为例,对于最新的相机应用来说,推荐使用android.hardware.camera2。
大致的步骤如下:
1.Detect and Access Camera 检查设备的相机是否可用,并请求使用
2.Create a Preview Class 自定义一个View继承SurfaceView并实现SurfaceHolder接口,创建预览视图
3.Build a Preview Layout 创建预览视图布局
4.Setup Listeners for Capture 设置用于交互的监听器
5.Capture and Save Files 获取数据并保存文件
6.Release the Camera 释放资源,让别的应用使用
当使用完Camera之后,调用Camera.release()来释放Camera对象,如果未释放,其他应用尝试访问的时候,可能会被shut down,包括你自己的应用。
Detecting camera hardware
如果你的应用没有在mainfest里面做特殊的声明,那么你就需要在运行时检查相机是否存在,如下代码:
/** Check if this device has a camera */
private boolean checkCameraHardware(Context context) {
if (context.getPackageManager().hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_CAMERA)){
// this device has a camera
return true;
} else {
// no camera on this device
return false;
}
}
android设备可能有多个摄像头,Android 2.3及以上可以使用 Camera.getNumberOfCameras()方法来获取可访问的摄像头个数。
Accessing cameras
确定设备上有相机之后,通过获取一个Camera的实例来获得使用权限,代码如下:
/** A safe way to get an instance of the Camera object. */
public static Camera getCameraInstance(){
Camera c = null;
try {
c = Camera.open(); // attempt to get a Camera instance
}
catch (Exception e){
// Camera is not available (in use or does not exist)
}
return c; // returns null if camera is unavailable
}
必须要检查Camera.open()是否会出异常,否则会被 shut down by the system。
android 2.3 (API Level 9)及以上,可以使用Camera.open(int)方法打开指定的摄像头。
Checking camera features
使用Camera.getParameters()方法,然后检查返回的对象Camera.Parameters 即可。API 9以及上 使用Camera.getCameraInfo()还可以知道摄像头是前置还是后置,图片的方向。
Creating a preview class
下面的demo创建了一个基本的视图预览类:
/** A basic Camera preview class */
public class CameraPreview extends SurfaceView implements SurfaceHolder.Callback {
private SurfaceHolder mHolder;
private Camera mCamera;
public CameraPreview(Context context, Camera camera) {
super(context);
mCamera = camera;
// Install a SurfaceHolder.Callback so we get notified when the
// underlying surface is created and destroyed.
mHolder = getHolder();
mHolder.addCallback(this);
// deprecated setting, but required on Android versions prior to 3.0
mHolder.setType(SurfaceHolder.SURFACE_TYPE_PUSH_BUFFERS);
}
public void surfaceCreated(SurfaceHolder holder) {
// The Surface has been created, now tell the camera where to draw the preview.
try {
mCamera.setPreviewDisplay(holder);
mCamera.startPreview();
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.d(TAG, "Error setting camera preview: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
public void surfaceDestroyed(SurfaceHolder holder) {
// empty. Take care of releasing the Camera preview in your activity.
}
public void surfaceChanged(SurfaceHolder holder, int format, int w, int h) {
// If your preview can change or rotate, take care of those events here.
// Make sure to stop the preview before resizing or reformatting it.
if (mHolder.getSurface() == null){
// preview surface does not exist
return;
}
// stop preview before making changes
try {
mCamera.stopPreview();
} catch (Exception e){
// ignore: tried to stop a non-existent preview
}
// set preview size and make any resize, rotate or
// reformatting changes here
// start preview with new settings
try {
mCamera.setPreviewDisplay(mHolder);
mCamera.startPreview();
} catch (Exception e){
Log.d(TAG, "Error starting camera preview: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
如果想指定相机的预览视图尺寸,在surfaceChanged()方法里面设置,setPreviewSize()方法可以实现设置视图大小功能,但是不能传递任意值,只能使用getSupportedPreviewSizes()获取的大小。
Placing preview in a layout
为预览视图写一个布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/camera_preview"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button_capture"
android:text="Capture"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
/>
</LinearLayout>
使用FrameLayout是可以让你更方便的在预览视图上覆盖你想要的东西,如遮罩之类的。
一般相机应用都使用横屏,你可以在activity里面设置:
<activity android:name=".CameraActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:screenOrientation="landscape">
<!-- configure this activity to use landscape orientation -->
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
如果不想要横屏,Android 2.2以及上提供了setDisplayOrientation()方法去控制视图的方向,要想实现视图旋转,在surfaceChanged()方法里面先Camera.stopPreview() 停止预览,设置方向,再Camera.startPreview()开启预览。
Activity代码如下:
public class CameraActivity extends Activity {
private Camera mCamera;
private CameraPreview mPreview;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
// Create an instance of Camera,实现见下面
mCamera = getCameraInstance();
// Create our Preview view and set it as the content of our activity.
mPreview = new CameraPreview(this, mCamera);
FrameLayout preview = (FrameLayout) findViewById(R.id.camera_preview);
preview.addView(mPreview);
}
}
Capturing pictures
给拍照动作加上监听,监听的实现如下:
private PictureCallback mPicture = new PictureCallback() {
@Override
public void onPictureTaken(byte[] data, Camera camera) {
File pictureFile = getOutputMediaFile(MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE);
if (pictureFile == null){
Log.d(TAG, "Error creating media file, check storage permissions: " +
e.getMessage());
return;
}
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(pictureFile);
fos.write(data);
fos.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
Log.d(TAG, "File not found: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.d(TAG, "Error accessing file: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
};
当用户点击某个按钮,就执行拍照动作(Camera.takePicture()),代码如下:
// Add a listener to the Capture button
Button captureButton = (Button) findViewById(id.button_capture);
captureButton.setOnClickListener(
new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// get an image from the camera
mCamera.takePicture(null, null, mPicture);
}
}
);
用完之后,记得释放Camera对象,Camera.release() 。
Capturing videos
录像需要Camera对象和MediaRecorder类协调使用。除了调用Camera.open() 和 Camera.release(),你还需要管理好Camera.lock() 和 Camera.unlock(),后两个方法是控制MediaRecorder访问相机硬件的。
从Android 4.0开始,Camera.lock() 和 Camera.unlock()系统为你管理。
录像不像拍照,调用有特定的顺序(不好简单翻译):
- Open Camera - Use the
Camera.open()to get an instance of the camera object. - Connect Preview - Prepare a live camera image preview by connecting a
SurfaceViewto the camera usingCamera.setPreviewDisplay(). - Start Preview - Call
Camera.startPreview()to begin displaying the live camera images. - Start Recording Video - The following steps must be completed in order to successfully record video:
- Unlock the Camera - Unlock the camera for use by
MediaRecorderby callingCamera.unlock(). - Configure MediaRecorder - Call in the following
MediaRecordermethods in this order. For more information, see theMediaRecorderreference documentation.setCamera()- Set the camera to be used for video capture, use your application's current instance ofCamera.setAudioSource()- Set the audio source, useMediaRecorder.AudioSource.CAMCORDER.setVideoSource()- Set the video source, useMediaRecorder.VideoSource.CAMERA.- Set the video output format and encoding. For Android 2.2 (API Level 8) and higher, use the
MediaRecorder.setProfilemethod, and get a profile instance usingCamcorderProfile.get(). For versions of Android prior to 2.2, you must set the video output format and encoding parameters:setOutputFormat()- Set the output format, specify the default setting orMediaRecorder.OutputFormat.MPEG_4.setAudioEncoder()- Set the sound encoding type, specify the default setting orMediaRecorder.AudioEncoder.AMR_NB.setVideoEncoder()- Set the video encoding type, specify the default setting orMediaRecorder.VideoEncoder.MPEG_4_SP.
setOutputFile()- Set the output file, usegetOutputMediaFile(MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO).toString()from the example method in the Saving Media Files section.setPreviewDisplay()- Specify theSurfaceViewpreview layout element for your application. Use the same object you specified for Connect Preview.
Caution: You must call these
MediaRecorderconfiguration methods in this order, otherwise your application will encounter errors and the recording will fail. - Prepare MediaRecorder - Prepare the
MediaRecorderwith provided configuration settings by callingMediaRecorder.prepare(). - Start MediaRecorder - Start recording video by calling
MediaRecorder.start().
- Unlock the Camera - Unlock the camera for use by
- Stop Recording Video - Call the following methods in order, to successfully complete a video recording:
- Stop MediaRecorder - Stop recording video by calling
MediaRecorder.stop(). - Reset MediaRecorder - Optionally, remove the configuration settings from the recorder by calling
MediaRecorder.reset(). - Release MediaRecorder - Release the
MediaRecorderby callingMediaRecorder.release(). - Lock the Camera - Lock the camera so that future
MediaRecordersessions can use it by callingCamera.lock(). Starting with Android 4.0 (API level 14), this call is not required unless theMediaRecorder.prepare()call fails.
- Stop MediaRecorder - Stop recording video by calling
- Stop the Preview - When your activity has finished using the camera, stop the preview using
Camera.stopPreview(). - Release Camera - Release the camera so that other applications can use it by calling
Camera.release().
在开始预览之前,将setRecordingHint(boolean)设置为true,可以减少启动录像的时间。
Configuring MediaRecorder
是用MediaRecorder类来录像,也有一个特定的配置步骤,如下:
private boolean prepareVideoRecorder(){
mCamera = getCameraInstance();
mMediaRecorder = new MediaRecorder();
// Step 1: Unlock and set camera to MediaRecorder
mCamera.unlock();
mMediaRecorder.setCamera(mCamera);
// Step 2: Set sources
mMediaRecorder.setAudioSource(MediaRecorder.AudioSource.CAMCORDER);
mMediaRecorder.setVideoSource(MediaRecorder.VideoSource.CAMERA);
// Step 3: Set a CamcorderProfile (requires API Level 8 or higher)
mMediaRecorder.setProfile(CamcorderProfile.get(CamcorderProfile.QUALITY_HIGH));
// Step 4: Set output file
mMediaRecorder.setOutputFile(getOutputMediaFile(MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO).toString());
// Step 5: Set the preview output
mMediaRecorder.setPreviewDisplay(mPreview.getHolder().getSurface());
// Step 6: Prepare configured MediaRecorder
try {
mMediaRecorder.prepare();
} catch (IllegalStateException e) {
Log.d(TAG, "IllegalStateException preparing MediaRecorder: " + e.getMessage());
releaseMediaRecorder();
return false;
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.d(TAG, "IOException preparing MediaRecorder: " + e.getMessage());
releaseMediaRecorder();
return false;
}
return true;
}
配置完成之后,调用MediaRecorder.prepare()方法,会检查配置并让其生效。
在android2.2之前,CamcorderProfile无法使用,你必须直接配置输出格式和编码格式:
// Step 3: Set output format and encoding (for versions prior to API Level 8)
mMediaRecorder.setOutputFormat(MediaRecorder.OutputFormat.MPEG_4);
mMediaRecorder.setAudioEncoder(MediaRecorder.AudioEncoder.DEFAULT);
mMediaRecorder.setVideoEncoder(MediaRecorder.VideoEncoder.DEFAULT);
还有一些其他的配置可调整:
setVideoEncodingBitRate()setVideoSize()setVideoFrameRate()setAudioEncodingBitRate()setAudioChannels()setAudioSamplingRate()
Starting and stopping MediaRecorder
使用MediaRecorder开始和停止录像,也有特定的顺序:
- Unlock the camera with
Camera.unlock() - Configure
MediaRecorderas shown in the code example above - Start recording using
MediaRecorder.start() - Record the video
- Stop recording using
MediaRecorder.stop() - Release the media recorder with
MediaRecorder.release() - Lock the camera using
Camera.lock()
下面给出demo(完成录像未释放camera,预览会被停止):
private boolean isRecording = false;
// Add a listener to the Capture button
Button captureButton = (Button) findViewById(id.button_capture);
captureButton.setOnClickListener(
new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if (isRecording) {
// stop recording and release camera
mMediaRecorder.stop(); // stop the recording
releaseMediaRecorder(); // release the MediaRecorder object
mCamera.lock(); // take camera access back from MediaRecorder
// inform the user that recording has stopped
setCaptureButtonText("Capture");
isRecording = false;
} else {
// initialize video camera
if (prepareVideoRecorder()) {
// Camera is available and unlocked, MediaRecorder is prepared,
// now you can start recording
mMediaRecorder.start();
// inform the user that recording has started
setCaptureButtonText("Stop");
isRecording = true;
} else {
// prepare didn't work, release the camera
releaseMediaRecorder();
// inform user
}
}
}
}
);
Releasing the camera
释放camera对象
public class CameraActivity extends Activity {
private Camera mCamera;
private SurfaceView mPreview;
private MediaRecorder mMediaRecorder;
...
@Override
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
releaseMediaRecorder(); // if you are using MediaRecorder, release it first
releaseCamera(); // release the camera immediately on pause event
}
private void releaseMediaRecorder(){
if (mMediaRecorder != null) {
mMediaRecorder.reset(); // clear recorder configuration
mMediaRecorder.release(); // release the recorder object
mMediaRecorder = null;
mCamera.lock(); // lock camera for later use
}
}
private void releaseCamera(){
if (mCamera != null){
mCamera.release(); // release the camera for other applications
mCamera = null;
}
}
}
Saving Media Files
保存文件,作为一个开发者,优先考虑下面两个路径(SD Card):
Environment.getExternalStoragePublicDirectory(Environment.DIRECTORY_PICTURES) 公共的目录 Android 2.2 以及上可用,2.2之前有另外的方法Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory()
Context.getExternalFilesDir(Environment.DIRECTORY_PICTURES) - 私有的目录,应用卸载时,目录会被删除。
下面给出demo:
public static final int MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE = 1;
public static final int MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO = 2;
/** Create a file Uri for saving an image or video */
private static Uri getOutputMediaFileUri(int type){
return Uri.fromFile(getOutputMediaFile(type));
}
/** Create a File for saving an image or video */
private static File getOutputMediaFile(int type){
// To be safe, you should check that the SDCard is mounted
// using Environment.getExternalStorageState() before doing this.
File mediaStorageDir = new File(Environment.getExternalStoragePublicDirectory(
Environment.DIRECTORY_PICTURES), "MyCameraApp");
// This location works best if you want the created images to be shared
// between applications and persist after your app has been uninstalled.
// Create the storage directory if it does not exist
if (! mediaStorageDir.exists()){
if (! mediaStorageDir.mkdirs()){
Log.d("MyCameraApp", "failed to create directory");
return null;
}
}
// Create a media file name
String timeStamp = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMdd_HHmmss").format(new Date());
File mediaFile;
if (type == MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE){
mediaFile = new File(mediaStorageDir.getPath() + File.separator +
"IMG_"+ timeStamp + ".jpg");
} else if(type == MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) {
mediaFile = new File(mediaStorageDir.getPath() + File.separator +
"VID_"+ timeStamp + ".mp4");
} else {
return null;
}
return mediaFile;
}
Camera Features
绝大部分的相机特性都能通过Camera.Parameters设置,但是有几个需要特别处理:
Checking feature availability
不是所有的相机都支持所有的相机特性,另外设备支持的特性还有不同的等级和选项,所以检查设备是否支持相机的特性,以及支持到哪个等级是很重要的,示例代码如下:
// get Camera parameters
Camera.Parameters params = mCamera.getParameters();
List<String> focusModes = params.getSupportedFocusModes();
if (focusModes.contains(Camera.Parameters.FOCUS_MODE_AUTO)) {
// Autofocus mode is supported
}
使用 Camera.Parameters 对象提供的 getSupported...(), is...Supported() 和 getMax...() 来检查特性是否被支持。
如果你的应用必须需要某个特性才能使用,在mainfest里面加上限制。
Using camera features
使用某个特性很简单:
// get Camera parameters Camera.Parameters params = mCamera.getParameters(); // set the focus mode params.setFocusMode(Camera.Parameters.FOCUS_MODE_AUTO); // set Camera parameters mCamera.setParameters(params);
On the software side, 特性需要花费几帧的时间才能开到效果。
Metering and focus areas
Android 4.0 开始支持,并没看懂这是做什么...
// Create an instance of Camera
mCamera = getCameraInstance();
// set Camera parameters
Camera.Parameters params = mCamera.getParameters();
if (params.getMaxNumMeteringAreas() > 0){ // check that metering areas are supported
List<Camera.Area> meteringAreas = new ArrayList<Camera.Area>();
Rect areaRect1 = new Rect(-100, -100, 100, 100); // specify an area in center of image
meteringAreas.add(new Camera.Area(areaRect1, 600)); // set weight to 60%
Rect areaRect2 = new Rect(800, -1000, 1000, -800); // specify an area in upper right of image
meteringAreas.add(new Camera.Area(areaRect2, 400)); // set weight to 40%
params.setMeteringAreas(meteringAreas);
}
mCamera.setParameters(params);
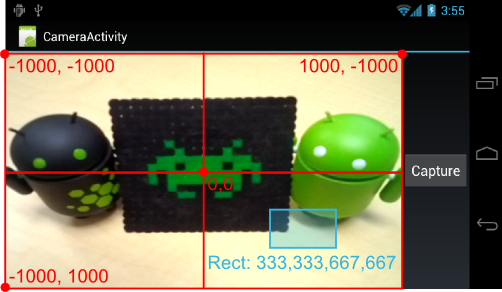
录像预览视图的坐标系。
Face detection
人脸识别,Android 4.0 开始支持
人脸识别运行的时候,setWhiteBalance(String), setFocusAreas(List) 和 setMeteringAreas(List) 都不会生效。
使用人脸识别特性,需要下面几个步骤:
- Check that face detection is supported on the device
- Create a face detection listener
- Add the face detection listener to your camera object
- Start face detection after preview (and after every preview restart)
检查是否支持人脸识别:
public void startFaceDetection(){
// Try starting Face Detection
Camera.Parameters params = mCamera.getParameters();
// start face detection only *after* preview has started
if (params.getMaxNumDetectedFaces() > 0){
// camera supports face detection, so can start it:
mCamera.startFaceDetection();
}
}
创建识别人脸成功后的监听:
class MyFaceDetectionListener implements Camera.FaceDetectionListener {
@Override
public void onFaceDetection(Face[] faces, Camera camera) {
if (faces.length > 0){
Log.d("FaceDetection", "face detected: "+ faces.length +
" Face 1 Location X: " + faces[0].rect.centerX() +
"Y: " + faces[0].rect.centerY() );
}
}
}
监听设置如下:
mCamera.setFaceDetectionListener(new MyFaceDetectionListener());
使用人脸识别,需要在每次启动(或者重新启动)预览的时候:
public void surfaceCreated(SurfaceHolder holder) {
try {
mCamera.setPreviewDisplay(holder);
mCamera.startPreview();
startFaceDetection(); // start face detection feature
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.d(TAG, "Error setting camera preview: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
public void surfaceChanged(SurfaceHolder holder, int format, int w, int h) {
if (mHolder.getSurface() == null){
// preview surface does not exist
Log.d(TAG, "mHolder.getSurface() == null");
return;
}
try {
mCamera.stopPreview();
} catch (Exception e){
// ignore: tried to stop a non-existent preview
Log.d(TAG, "Error stopping camera preview: " + e.getMessage());
}
try {
mCamera.setPreviewDisplay(mHolder);
mCamera.startPreview();
startFaceDetection(); // re-start face detection feature
} catch (Exception e){
// ignore: tried to stop a non-existent preview
Log.d(TAG, "Error starting camera preview: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
启动人脸识别需要在startPreview()之后,不要再onCreate方法里面启动人脸识别,因为这个时候视图预览不可用。
Time lapse video
Time lapse video allows users to create video clips that combine pictures taken a few seconds or minutes apart.
// Step 3: Set a CamcorderProfile (requires API Level 8 or higher) mMediaRecorder.setProfile(CamcorderProfile.get(CamcorderProfile.QUALITY_TIME_LAPSE_HIGH)); ... // Step 5.5: Set the video capture rate to a low number mMediaRecorder.setCaptureRate(0.1); // capture a frame every 10 seconds