1.help select

mysql> help select Name: 'SELECT' Description: Syntax: SELECT [ALL | DISTINCT | DISTINCTROW ] [HIGH_PRIORITY] [STRAIGHT_JOIN] [SQL_SMALL_RESULT] [SQL_BIG_RESULT] [SQL_BUFFER_RESULT] [SQL_CACHE | SQL_NO_CACHE] [SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS] select_expr [, select_expr ...] [FROM table_references [PARTITION partition_list] [WHERE where_condition] [GROUP BY {col_name | expr | position} [ASC | DESC], ... [WITH ROLLUP]] [HAVING where_condition] [ORDER BY {col_name | expr | position} [ASC | DESC], ...] [LIMIT {[offset,] row_count | row_count OFFSET offset}] [PROCEDURE procedure_name(argument_list)] [INTO OUTFILE 'file_name' [CHARACTER SET charset_name] export_options | INTO DUMPFILE 'file_name' | INTO var_name [, var_name]] [FOR UPDATE | LOCK IN SHARE MODE]] SELECT is used to retrieve rows selected from one or more tables, and can include UNION statements and subqueries. See [HELP UNION], and http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/subqueries.html. The most commonly used clauses of SELECT statements are these: o Each select_expr indicates a column that you want to retrieve. There must be at least one select_expr. o table_references indicates the table or tables from which to retrieve rows. Its syntax is described in [HELP JOIN]. o Starting in MySQL 5.6.2, SELECT supports explicit partition selection using the PARTITION keyword with a list of partitions or subpartitions (or both) following the name of the table in a table_reference (see [HELP JOIN]). In this case, rows are selected only from the partitions listed, and any other partitions of the table are ignored. For more information and examples, see http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/partitioning-selection.html. In MySQL 5.6.6 and later, SELECT ... PARTITION from tables using storage engines such as MyISAM that perform table-level locks (and thus partition locks) lock only the partitions or subpartitions named by the PARTITION option. See http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/partitioning-limitations-locki ng.html, for more information. o The WHERE clause, if given, indicates the condition or conditions that rows must satisfy to be selected. where_condition is an expression that evaluates to true for each row to be selected. The statement selects all rows if there is no WHERE clause. In the WHERE expression, you can use any of the functions and operators that MySQL supports, except for aggregate (summary) functions. See http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/expressions.html, and http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/functions.html. SELECT can also be used to retrieve rows computed without reference to any table. URL: http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/select.html
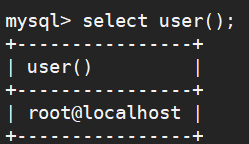
2.select 可以不使用from 子句
select user();
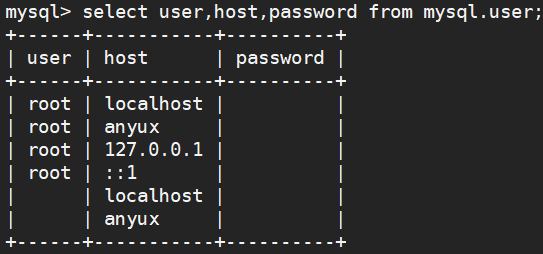
3.指定查询条件,使用数据过滤的更加准确
select user,host,password from mysql.user;
4.模糊查询
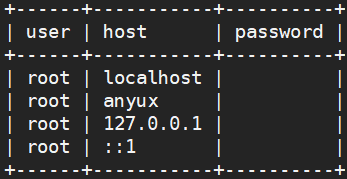
select user,host,password from mysql.user where user like 'roo%';
5.排序order by
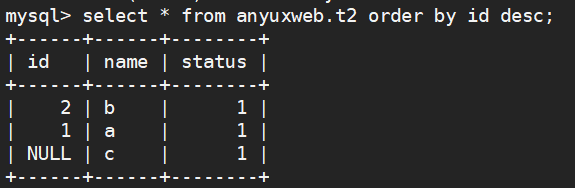
--降序排列 select * from anyuxweb.t2 order by id desc;
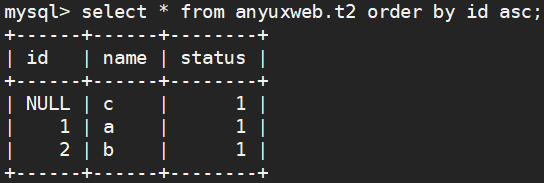
--升序排列 select * from anyuxweb.t2 order by id asc;
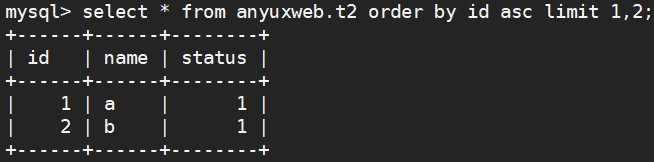
6.limit 使用
select * from anyuxweb.t2 order by id asc limit 1,2;