开局一张图,我们先上张图
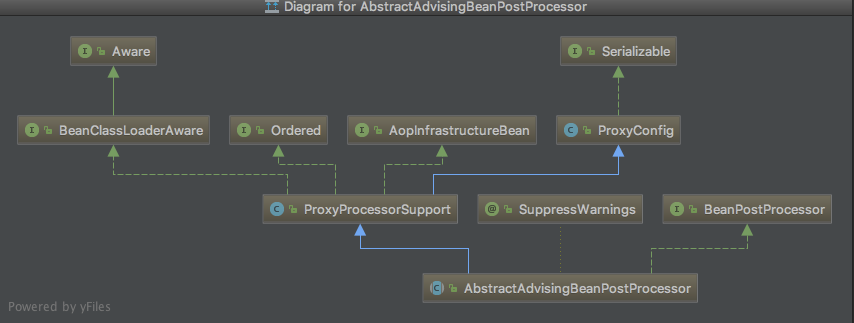
类的说明和继承关系
/**
* Base class for {@link BeanPostProcessor} implementations that apply a
* Spring AOP {@link Advisor} to specific beans.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 3.2
*/
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public abstract class AbstractAdvisingBeanPostProcessor extends ProxyProcessorSupport implements BeanPostProcessor
具体来看怎么处理的bean 主要两个方法
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean instanceof AopInfrastructureBean || this.advisor == null) {
// Ignore AOP infrastructure such as scoped proxies.
return bean;
}
if (bean instanceof Advised) {
Advised advised = (Advised) bean;
if (!advised.isFrozen() && isEligible(AopUtils.getTargetClass(bean))) {
// Add our local Advisor to the existing proxy's Advisor chain...
if (this.beforeExistingAdvisors) {
advised.addAdvisor(0, this.advisor);
}
else {
advised.addAdvisor(this.advisor);
}
return bean;
}
}
if (isEligible(bean, beanName)) {
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = prepareProxyFactory(bean, beanName);
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(bean.getClass(), proxyFactory);
}
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(this.advisor);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
// No async proxy needed.
return bean;
}
这段代码 主要逻辑 advised.addAdvisor(this.advisor);//添加上需要的advisor
再看个实现
*
* <p>Note: The underlying async advisor applies before existing advisors by default,
* in order to switch to async execution as early as possible in the invocation chain.
*
* @author Mark Fisher
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @since 3.0
* @see Async
* @see AsyncAnnotationAdvisor
* @see #setBeforeExistingAdvisors
* @see ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
*/
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor extends AbstractBeanFactoryAwareAdvisingPostProcessor {
/**
* The default name of the {@link TaskExecutor} bean to pick up: "taskExecutor".
* <p>Note that the initial lookup happens by type; this is just the fallback
* in case of multiple executor beans found in the context.
* @since 4.2
* @see AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor#DEFAULT_TASK_EXECUTOR_BEAN_NAME
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_TASK_EXECUTOR_BEAN_NAME =
AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor.DEFAULT_TASK_EXECUTOR_BEAN_NAME;
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
@Nullable
private Class<? extends Annotation> asyncAnnotationType;
@Nullable
private Executor executor;
@Nullable
private AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler exceptionHandler;
public AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() {
setBeforeExistingAdvisors(true);
}
/**
* Set the 'async' annotation type to be detected at either class or method
* level. By default, both the {@link Async} annotation and the EJB 3.1
* {@code javax.ejb.Asynchronous} annotation will be detected.
* <p>This setter property exists so that developers can provide their own
* (non-Spring-specific) annotation type to indicate that a method (or all
* methods of a given class) should be invoked asynchronously.
* @param asyncAnnotationType the desired annotation type
*/
public void setAsyncAnnotationType(Class<? extends Annotation> asyncAnnotationType) {
Assert.notNull(asyncAnnotationType, "'asyncAnnotationType' must not be null");
this.asyncAnnotationType = asyncAnnotationType;
}
/**
* Set the {@link Executor} to use when invoking methods asynchronously.
* <p>If not specified, default executor resolution will apply: searching for a
* unique {@link TaskExecutor} bean in the context, or for an {@link Executor}
* bean named "taskExecutor" otherwise. If neither of the two is resolvable,
* a local default executor will be created within the interceptor.
* @see AsyncAnnotationAdvisor#AsyncAnnotationAdvisor(Executor, AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler)
* @see AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor#getDefaultExecutor(BeanFactory)
* @see #DEFAULT_TASK_EXECUTOR_BEAN_NAME
*/
public void setExecutor(Executor executor) {
this.executor = executor;
}
/**
* Set the {@link AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler} to use to handle uncaught
* exceptions thrown by asynchronous method executions.
* @since 4.1
*/
public void setExceptionHandler(AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler exceptionHandler) {
this.exceptionHandler = exceptionHandler;
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
super.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
AsyncAnnotationAdvisor advisor = new AsyncAnnotationAdvisor(this.executor, this.exceptionHandler);
if (this.asyncAnnotationType != null) {
advisor.setAsyncAnnotationType(this.asyncAnnotationType);
}
advisor.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
this.advisor = advisor;
}
}
其中AbstractBeanFactoryAwareAdvisingPostProcessor继承了AbstractAdvisingBeanPostProcessor 类,所以AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor也是AbstractAdvisingBeanPostProcessor的一个子类。它并没有重写 postProcessAfterInitialization 方法,所以方法和原类的实现一样。
